sqliteSQL基础
SQL基础
SQLite 数据库简介
SQLite 是一个开源的、 内嵌式的关系型数据库, 第一个版本诞生于 2000 年 5 月, 目前最高版本为 SQLite3。
下载地址: https://www.sqlite.org/download.html
菜鸟教程 : https://www.runoob.com/sqlite/sqlite-tutorial.html
Linux 下 字符界面
sudo apt-get install sqlite3
Linux 下 图形界面
sudo apt-get install sqlitebrowser
该教程没有使用这个, 因为我下载时找不到
sudo apt-get install sqliteman
SQLite 特性:
- 零配置
- 灵活
- 可移植
- 自由的授权
- 紧凑
- 可靠
- 简单
- 易用
SQL 语句基础
SQL 是一种结构化查询语言(Structured Query Language) 的缩写, SQL 是一种专门用来与数据库通信的语言。
SQL 目前已成为应用最广的数据库语言。
SQL 已经被众多商用数据库管理系统产品所采用, 不同的数据库管理系统在其实践过程中都对 SQL 规范作了某些编改和扩充。 故不同数据库管理系统之间的 SQL 语言不能完全相互通用。
SQLite 数据类型 :
一般数据采用固定的静态数据类型, 而 SQLite 采用的是动态数据类型, 会根据存入值自动判断。
SQLite 具有以下五种基本数据类型 :
integer: 带符号的整型(最多 64 位) 。real: 8 字节表示的浮点类型。text: 字符类型, 支持多种编码(如 UTF-8、 UTF-16) , 大小无限制。blob: 任意类型的数据, 大小无限制。BLOB(binary large object)二进制大对象, 使用二进制保存数据null: 表示空值
