CompletableFuture 基本用法
一、 CompletableFuture简介
CompletableFuture 是 Java 8 引入的一个功能强大的类,用于异步编程和并发处理。它提供了丰富的 API 来处理异步任务的结果,支持函数式编程风格,并允许通过链式调用组合多个异步操作。
二、CompletableFuture中的方法
1. 创建 CompletableFuture 对象
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier): 异步执行给定的Supplier函数,并返回一个新的CompletableFuture,当函数完成时,该CompletableFuture将以函数的结果完成。
示例代码:
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException; public class CompletableFutureExample { public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException { // 使用 supplyAsync 异步执行一个计算 CompletableFuture<String> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> { // 模拟一个耗时的计算 try { Thread.sleep(2000); // 等待 2 秒 } catch (InterruptedException e) { Thread.currentThread().interrupt(); throw new IllegalStateException(e); } return "Hello, CompletableFuture!"; }); // 主线程可以继续执行其他任务,而不需要等待上面的计算完成 // 当需要结果时,可以调用 get() 方法(这会阻塞,直到结果可用) String result = future.get(); // 这里会等待上面的计算完成,然后返回结果 System.out.println(result); // 输出 "Hello, CompletableFuture!" }
}这里顺便讲一下get方法:
(1)get方法的作用是等待此 CompletableFuture 完成,然后返回其结果(或抛出异常)。
(2)get方法的返回值是CompletableFuture<T> 里面的泛型的类型;比如上面的例子中CompletableFuture<String> 泛型是String 所以这里future.get()的返回值是String类型
示例1:
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException; public class CompletableFutureExample { public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException { CompletableFuture<String> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> { ...... }); String result = future.get(); // 因为 CompletableFuture<String> 泛型是String 所以这里future.get()的返回值是String类型}
}示例2:
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException; public class CompletableFutureExample { public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException { CompletableFuture<Integer> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> { ...... }); Integerresult = future.get(); // 因为 CompletableFuture<Integer> 泛型是Integer所以这里future.get()的返回值是Integer类型}
