cs144 LAB1 基于滑动窗口的碎片字节流重组器
一.StreamReassembler.capacity 的意义
StreamReassembler._capacity 的含义:
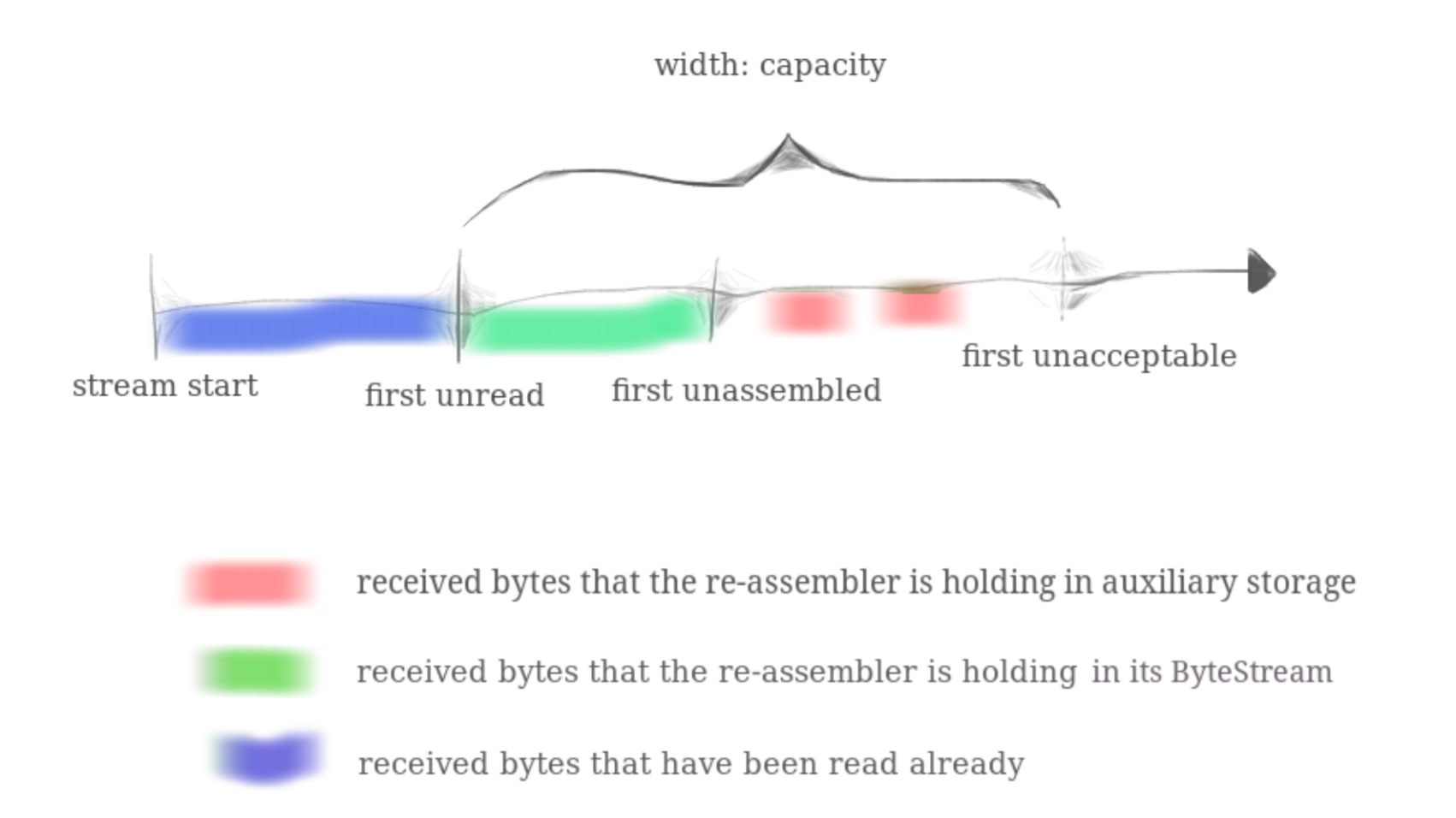
ByteStream的空间上限是capacityStreamReassembler用于暂存未重组字符串片段的缓冲区空间StreamReassembler.buffer上限也是capacity- 蓝色部分代表了已经被上层应用读取的已重组数据
- 绿色部分代表了
ByteStream中已经重组并写入但还未被读取的字节流所占据的空间大小 - 红色部分代表了
StreamReassembler中已经缓存但未经重组的若干字符串片段所占据的空间大小 - 同时绿色和红色两部分加起来的空间总占用大小不会超过
capacity(事实上会一直小于它)
从代码层面来看:
- first unread 的索引等于
ByteStream的bytes_read()函数的返回值(我们一般不关注这个值) - first unassembled 的索引等于
ByteStream的bytes_write()函数的返回值(起始就是下一个期望的字节在流中的序号) - first unacceptable 的索引等于
ByteStream的bytes_read()加上capacity的和(已超过ByteStream的 buffer 限制) - first unread 和 first unacceptable 这两个边界是动态变化的,每次重组结束都需要更新。
最后,有个很重要点,ByteStream 和 StreamReassembler 的总容量有固定的限制,多余的数据需要丢弃(此需要对端重传数据,这就引出了重传等知识点)
二.滑动窗口碎片重组算法
每次收到的data数据由于网络传输不可靠的原因会产生乱序,重叠。需要对每次收到的碎片序列进行重组。可以定义装配器的窗口大小为capacity,范围为[_first_unassembled,_first_unassembled + _capacity]。超出此范围的字节将被丢弃(实验要求,之后会引出重传)。窗口会随着第一个期望的字节序号进行移动即_first_unassembled。每次计算缓冲区第一个期望字节序号,并保障每个字节碎片都在窗口范围内,这需要对碎片进行裁剪,裁剪过后的碎片可以直接加入缓存区。
可分为下面几个步骤完成:
1.计算重组器窗口起始位置,结束位置。
2.判断碎片是否合法,不合法则直接丢弃。
3.裁剪碎片,使其满足缓冲区要求。
4.碎片加入缓存区。
5.缓存区写入流。(如果缓冲区头部有元素的话)
6.判断EOF。
需要注意EOF这里有几个大坑,首先是EOF可能会提早到来,这时不能直接结束流写入需要进行判断。第二是EOF可能与其他流重叠,故而可以记录EOF的合法结束字节位置来判断是否真正需要停止流写入。
#ifndef SPONGE_LIBSPONGE_STREAM_REASSEMBLER_HH
#define SPONGE_LIBSPONGE_STREAM_REASSEMBLER_HH#include "byte_stream.hh"#include <cstdint>
#include <string>
#include <deque>//! \brief A class that assembles a series of excerpts from a byte stream (possibly out of order,
//! possibly overlapping) into an in-order byte stream.