对数据库文件 SQL 语句:
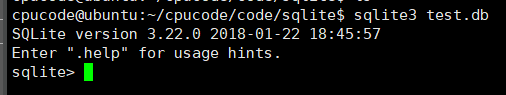
创建、 打开数据库:
当*.db 文件不存在时, sqlite 会创建并打开数据库文件。
当*.db 文件存在时, sqlite 会打开数据库文件。
sqlite3 test.db
SQL 的语句格式:
所有的 SQL 语句都是以分号结尾的, SQL 语句不区分大小写。 两个减号“–” 则代表注释。
关系数据库的核心操作:
- 创建、 修改、 删除表
- 添加、 修改、 删除行
- 查表
创建表: create 语句
语法:
create table 表名称 (列名称1 数据类型, 列名称2 数据类型, 列名称3 数据类型, ...);
创建一表格该表包含 3 列, 列名分别是: “id” 、 “name” 、 “addr” 。
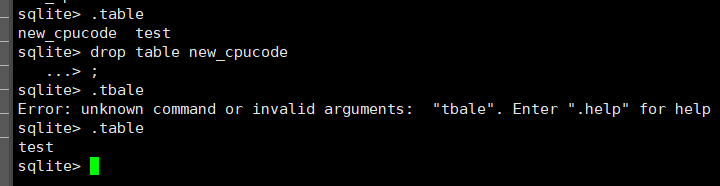
create table cpucode (id integer, name text, addr text);

创建表: create 语句 (设置主键)
在用 sqlite 设计表时, 每个表都可以通过 primary key 手动设置主键, 每个表只能有一个主键, 设置为主键的列数据不可以重复。
语法:
create table 表名称 ( 列名称1 数据类型 primary key, 列名称2 数据类型,列名称3 数据类型, ...);
create table test (id integer primary key, name text, addr text);

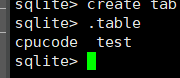
查看表: .table