}另外,supplyAsync 方法还有一个重载版本,它接受一个 Executor 作为参数,允许你指定用于执行计算的线程池。这对于控制异步任务的执行环境非常有用。例如:
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10); // 创建一个固定大小的线程池
CompletableFuture<String> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> { // ... 耗时的计算 ...
}, executor); // 使用指定的线程池执行计算
CompletableFuture.runAsync(Runnable runnable): 异用于异步地执行一个Runnable任务,并且不返回任何结果(返回类型为CompletableFuture<Void>)。这在你只关心任务的执行而不关心其返回值时非常有用。
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture; public class CompletableFutureExample { public static void main(String[] args) { // 使用默认的 ForkJoinPool 异步执行任务 CompletableFuture<Void> future = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> { // 模拟一个耗时的任务 try { Thread.sleep(2000); // 假设任务需要2秒来完成 } catch (InterruptedException e) { Thread.currentThread().interrupt(); // 恢复中断状态 throw new RuntimeException(e); // 抛出运行时异常以便可以看到异常信息 } System.out.println("任务执行完毕!"); }); // 在主线程中继续执行其他操作,不需要等待上面的任务完成 System.out.println("主线程继续执行..."); // 如果你想等待任务完成,可以调用 future.join() 或 future.get(),但请注意这可能会阻塞当前线程 // 这里我们只是打印出任务是否已经完成 System.out.println("任务是否完成: " + future.isDone()); // 注意:由于任务是异步执行的,所以上面的 isDone() 方法可能返回 false,因为任务可能还没有完成 // 你可以通过 future.thenRun(...) 来添加在任务完成后要执行的代码 future.thenRun(() -> System.out.println("任务完成后执行的代码")); // 注意:thenRun 中的代码也是异步执行的,并且可能在主线程之后执行 // 为了确保主线程在异步任务完成后才结束,可以调用 future.join() try { future.join(); // 等待异步任务完成 } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } // 现在可以确定异步任务已经完成 System.out.println("主线程结束"); }
}
2. 处理异步任务的结果
thenApply(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn): 当此CompletableFuture完成时,将结果应用于给定的函数,并返回一个新的CompletableFuture,该CompletableFuture将以函数的结果完成。thenAccept(Consumer<? super T> action): 当此CompletableFuture完成时,对结果执行给定的操作,然后返回this。thenRun(Runnable action): 当此CompletableFuture完成时,执行给定的操作,然后返回this。