class StreamReassembler {private:// Your code here -- add private members as necessary.std::deque<std::string::value_type> _reassembler_buffer; //重组器缓冲区std::deque<bool> _bytes_flag; //重组器字节标志位std::size_t _unassembaled_bytes = 0; //未被装配的字节bool _is_eof = false; //判断子序列是否含有EOFstd::size_t _eof_index = 0; //记录EOF段最后一个字节的位置ByteStream _output; //!< The reassembled in-order byte streamsize_t _capacity; //!< The maximum number of bytespublic://! \brief Construct a `StreamReassembler` that will store up to `capacity` bytes.//! \note This capacity limits both the bytes that have been reassembled,//! and those that have not yet been reassembled.StreamReassembler(const size_t capacity);//! \brief Receive a substring and write any newly contiguous bytes into the stream.//!//! The StreamReassembler will stay within the memory limits of the `capacity`.//! Bytes that would exceed the capacity are silently discarded.//!//! \param data the substring//! \param index indicates the index (place in sequence) of the first byte in `data`//! \param eof the last byte of `data` will be the last byte in the entire streamvoid push_substring(const std::string &data, const uint64_t index, const bool eof);//! \name Access the reassembled byte stream//!@{const ByteStream &stream_out() const { return _output; }ByteStream &stream_out() { return _output; }//!@}//! The number of bytes in the substrings stored but not yet reassembled//!//! \note If the byte at a particular index has been pushed more than once, it//! should only be counted once for the purpose of this function.size_t unassembled_bytes() const;//! \brief Is the internal state empty (other than the output stream)?//! \returns `true` if no substrings are waiting to be assembledbool empty() const;
};#endif // SPONGE_LIBSPONGE_STREAM_REASSEMBLER_HH
#include "stream_reassembler.hh"// Dummy implementation of a stream reassembler.// For Lab 1, please replace with a real implementation that passes the
// automated checks run by `make check_lab1`.// You will need to add private members to the class declaration in `stream_reassembler.hh`template <typename... Targs>
void DUMMY_CODE(Targs &&... /* unused */) {}using namespace std;StreamReassembler::StreamReassembler(const size_t capacity) :
_reassembler_buffer(capacity, '\0'),
_bytes_flag(capacity, false),
_output(capacity),
_capacity(capacity) {}//! \details This function accepts a substring (aka a segment) of bytes,
//! possibly out-of-order, from the logical stream, and assembles any newly
//! contiguous substrings and writes them into the output stream in order.
void StreamReassembler::push_substring(const string &data, const size_t index, const bool eof) {//判断index是否合法std::size_t _first_unassembled = _output.bytes_written(); //每次计算期望的字节序号std::size_t _first_unacceptable = _first_unassembled + _capacity; //第一个不允许装配的字节序号if(index >= _first_unacceptable || index + data.length() < _first_unassembled)return;//滑动窗口位于[_first_unassembled,_first_unassembled + _capacity]之间只有其中元素可以入队,对data进行裁剪std::size_t new_index = index;std::size_t new_end = index + data.length();if(new_index < _first_unassembled)new_index = _first_unassembled;if(new_end >= _first_unacceptable)new_end = _first_unacceptable;//裁剪完成后data的起始位置符合滑动窗口要求,入队for(std::size_t i = new_index; i < new_end; ++i){if(!_bytes_flag[i - _first_unassembled]){_reassembler_buffer[i - _first_unassembled] = data[i - index]; //入队_bytes_flag[i - _first_unassembled] = true; //相应标志位置位++_unassembaled_bytes; //缓冲区计数增加}}//写入流操作(当装配缓冲区头部有元素那么一定是顺序的直接写入流)string wait_to_write{};while(_bytes_flag.front()){wait_to_write += _reassembler_buffer.front();_bytes_flag.pop_front();_reassembler_buffer.pop_front();_bytes_flag.emplace_back(false); //维护缓冲区大小_reassembler_buffer.emplace_back('\0'); //维护缓冲区大小}if(wait_to_write.size() > 0){int out_bytes = _output.write(std::move(wait_to_write));_unassembaled_bytes -= out_bytes;}//检查eofif(eof){_is_eof = true;_eof_index = new_end;}if(_is_eof && _eof_index == _output.bytes_written())_output.end_input();
}size_t StreamReassembler::unassembled_bytes() const { return _unassembaled_bytes; }bool StreamReassembler::empty() const { return _unassembaled_bytes == 0; }