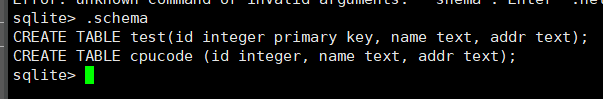
查看数据表的结构:
.schema[表名]
.tables
.schema
退出数据库命令
.quit
.exit
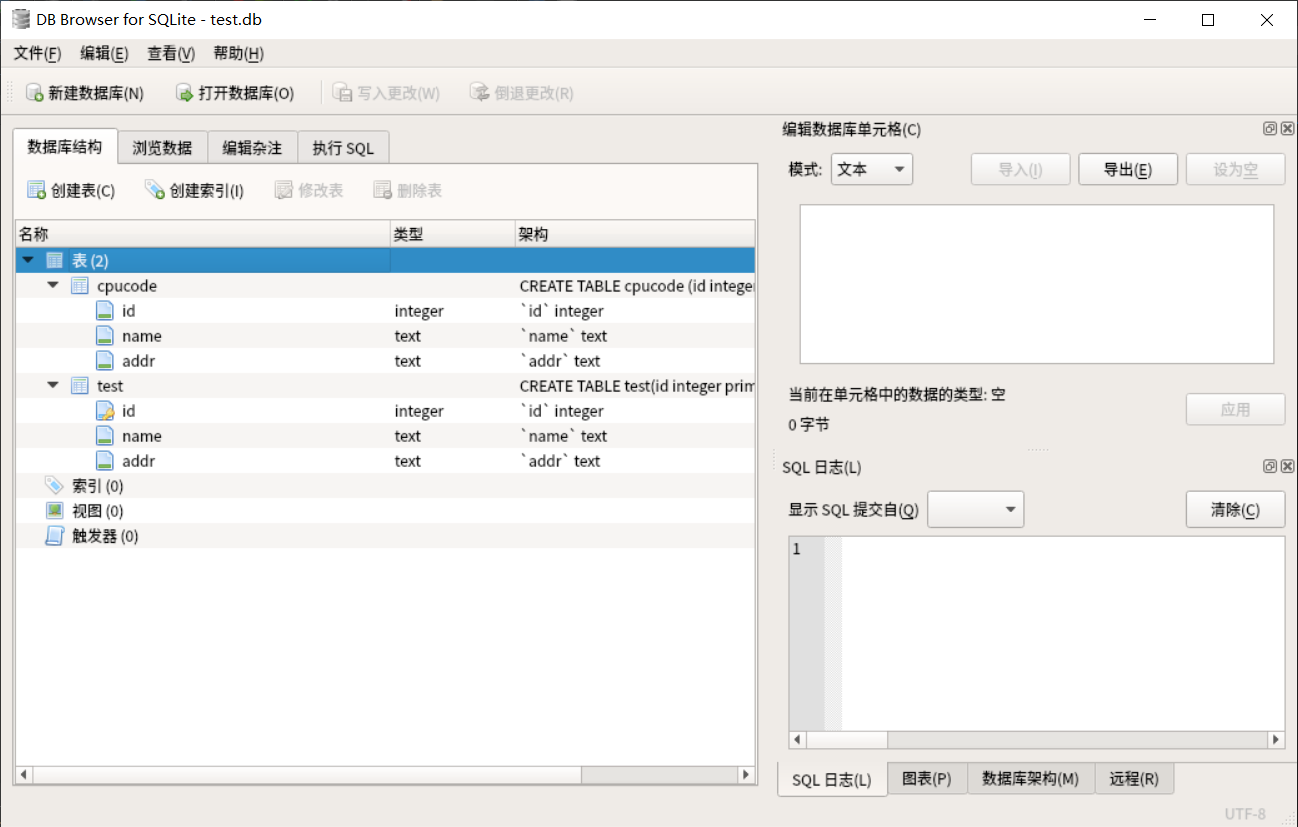
图形化的软件查看表的结构 :
sqlitebrowser test.db
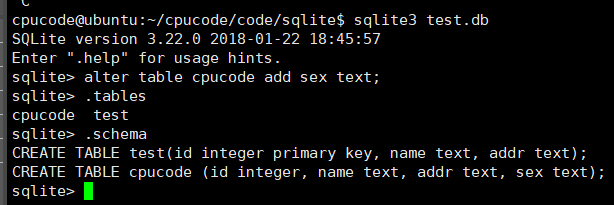
修改表: alter 语句
在已有的表中添加或删除列以及修改表名。(添加、 删除-sqlite3 暂不支持、 重命名)
语法 :
alter table 表名 add 列名 数据类型;
alter table cpucode add sex text;
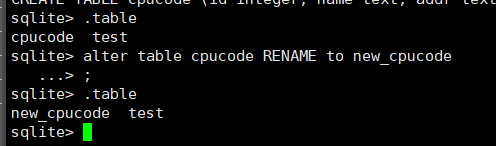
语法: (alter 修改表名)
alter table 表名 rename to 新表名;
.tables
alter table cpucode rename to new_cpucode;
.tables
删除表: drop table 语句
用于删除表(表的结构、 属性以及表的索引也会被删除)
语法:
drop table 表名称;
drop table new_cpucode;
插入新行: insert into 语句(全部赋值)
给一行中的所有列赋值。
当列值为字符串时要加上‘ ’ 号。
语法:
insert into 表名 values (列值 1, 列值 2, 列值 3, 列值 4, ...);
create table cpucode (id integer, name text, addr text);
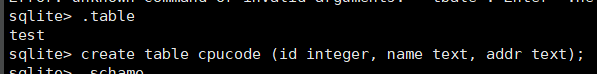
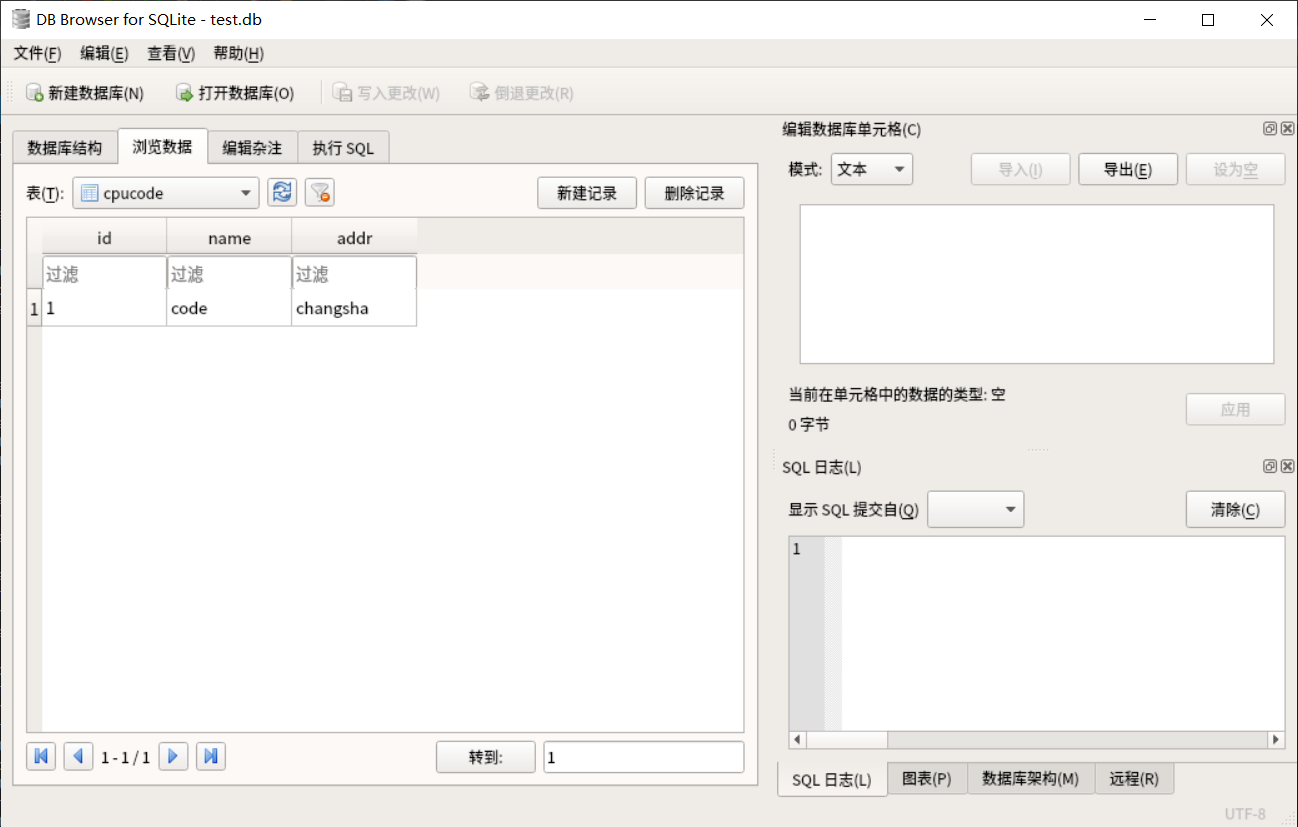
