C++系列-泛型编程之类模板
泛型编程之类模板
- 类模板
- 类模板的定义方式
- 类模板的举例
- 类模板和函数模板的区别
- 类模板中的成员函数创建时机
- 类模板的对象做函数的参数
- 指定传入类型
- 类中的参数模板化
- 整个类模板化
- 类模板与继承
- 类模板中成员函数的类外实现
- 类模板分文件编写
- 类模板分文件编写的问题
- 问题原因
- 解决方案
- 类模板与友元
- 全局函数类内实现
- 全局函数类外实现
宿王昌龄隐居
常建〔唐代〕
清溪深不测,隐处唯孤云。
松际露微月,清光犹为君。
茅亭宿花影,药院滋苔纹。
余亦谢时去,西山鸾鹤群。
类模板
类模板的作用:建立一个通用的类,类中成员的数据类型不指定,用一个虚拟的类型来表示。
类模板的定义方式
- template<class T> 类的定义,template:说明其下紧跟的类是一个类模板。
- typename:表明其后的符号代表一种数据类型,也可以用class代替。后面可以有多个typename。
- T:通用数据类型,也可以用其它符号代替。
类模板的举例
code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;template<class T_NAME, class T_AGE>
class Person
{
public:Person(T_NAME name, T_AGE age){m_name = name;m_age = age;}void print_info(){cout << "名字: " << m_name << ", 年龄: " << m_age << endl;}T_NAME m_name;T_AGE m_age;
};void test01()
{Person<string, int> p1("张三", 99); // 类型参数化,<string, int> 模板参数列表p1.print_info();
}int main()
{test01();system("pause");return 0;
}result:
名字: 张三, 年龄: 99
类模板和函数模板的区别
- 类模板没有自动类型推导的方式。
- 类模板在模板的参数列表(<>里面的参数)中可以有默认参数。
code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;template<class T_NAME, class T_AGE=int> // 类模板可以有模板默认参数
class Person
{
public:Person(T_NAME name, T_AGE age){m_name = name;m_age = age;}void print_info(){cout << "名字: " << m_name << ", 年龄: " << m_age << endl;}T_NAME m_name;T_AGE m_age;
};void test01()
{Person<string> p1("张三", 99); // 类型参数化,<string> 模板参数列表, 省略了模板默认参数p1.print_info();
}int main()
{test01();system("pause");return 0;
}result:
名字: 张三, 年龄: 99
类模板中的成员函数创建时机
- 普通类中的成员函数一开始就创建
- 类模板中的成员函数在调用时才创建
下面的代码运行并不会出错,PersonClass中的成员函数func1, func2并不会创建,因为并没有调用到它们。
code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;class Person1
{
public:void print_info1(){cout << "Person1的成员函数调用 " << endl;}
};class Person2
{
public:void print_info2(){cout << "Person2的成员函数调用 " << endl;}
};template<class T>
class PersonClass
{
public:T obj; void func1(){obj.print_info1(); // T的类型是Person1时,此句才能正确执行}void func2(){obj.print_info2(); // T的类型是Person2时,此句才能正确执行}
};
int main()
{cout << "代码运行" << endl;system("pause");return 0;
}result:
代码运行
下面的代码中调用了成员函数,则会在调用的时候创建,此时可以知道是否调用正确。
code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;class Person1
{
public:void print_info1(){cout << "Person1的成员函数调用 " << endl;}
};class Person2
{
public:void print_info2(){cout << "Person2的成员函数调用 " << endl;}
};template<class T>
class PersonClass
{
public:T obj; void func1(){obj.print_info1(); // T的类型是Person1时,此句才能正确执行}void func2(){obj.print_info2(); // T的类型是Person2时,此句才能正确执行}
};void test01()
{PersonClass<Person1> p1;p1.func1();// p1.func2(); // 错误,因为在调用p1.func2时,知道p1的类型,创建成员函数,发现p1没有func2PersonClass<Person2> p2;p2.func2();
}
int main()
{cout << "代码运行" << endl;test01();system("pause");return 0;
}result:
代码运行
Person1的成员函数调用
Person2的成员函数调用
