c++类和对象(3):默认成员函数(下)
1.拷贝构造函数
c++规定:类类型的传值传参必须用拷贝构造
1.1拷贝构造函数的特点
class Date
{
public:Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}//同名函数,形参不同,构成重载//参数是自身类类型的引用Date(Date& d){_year = d._year;_month = d._month;_day = d._day;}private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
};
class Date
{
public:Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}//对类类型对象的引用Date(Date& d){_year = d._year;_month = d._month;_day = d._day;}private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
};
int main()
{Date d1(2024,6,6);Date d2(d1);return 0;
}
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;class Date
{
public:Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}Date( const Date& d){_year = d._year;_month = d._month;_day = d._day;}//不是拷贝构造,就是一个普通构造Date(Date* d){_year = d->_year;_month = d->_month;_day = d->_day;}private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
};Date F1()
{Date ret;//..return ret;
}int main()
{Date d1(2024, 2, 3);// C++规定⾃定义类型对象进⾏拷⻉⾏为必须调⽤拷⻉构造,// 所以这⾥的d1传值传参给d要调⽤拷⻉构造完成拷⻉//都是拷贝构造Date d2(d1);Date d3 = d1;Date d4(F1());Date d5 = F1();return 0;
}
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;class Date
{
public:Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}//Date(Date& d)//{// _year = d._year;// _month = d._month;// _day = d._day;//}private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
};int main()
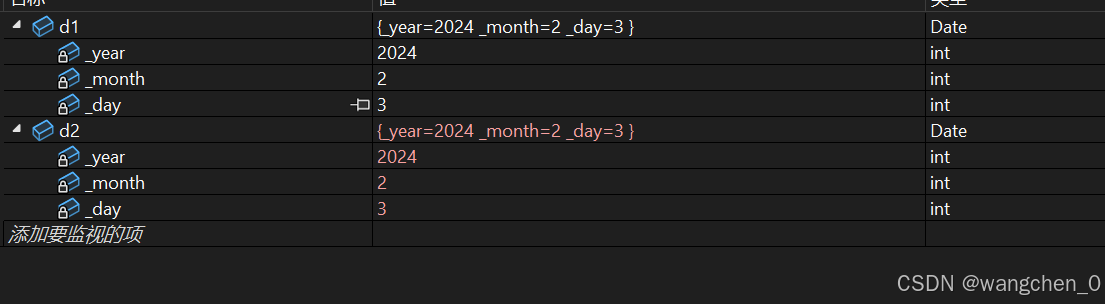
{Date d1(2024,2,3);// C++规定⾃定义类型对象进⾏拷⻉⾏为必须调⽤拷⻉构造,// 所以这⾥的d1传值传参给d要调⽤拷⻉构造完成拷⻉Date d2(d1);return 0;
}
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;typedef int STDataType;
class Stack
{
public:Stack(int n = 4){_a = (STDataType*)malloc(sizeof(STDataType) * n);if (nullptr == _a){perror("malloc申请空间失败");return;}_capacity = n;_top = 0;}Stack(const Stack& st){// 需要对_a指向资源创建同样⼤的资源再拷⻉值_a = (STDataType*)malloc(sizeof(STDataType) * st._capacity);if (nullptr == _a){perror("malloc申请空间失败!!!");return;}memcpy(_a, st._a, sizeof(STDataType) * st._top);_top = st._top;_capacity = st._capacity;}void Push(STDataType x){if (_top == _capacity){int newcapacity = _capacity * 2;STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(_a, newcapacity *sizeof(STDataType));if (tmp == NULL){perror("realloc fail");return;}_a = tmp;_capacity = newcapacity;}_a[_top++] = x;}~Stack(){cout << "~Stack()" << endl;free(_a);_a = nullptr;_top = _capacity = 0;}
private:STDataType* _a;size_t _capacity;size_t _top;
};
// 两个Stack实现队列
class MyQueue
{
public:
private:Stack pushst;Stack popst;
};
int main()
{Stack st1;st1.Push(1);st1.Push(2);// Stack不显⽰实现拷⻉构造,⽤⾃动⽣成的拷⻉构造完成浅拷⻉// 会导致st1和st2⾥⾯的_a指针指向同⼀块资源,析构时会析构两次,程序崩溃Stack st2 = st1;MyQueue mq1;// MyQueue⾃动⽣成的拷⻉构造,会⾃动调⽤Stack拷⻉构造完成pushst/popst// 的拷⻉,只要Stack拷⻉构造⾃⼰实现了深拷⻉,他就没问题MyQueue mq2 = mq1;return 0;
}
typedef int STDataType;
class Stack
{