insert into cpucode values (1, 'code', 'changsha');

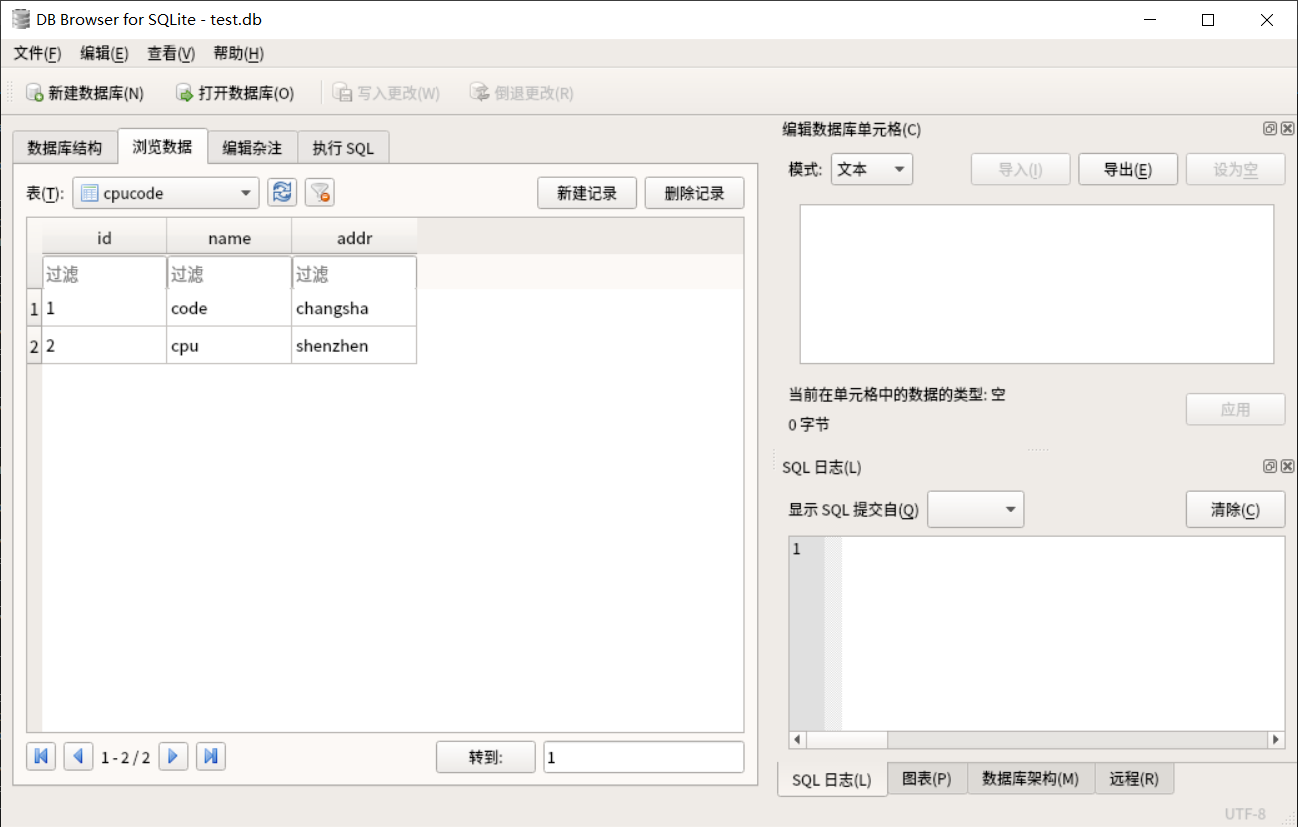
sqlitebrowser test.db
插入新行: insert into 语句部分赋值)
给一行中的部分列赋值
语法:
insert into 表名 (列名 1, 列名 2, ...) values (列值 1, 列值 2, ...);
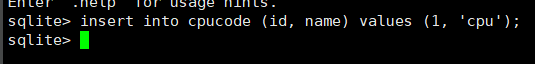
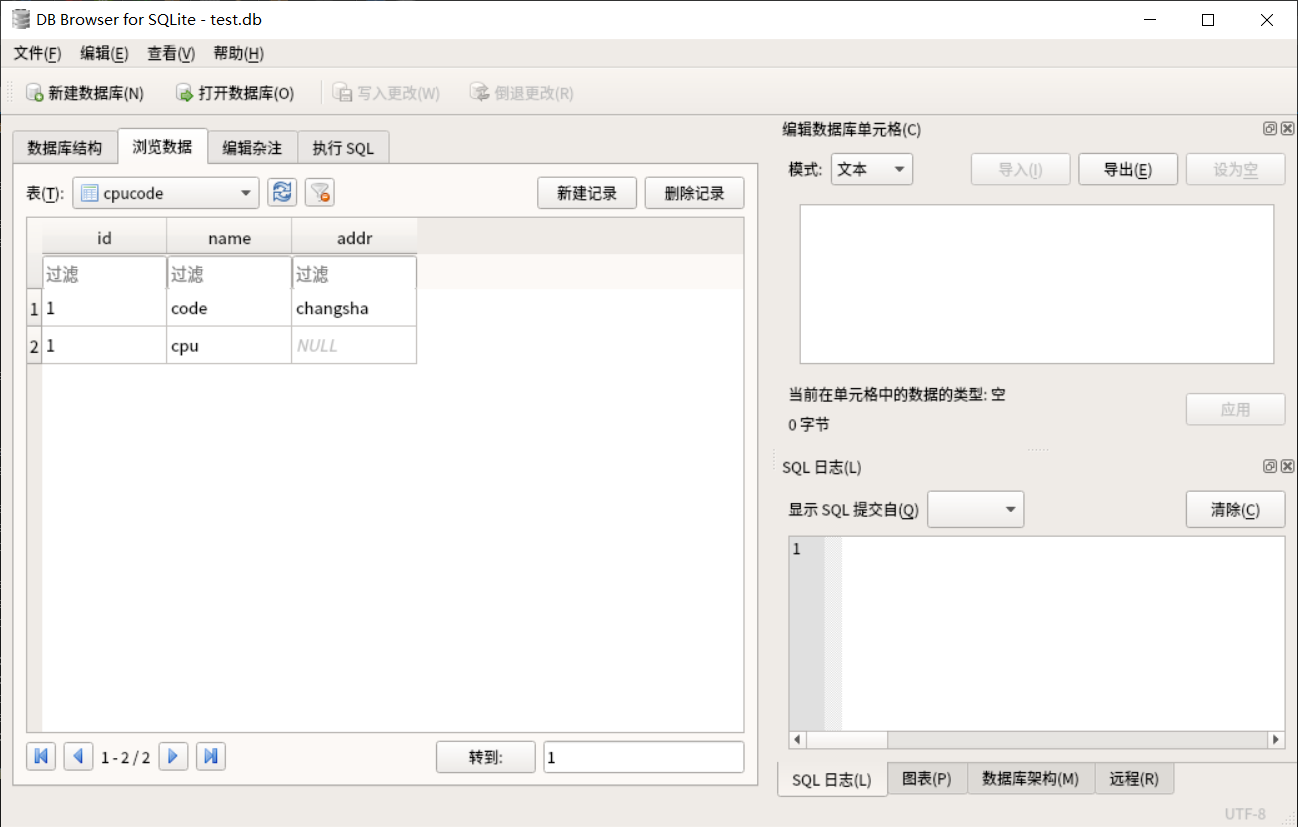
insert into cpucode (id, name) values (1, 'cpu');
sqlitebrowser test.db
修改表中的数据: update 语句
使用 where 根据匹配条件, 查找一行或多行, 根据查找的结果修改表中相应行的列值(修改哪一列由列名指定)。
语法:
update 表名 set 列 1 = 值1 [, 列2 = 值2, ...] [匹配条件];
匹配: where 子句
where 子句用于规定匹配的条件。
| 操作数 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| = | 等于 |
| <> | 不等于 |
| > | 大于 |
| < | 小于 |
| >= | 大于等于 |
| <= | 小于等于 |
匹配条件语法:
where 列名 操作符 列值
update cpucode set id=2, addr='shenzhen' where name='cpu';

sqlitebrowser test.db
当表中有多列、 多行符合匹配条件时会修改相应的多行。 当匹配条件为空时则匹配所有。