类模板的对象做函数的参数
通过类模板定义的对象,如果作为函数的参数,有几种方式传参
- 指定传入参数,最为常用
- 类中的参数模板化,其实是类模板配合函数模板
- 整个类模板化,其实是类模板配合函数模板
指定传入类型
- 在函数定义中,参数类型直接指定为对象的类型,void print_info(Person &p1),直接指定形参为Person类型
code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;template<class T_NAME, class T_AGE = int> // 类模板可以有模板默认参数
class Person
{
public:Person(T_NAME name, T_AGE age){m_name = name;m_age = age;}T_NAME m_name;T_AGE m_age;
};// 在类模板的对象作为函数参数时,在形参列表中指定传入的类型(p1的传入类型指定为Person<>)
void print_info(Person<string> &p1)
{cout << "名字: " << p1.m_name << ", 年龄: " << p1.m_age << endl;p1.m_age = 20;
}void test01()
{Person<string> p1("张三", 99);print_info(p1);
}int main()
{test01();system("pause");return 0;
}result:
名字: 张三, 年龄: 99
类中的参数模板化
- typeid(T1).name()是求T1的类型
- 在函数定义时,如果形参是类的对象,那么类中的参数模板化时,要在函数前面加template<class T1, class T2>,这相当于函数也是模板函数。
code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;template<class T_NAME, class T_AGE>
class Person
{
public:Person(T_NAME name, T_AGE age){m_name = name;m_age = age;}T_NAME m_name;T_AGE m_age;
};// 函数的参数是类模板的对象,类中的模板参数也可以作为模板传入,
// 这其实相当于这个函数也是函数模板
template<class T1, class T2>
void print_info(Person<T1, T2> &p1)
{cout << "名字: " << p1.m_name << ", 年龄: " << p1.m_age << endl;cout << "T1类型: " << typeid(T1).name() << endl;cout << "T2类型: " << typeid(T2).name() << endl;
}
// 如果有下面的函数,会优先调用,说明上面的函数是一个函数模板
//void print_info(Person<string, int>& p1)
//{
// cout << "普通函数" << endl;
//}void test01()
{Person<string, int> p1("张三", 99);print_info(p1);
}int main()
{test01();system("pause");return 0;
}result:
名字: 张三, 年龄: 99
T1类型: class std::basic_string<char,struct std::char_traits<char>,class std::allocator<char> >
T2类型: int
整个类模板化
code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;template<class T_NAME, class T_AGE>
class Person
{
public:Person(T_NAME name, T_AGE age){m_name = name;m_age = age;}T_NAME m_name;T_AGE m_age;
};// 整个类模板化
template<class T>
void print_info(T &p1)
{cout << "名字: " << p1.m_name << ", 年龄: " << p1.m_age << endl;cout << "T类型: " << typeid(T).name() << endl;
}void test01()
{Person<string, int> p1("张三", 99);print_info(p1);
}int main()
{test01();system("pause");return 0;
}result:
名字: 张三, 年龄: 99
T类型: class Person<class std::basic_string<char,struct std::char_traits<char>,class std::allocator<char> >,int>
类模板与继承
- 当子类继承的父类是一个类模板时,子类在声明的时候,需要指明父类中T的类型,如果不指定,编译器无法给子类分配内存。
- 如果要灵活指定父类中T的类型,子类也需要变为类模板。
code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;template<class T>
class Base
{T m_name;
};// class Son : public Base // 这一句会报错,因为子类在声明时,没有指明父类T的类型
// 可以直接指定父类中T的类型,但是会导致通用性不强。
class Son1 : public Base<int>
{
public:Son1(){cout << "Son1 instance" << endl;}
};// 子类也模板化,这样就更通用了
template<class T_Base, class T>
class Son2: public Base<T_Base>
{