3. 组合多个 CompletableFuture
thenCombine(CompletableFuture<? extends U> other, BiFunction<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn): 当此CompletableFuture和另一个给定的CompletableFuture都完成时,使用这两个结果作为参数应用给定的函数,并返回一个新的CompletableFuture,该CompletableFuture将以函数的结果完成。
传统写法:
public static void main(String[] args) {CompletableFuture<Integer> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {// 模拟耗时计算,返回结果try {Thread.sleep(1000); // 等待1秒} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return 42; // 假设这是第一个任务的结果});CompletableFuture<Integer> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {// 模拟耗时计算,返回结果try {Thread.sleep(500); // 等待0.5秒} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return 13; // 假设这是第二个任务的结果});// 使用 thenCombine 合并两个任务的结果CompletableFuture<Integer> resultFuture = future1.thenCombine(future2, (a, b) -> a + b);// 等待结果并打印Integer join = resultFuture.join();System.out.println(join);//55}链式调用:
public static void main(String[] args) {CompletableFuture<Integer> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {// 模拟耗时计算,返回结果try {Thread.sleep(1000); // 等待1秒} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return 42; // 假设这是第一个任务的结果}).thenCombine(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {// 模拟耗时计算,返回结果try {Thread.sleep(500); // 等待0.5秒} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return 13; // 假设这是第二个任务的结果}),(res1,res2)->{int total = res1 + res2;return total;});// 等待结果并打印Integer total = future1.join();System.out.println(total); // 42+13=55}thenCompose(Function<? super T,? extends CompletionStage<U>> fn): 当此CompletableFuture完成时,对其结果应用给定的函数,该函数返回一个新的CompletionStage,然后返回表示该CompletionStage结果的CompletableFuture。
thenCompose是 CompletableFuture 类中的一个方法,它允许你将一个 CompletableFuture 的结果用作另一个 CompletableFuture 计算的输入,从而链式地组合多个异步操作。
使用场景
thenCompose 适用于以下场景:
- 连续异步处理:当你需要对一个异步操作的结果进行另一个异步操作时,可以使用
thenCompose将这两个操作连接在一起。 - 避免嵌套:使用