当表中有多列、 多行符合匹配条件时会修改相应的多行 :
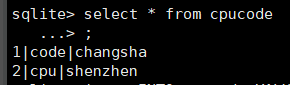
查询
select * from cpucode;
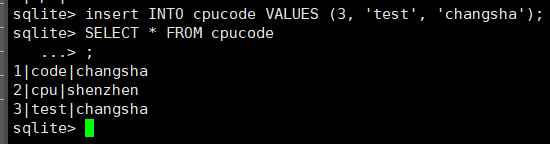
插入
insert into cpucode values (3, 'test', 'changsha');
查询
select * from cpucode;
修改
update cpucode set name='cpu' where addr='changsha';
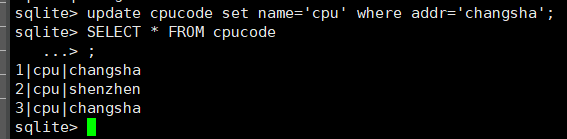
查看
select * from cpucode;
当匹配条件为空时则匹配所有 :
修改 :
update cpucode set addr='shenzhen';
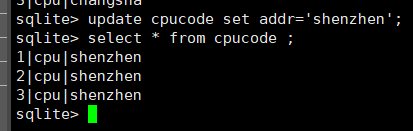
删除表中的数据: delete 语句
使用 where 根据匹配条件, 查找一行或多行, 根据查找的结果删除表中的查找到的行。
当表中有多列、 多行符合匹配条件时会删除相应的多行。
语法:
delete from 表名 [匹配条件];
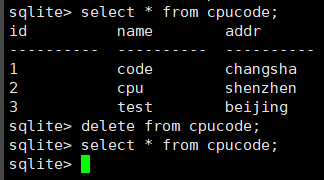
删除
delete from cpucode where name='cpu';
查看
select * from cpucode;
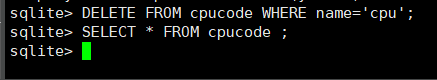
insert into cpucode values (1, 'code', 'changsha');
insert into cpucode values (2, 'cpu', 'shenzhen');