public:T age;Son2(){cout << "T_Base类型: " << typeid(T_Base).name() << endl;cout << "T类型: " << typeid(T).name() << endl;}
};void test01()
{Son1 s1; Son2<int, char>s2;
}int main()
{test01();system("pause");return 0;
}result:
Son1 instance
T_Base类型: int
T类型: char
类模板中成员函数的类外实现
- 类模板中的成员函数在类外实现时,除了作用域,要加上类模板参数列表
- ::作用域,是个模板<>, <参数类型>注明模板参数,template<class T_NAME, class T_AGE>:声明模板
code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;template<class T_NAME, class T_AGE>
class Person
{
public:Person(T_NAME name, T_AGE age);void print_info();private:T_NAME m_name;T_AGE m_age;
};// ::Person作用域下,Person是个模板<>,注明模板参数,声明模板
template<class T_NAME, class T_AGE>
Person<T_NAME, T_AGE>::Person(T_NAME name, T_AGE age)
{m_name = name;m_age = age;
}template<class T_NAME, class T_AGE>
void Person<T_NAME, T_AGE>::print_info()
{cout << "名字: " << m_name << ", 年龄: " << m_age << endl;
}void test01()
{Person<string, int> s1("张三", 18);s1.print_info();
}int main()
{test01();system("pause");return 0;
}result:
名字: 张三, 年龄: 18
类模板分文件编写
类模板中的成员函数创建是在调用阶段,导致分文件编写时链接不到(传统的方式,如果只#include .h文件,h文件中只有函数的声明)
类模板分文件编写的问题
类的声明放在person.h文件中
code:
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;template<class T_NAME, class T_AGE>
class Person
{
public:Person(T_NAME name, T_AGE age);void print_info();private:T_NAME m_name;T_AGE m_age;
};
类的成员函数实现放在person.cpp文件中
#include "person.h"
// ::Person作用域下,Person是个模板<>,注明模板参数,声明模板
template<class T_NAME, class T_AGE>
Person<T_NAME, T_AGE>::Person(T_NAME name, T_AGE age)
{m_name = name;m_age = age;
}template<class T_NAME, class T_AGE>
void Person<T_NAME, T_AGE>::print_info()
{cout << "名字: " << m_name << ", 年龄: " << m_age << endl;
}
在调用时会报错
#include <iostream>
#include "person.h"using namespace std;
void test01()
{Person<string, int> s1("张三", 18); // 代码报错,无法解析的外部命令s1.print_info(); // 代码报错,无法解析的外部命令
}int main()
{test01();system("pause");return 0;
}
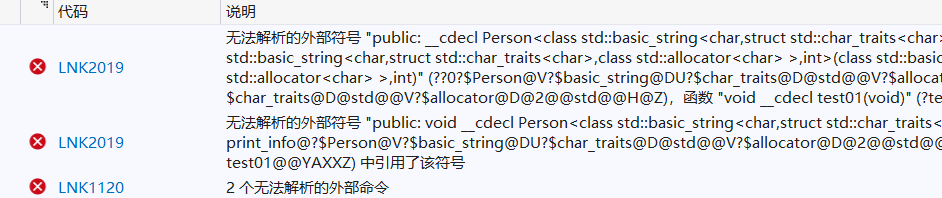
问题原因
- 在main函数中调用关于类的代码时,包含头文件person.h,因为类中的成员函数是在调用的时候创建,在链接阶段看到person.h的时候并不创建函数,看不到cpp的文件,所以在link的过程中会报错。
解决方案
- 解决方法1,直接包含cpp文件,但是一般都不会直接包含cpp文件。
- 解决方法2,将.h和.cpp中的文件写在同一个文件中,后缀名改为hpp,这个是主流解决方案
.hpp文件的代码
code:
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;template<class T_NAME, class T_AGE>
class Person
{
public:Person(T_NAME name, T_AGE age);void print_info();private:T_NAME m_name;T_AGE m_age;
};// ::Person作用域下,Person是个模板<>,注明模板参数,声明模板
template<class T_NAME, class T_AGE>
Person<T_NAME, T_AGE>::Person(T_NAME name, T_AGE age)
{m_name = name;m_age = age;
}template<class T_NAME, class T_AGE>
void Person<T_NAME, T_AGE>::print_info()
{cout << "名字: " << m_name << ", 年龄: " << m_age << endl;
}
上层调用代码
code:
#include <iostream>
#include "person.hpp"using namespace std;
void test01()