thenCompose可以避免Future的嵌套,使得代码更加简洁和平坦。
传统写法:
package com.etime.test;import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;/*** @Date 2024/6/22 20:08* @Author liukang**/
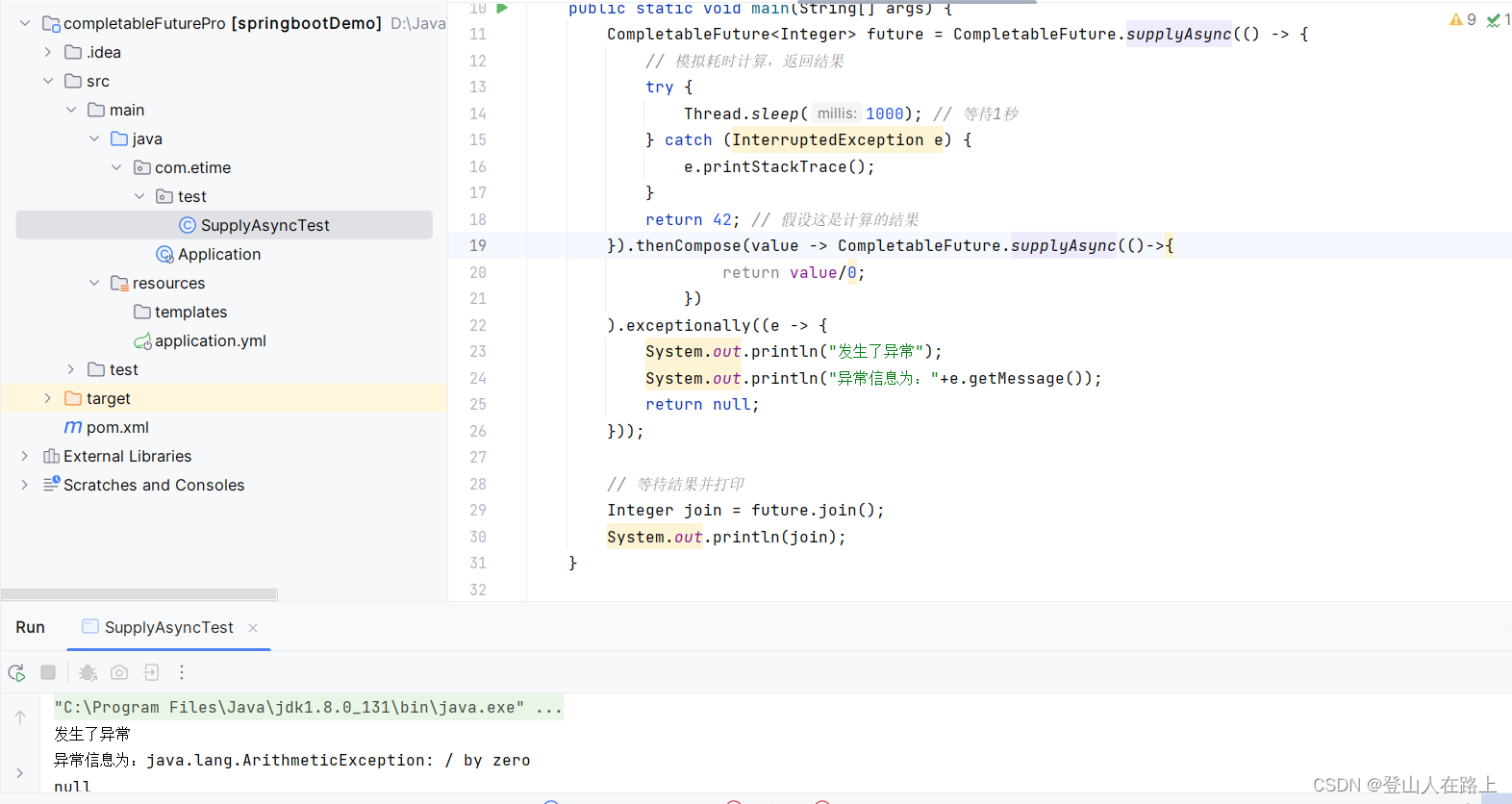
public class SupplyAsyncTest {public static void main(String[] args) {CompletableFuture<Integer> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {// 模拟耗时计算,返回结果try {Thread.sleep(1000); // 等待1秒} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return 42; // 假设这是计算的结果});CompletableFuture<Integer> resultFuture = future.thenCompose(value -> {// 使用前一个任务的结果(value)作为输入,创建并返回一个新的CompletableFuturereturn CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> value * 2); // 将结果乘以2});// 等待结果并打印Integer join = resultFuture.join();System.out.println(join);//84}}
链式调用:
public static void main(String[] args) {CompletableFuture<Integer> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {// 模拟耗时计算,返回结果try {Thread.sleep(1000); // 等待1秒} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return 42; // 假设这是计算的结果}).thenCompose(value -> CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{return value*2;}));Integer join = future.join();System.out.println(join);}
allOf(CompletableFuture<?>... cfs): 返回一个新的CompletableFuture,该CompletableFuture在所有给定的CompletableFuture都完成时完成。anyOf(CompletableFuture<?>... cfs): 返回一个新的CompletableFuture,该CompletableFuture在任何一个给定的CompletableFuture完成时完成。
4. 异常处理
exceptionally(Function<Throwable,? extends T> fn): 当此CompletableFuture异常完成时,应用给定的函数到异常,并返回一个新的CompletableFuture,该CompletableFuture将以函数的结果完成。
exceptionally是Java中CompletableFuture类的一个方法,用于处理异步操作中可能发生的异常。通过调用exceptionally方法并定义一个异常处理函数,你可以确保在异步操作出现异常时能够优雅地处理,并返回一个默认值或其他的值。