insert into cpucode values (3, 'test', 'beijing');
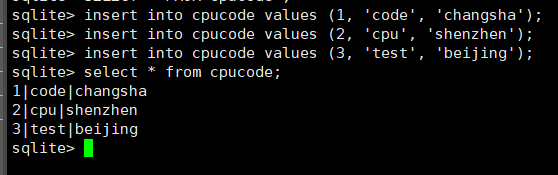
查询: select 语句
用于从表中选取数据, 结果被存储在一个结果表中(称为结果集) 。
星号(*) 是选取所有列的通配符
语法:
select * from 表名 [匹配条件];
select 列名 1[, 列名 2, ...] from 表名 [匹配条件];
select * from cpucode
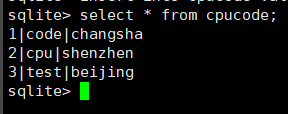
查看
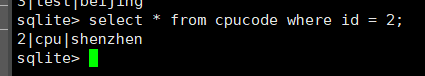
select * from cpucode where id=2;
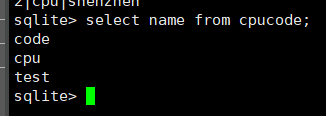
select name from cpucode;
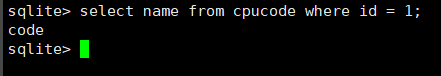
select name from cpucode where id = 1;
列名显示
.headers on
左对齐
.mode column
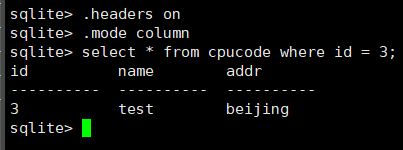
select * from cpucode where id = 3;
匹配条件语法
数据库提供了丰富的操作符配合 where 子句实现了多种多样的匹配方法。
- in 操作符
- and 操作符
- or 操作符
- between and 操作符
- like 操作符
- not 操作符
in 允许我们在 where 子句中规定多个值。
匹配条件语法:
where 列名 in (列值 1, 列值 2, ...)