{Person<string, int> s1("张三", 18);s1.print_info();
}int main()
{test01();system("pause");return 0;
}
类模板与友元
全局函数类内实现
- 直接在类内声明友元即可
code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;template<class T_NAME, class T_AGE>
class Person
{// void print_info(Person<T_NAME, T_AGE>& p) // 如果没有friend,是一个私有成员函数friend void print_info(Person<T_NAME, T_AGE>& p){cout << "名字: " << p.m_name << ", 年龄: " << p.m_age << endl;}public:Person(T_NAME name, T_AGE age);private:T_NAME m_name;T_AGE m_age;
};// ::Person作用域下,Person是个模板<>,注明模板参数,声明模板
template<class T_NAME, class T_AGE>
Person<T_NAME, T_AGE>::Person(T_NAME name, T_AGE age)
{m_name = name;m_age = age;
}void test01()
{Person<string, int> s1("张三", 18);print_info(s1);
}int main()
{test01();system("pause");return 0;
}result:
名字: 张三, 年龄: 18
全局函数类外实现
- 需要提前让编译器知道全局函数的存在,要提前声明,其中使用到的类等也要提前声明。
- 在声明友元时,全局函数是函数模板,需要在函数名后加<>
code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;// 因为友元全局函数用到了Person,需要让编译器先知道有个类模板Person
template<class T_NAME, class T_AGE>
class Person;// 全局函数在类模板外部实现时,需要在友元声明前让编译器知道这个全局函数的存在
template<class T_NAME, class T_AGE>
void print_info(Person<T_NAME, T_AGE>& p);template<class T_NAME, class T_AGE>
class Person
{// 下面语句错误,这是普通函数作友元的方式,而这个全局函数是函数模板,需要在函数名后加<>// friend void print_info(Person<T_NAME, T_AGE>& p); friend void print_info<>(Person<T_NAME, T_AGE>& p); // public:Person(T_NAME name, T_AGE age);private:T_NAME m_name;T_AGE m_age;
};// print_info是一个全局函数,代码在类外实现,这是一个函数模板
// 全局函数想访问类中的私有成员,需要将其声明为类的友元函数
template<class T_NAME, class T_AGE>
void print_info(Person<T_NAME, T_AGE>& p)
{cout << "名字: " << p.m_name << ", 年龄: " << p.m_age << endl;
}// ::Person作用域下,Person是个模板<>,注明模板参数,声明模板
template<class T_NAME, class T_AGE>
Person<T_NAME, T_AGE>::Person(T_NAME name, T_AGE age)
{m_name = name;m_age = age;
}void test01()
{Person<string, int> s1("张三", 18);print_info(s1);
}int main()
{test01();system("pause");return 0;
}result:
名字: 张三, 年龄: 18
更为简单的方式如下
code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;template<class T_NAME, class T_AGE>
class Person
{ template<class T_NAME, class T_AGE>friend void print_info(Person<T_NAME, T_AGE>& p);public:Person(T_NAME name, T_AGE age);private:T_NAME m_name;T_AGE m_age;
};// print_info是一个全局函数,代码在类外实现,这是一个函数模板
// 全局函数想访问类中的私有成员,需要将其声明为类的友元函数
template<class T_NAME, class T_AGE>
void print_info(Person<T_NAME, T_AGE>& p)
{cout << "名字: " << p.m_name << ", 年龄: " << p.m_age << endl;
}// ::Person作用域下,Person是个模板<>,注明模板参数,声明模板
template<class T_NAME, class T_AGE>
Person<T_NAME, T_AGE>::Person(T_NAME name, T_AGE age)
{m_name = name;m_age = age;
}void test01()
{Person<string, int> s1("张三", 18);print_info(s1);
}int main()
{test01();system("pause");return 0;
}result:
名字: 张三, 年龄: 18
注意:本文部分内容来自黑马