public static void main(String[] args) {CompletableFuture<Integer> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {// 模拟耗时计算,返回结果try {Thread.sleep(1000); // 等待1秒} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return 42; // 假设这是计算的结果}).thenCompose(value -> CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{return value/0;})).exceptionally((e -> {System.out.println("发生了异常");System.out.println("异常信息为:"+e.getMessage());return null;}));// 等待结果并打印Integer join = future.join();System.out.println(join);}
handle(BiFunction<? super T,Throwable,? extends U> fn): 当此CompletableFuture完成时,无论是正常完成还是异常完成,都将结果和异常(如果有)应用于给定的函数,并返回一个新的CompletableFuture,该CompletableFuture将以函数的结果完成。
5. 其他方法
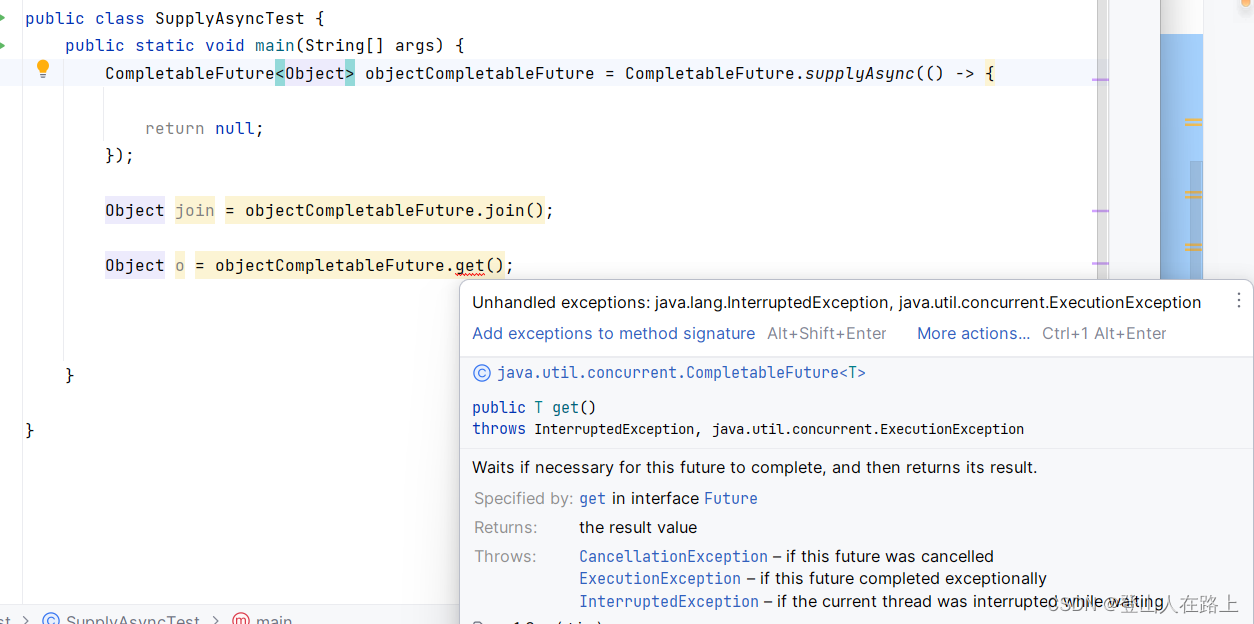
join(): 等待此CompletableFuture完成,然后返回其结果(或抛出异常),是get方法的升级版。get(): 等待此CompletableFuture完成,然后返回其结果(或抛出异常)。与join()类似,但可能抛出InterruptedException和ExecutionException。
join()和get()的区别
- 抛出异常的方式不同:
get方法会抛出ExecutionException异常(如果异步任务执行过程中出现异常),这个异常是具体的,需要显式捕获。此外,如果线程在等待过程中被中断,它还会抛出InterruptedException。join方法则会抛出CompletionException异常(如果异步任务执行过程中出现异常),这个异常是 unchecked 的,因此不需要显式捕获。如果线程在等待过程中被中断,它不会抛出InterruptedException,因为它本身是不可中断的。
- 方法调用限制不同:
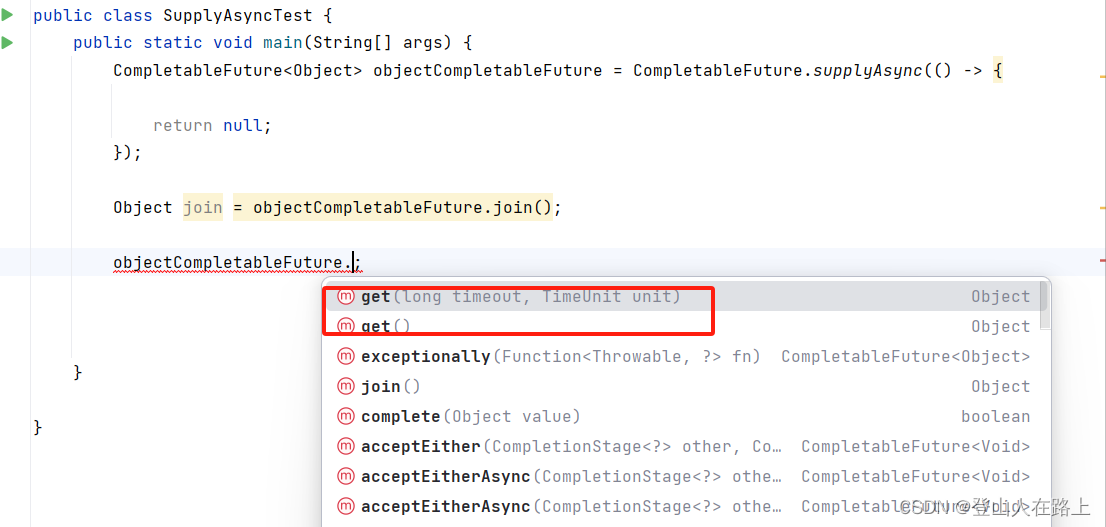
get方法可以在调用时设置等待的超时时间,如果超时还没有获取到结果,就会抛出TimeoutException异常。这使得get方法在使用时具有更大的灵活性。join方法则没有这样的超时机制,一旦调用就必须等待任务执行完成才能返回结果。它不能被中断,除非异步任务本身完成。
- 返回结果类型不同:
get方法返回的是异步任务的执行结果,该结果是泛型类型T的,需要强制转换才能获取真正的结果。join方法同样返回的是异步任务的执行结果,但不需要强制类型转换,因为其结果就是泛型类型T。
- 推荐使用方式不同:
join方法通常被推荐用于CompletableFuture,因为它没有受到interrupt的干扰,不需要捕获异常,也不需要强制类型转换。这使得代码更加简洁和易于阅读。get方法则提供了更多的控制选项,如设置超时时间,这在某些需要更细粒度控制的场景下可能是有用的。但需要注意的是,它可能会抛出InterruptedException,这需要在代码中显式处理。
- 阻塞行为:
- 两者都是阻塞方法,都会阻塞当前线程直到异步任务完成。但如上所述,
join方法是不可中断的,而get方法可以被中断。
- 两者都是阻塞方法,都会阻塞当前线程直到异步任务完成。但如上所述,
总结来说,join 和 get 方法在 CompletableFuture 中都用于获取异步任务的执行结果,但在抛出异常的方式、方法调用限制、返回结果类型以及推荐使用方式等方面存在显著的区别。根据具体的需求和场景,可以选择使用 join 或 get 方法。
complete(T value): 如果尚未完成,则尝试以给定值完成此CompletableFuture。completeExceptionally(Throwable ex): 如果尚未完成,则尝试以给定异常完成此CompletableFuture。
这些只是 CompletableFuture 提供的一部分方法,但它已经足够强大,可以处理大多数异步编程和并发处理的场景。