select * from 表名 where 列名 in (值 1, 值 2, ...);
select 列名 1[,列名 2,...] from 表名 where 列名 in (列值 1, 列值 2, ...);
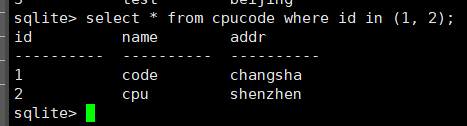
select * from cpucode where id in (1, 2);
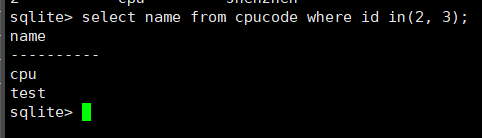
select name from cpucode where id in(2, 3);
and 可在 where 子语句中把两个或多个条件结合起来(多个条件之间是与的关系) 。
匹配条件语法:
where 列 1 = 值 1 [and 列 2 = 值 2 and ...]
select * from 表名 where 列 1 = 值 1 [and 列 2 = 值 2 and ...];
select 列名 1[, 列名 2, ...] from 表名 where 列 1 = 值 1 [and 列 2 = 值 2 and ...];
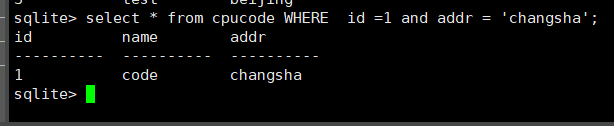
select * from cpucode where id =1 and addr = 'changsha';
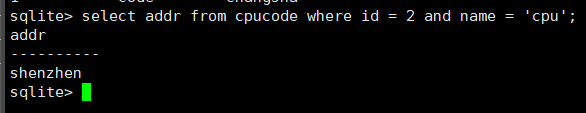
select addr from cpucode where id = 2 and name = 'cpu';
or 可在 where 子语句中把两个或多个条件结合起来(多个条件之间是或的关系) 。
匹配条件语法:
where 列 1 = 值 1 [or 列 2 = 值 2 or ...]
select * from 表名 where 列 1 = 值 1 [or 列 2 = 值 2 or ...];
select 列名 1[,列名 2,...] from 表名 列 1 = 值 1 [or 列 2 = 值 2 or ...];
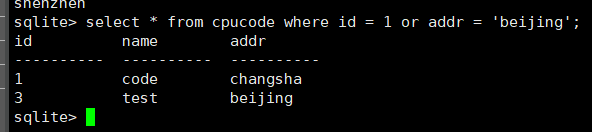
select * from cpucode where id = 1 or addr = 'beijing';
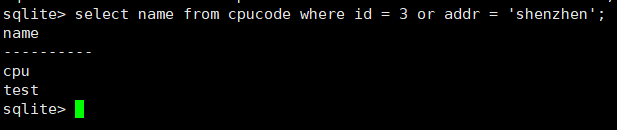
select name from cpucode where id = 3 or addr = 'shenzhen';
between A and B 会选取介于 A、 B 之间的数据范围。 这些值可以是数值、 文本或者日期。
匹配字符串时会以 ascii 顺序匹配。
不同的数据库对 between A and B 操作符的处理方式是有差异的。
- 有些数据库包含 A 不包含 B。
- 有些包含 B 不包含 A
- 有些既不包括 A 也不包括 B。
- 有些既包括 A 又包括 B
匹配条件语法:
where 列名 between A and B
select * from 表名 where 列名 between A and B;
select 列名 1[,列名 2,...] from 表名 where 列名 between A and B;
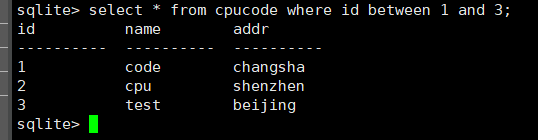
select * from cpucode where id between 1 and 3;
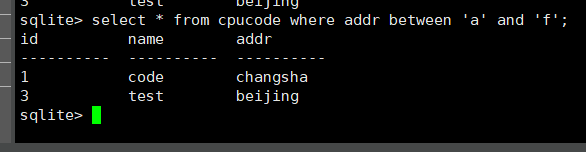
select * from cpucode where addr between 'a' and 'f';
like 用于模糊查找
匹配条件语法:
若列值为数字 , 相当于列名=列值
若列值为字符串 , 可以用通配符“ % ” 代表缺少的字符(一个或多个) 。
where 列名 like 列值
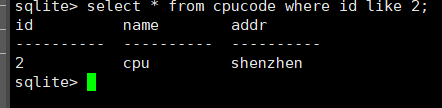
select * from cpucode where id like 2;
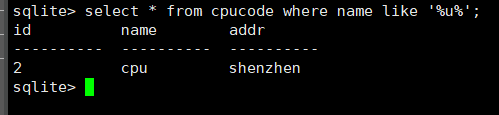
select * from cpucode where name like '%u%';
not 可取出原结果集的补集
匹配条件语法:
where 列名 not in 列值等
where 列名 not in (列值 1, 列值 2, ...)
where not (列 1 = 值 1 [and 列 2 = 值 2 and ...])
where not (列 1 = 值 1 [or 列 2 = 值 2 or ...])
where 列名 not between A and B
where 列名 not like 列值
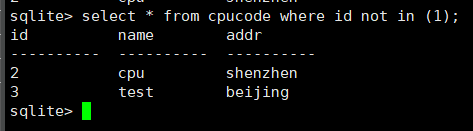
select * from cpucode where id not in (1);
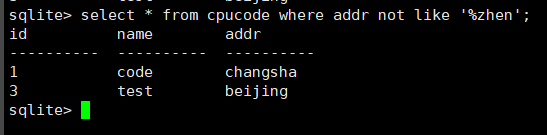
select * from cpucode where addr not like '%zhen';
order by 语句
根据指定的列对结果集进行排序。
默认按照升序对结果集进行排序, 可使用 desc 关键字按照降序对结果集进行排序。
升序
select * from 表名 order by 列名;
降序
select * from 表名 order by 列名 desc;
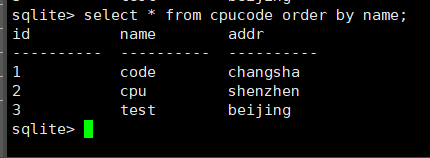
select * from cpucode order by name;
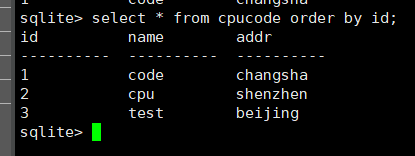
select * from cpucode order by id;
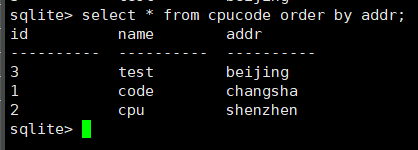
select * from cpucode order by addr;
select * from cpucode order by id desc;
事务
事务(Transaction) 可以使用 BEGIN TRANSACTION 命令或简单的 BEGIN 命令来启动。 此类事务通常会持续执行下去, 直到遇到下一个 COMMIT 或 ROLLBACK 命令。 不过在数据库关闭或发生错误时, 事务处理也会回滚。 以下是启动一个事务的简单语法:
在 SQLite 中, 默认情况下, 每条 SQL 语句自成事务。
begin: 开始一个事务, 之后的所有操作都可以取消
commit: 使 begin 后的所有命令得到确认。
rollback: 取消 begin 后的所有操作。
begin;delete from cpucode;rollback;select * from cpucode;