public:Stack(int n = 4){_a = (STDataType*)malloc(sizeof(STDataType) * n);if (nullptr == _a){perror("malloc申请空间失败");return;}_capacity = n;_top = 0;}Stack(const Stack& st){// 需要对_a指向资源创建同样⼤的资源再拷⻉值_a = (STDataType*)malloc(sizeof(STDataType) * st._capacity);if (nullptr == _a){perror("malloc申请空间失败!!!");return;}memcpy(_a, st._a, sizeof(STDataType) * st._top);_top = st._top;_capacity = st._capacity;}STDataType Top(){return _a[_top - 1];}void Push(STDataType x){if (_top == _capacity){int newcapacity = _capacity * 2;STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(_a, newcapacity *sizeof(STDataType));if (tmp == NULL){perror("realloc fail");return;}_a = tmp;_capacity = newcapacity;}_a[_top++] = x;}~Stack(){cout << "~Stack()" << endl;free(_a);_a = nullptr;_top = _capacity = 0;}
private:STDataType* _a;size_t _capacity;size_t _top;
};
// 两个Stack实现队列
class MyQueue
{
public:
private:Stack pushst;Stack popst;
};
Stack& Func()
{Stack st;st.Push(1);st.Push(2);st.Push(3);return st;
}int main()
{Stack ret = Func();cout << ret.Top() << endl;return 0;
}上面代码会程序崩溃。因为当函数Func结束时会调用Stack的析构函数,会把局部变量st销毁。

当我们把用static修饰st,使其存储到静态区,不会因函数结束而被销毁时,代码正常运行:
typedef int STDataType;
class Stack
{
public:Stack(int n = 4){_a = (STDataType*)malloc(sizeof(STDataType) * n);if (nullptr == _a){perror("malloc申请空间失败");return;}_capacity = n;_top = 0;}Stack(const Stack& st){// 需要对_a指向资源创建同样⼤的资源再拷⻉值_a = (STDataType*)malloc(sizeof(STDataType) * st._capacity);if (nullptr == _a){perror("malloc申请空间失败!!!");return;}memcpy(_a, st._a, sizeof(STDataType) * st._top);_top = st._top;_capacity = st._capacity;}STDataType Top(){return _a[_top - 1];}void Push(STDataType x){if (_top == _capacity){int newcapacity = _capacity * 2;STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(_a, newcapacity *sizeof(STDataType));if (tmp == NULL){perror("realloc fail");return;}_a = tmp;_capacity = newcapacity;}_a[_top++] = x;}~Stack(){cout << "~Stack()" << endl;free(_a);_a = nullptr;_top = _capacity = 0;}
private:STDataType* _a;size_t _capacity;size_t _top;
};
// 两个Stack实现队列
class MyQueue
{
public:
private:Stack pushst;Stack popst;
};
Stack& Func()
{static Stack st;st.Push(1);st.Push(2);st.Push(3);return st;
}int main()
{Stack ret = Func();cout << ret.Top() << endl;return 0;
} 
2.赋值运算符重载
赋值运算符重载是c++的一种操作,它允许程序员为自定义类型重新定义赋值运算符(=)的行为。
2.1运算符重载
运算符重载是c++的一种强大的特性,它允许程序员为自定义类型定义已有的运算符行为。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;class Date
{
public:Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}void Print(){cout << _year << "-" << _month << "-" << _day << endl;}
//私有成员函数外部运算符重载函数不可访问
//private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
};
//除了注释private的三种方法
//1.提供对应的getxxx函数
//2.友元
//3.重载成为成员函数bool operator==(const Date& d1, const Date& d2)
{return d1._year == d2._year&& d1._month == d2._month&& d1._day == d2._day;
}bool operator<(const Date& d1, const Date& d2)
{if (d1._year < d2._year){return true;}else if (d1._year == d2._year && d1._month < d2._month){return true;}else if (d1._year == d2._year && d1._month == d2._month&& d1._day < d2._day){return true;}return false;
}int main()
{Date d1(2024, 6, 6);Date d2(2024, 8, 8);// 运算符重载函数可以显⽰调⽤bool ret1 = operator==(d1, d2);// 编译器会转换成调用对应的// 运算符重载函数 operator==(d1, d2);//operator==(d1, d2)与d1 == d2;效果相同bool ret2 = d1 == d2;bool ret3 = d1 < d2;//内置类型调用简单int i = 1, j = 2;bool ret4 = i < j;cout << ret1 << endl;cout << ret2 << endl;cout << ret3 << endl;cout << ret4 << endl;return 0;
}#include <iostream>
using namespace std;class Date
{
public:Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}void Print(){cout << _year << "-" << _month << "-" << _day << endl;}bool operator==(const Date& d){return _year == d._year&& _month == d._month&& _day == d._day;}bool operator<(const Date& d){if (_year < d._year){return true;}else if (_year == d._year&& _month < d._month){return true;}else if (_year == d._year&& _month == d._month&& _day < d._day){return true;}return false;}private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
};int main()
{Date d1(2024, 6, 6);Date d2(2024, 8, 8);bool ret1 = d1.operator==(d2);bool ret2 = d1.operator<(d2);cout << ret1 << endl;cout << ret2 << endl;return 0;
}(6).* :: sizeof ?: .这5个运算符不能重载。
(7)重载操作符至少有⼀个类类型参数,不能通过运算符重载改变内置类型对象的含义,内置类型入int,double等,不能把两个整数相加的“+”运算符重载为两个整数相减的操作
//错误示范
int operator+( int x, int y)
{return x - y;
}#include <iostream>
using namespace std;class Date
{
public:Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}void Print(){cout << _year << "-" << _month << "-" << _day << endl;}//前置++,返回++后的Date& operator++(){cout << "前置++" << endl;// *this就是d1//*this += 1;return *this;}//后置++,返回++前的Date operator++(int){cout << "后置++" << endl;Date tmp;//Date tmp(*this);//*this += 1;return tmp;}private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
};int main()
{Date d1(2024, 9, 9);//编译器会将其转换成d1.operator();d1++;//编译器会将其转换成d1.operator(0);++d1;return 0;
}一、重载 << 运算符
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;//1. 作用:通常用于将自定义类型的对象输出到标准输出流(如 cout )或其他输出流对象。
//2. 语法:
ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, const YourClass& obj);
//其中 ostream& 是返回类型,表示可以进行链式输出。
//os 是输出流对象,
//const YourClass& obj 是要输出的自定义类型对象。
class Point
{
public:int _x, _y;Point(int x, int y){_x = x;_y = y;}
};
//重载为全局函数
ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, const Point& p)
{os << "(" << p._x << "," << p._y << ")" << endl;return os;
}int main()
{Point p(3, 4);cout << p << endl;return 0;
}
二、重载 >> 运算符
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;//1. 作用:用于从输入流(如 cin )读取数据并存储到自定义类型的对象中。
//2. 语法:
//istream & operator>>(istream & is, YourClass & obj);
//istream& 是返回类型, is 是输入流对象,
// YourClass& obj 是要接收输入数据的自定义类型对象。
class Point
{
public:int _x, _y;Point(int x = 0, int y = 0){_x = x;_y = y;}
};istream& operator>>(istream& is, Point& p)
{is >> p._x >> p._y;return is;
}ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, const Point& p)
{os << "(" << p._x << "," << p._y << ")" << endl;return os;
}int main()
{Point p;cout << "输入x和y的值: ";cin >> p;cout << "Point: " << p << endl;return 0;
}
通过重载 << 和 >> 运算符,可以使自定义类型的对象像内置类型一样方便地进行输入输出操作。
2.2 赋值运算符重载
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;class Date
{
public:Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}Date(const Date& d){_year = d._year;_month = d._month;_day = d._day;}//传引用返回减少拷贝//d2 = d3 //d2.operator= d3Date& operator=(const Date& d){// 检查⾃⼰给⾃⼰赋值的情况 if (this != &d){_year = d._year;_month = d._month;_day = d._day;}// d2 = d3表达式的返回对象应该为d1,也就是*thisreturn *this;}
private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
};int main()
{Date d1(2024, 9, 9);//拷贝构造用于一个已经存在的对象拷贝初始化给一个要创建的对象Date d2(d1);//赋值运算符重载用于两个已经存在的对象的直接拷贝赋值Date d3(2024, 6, 6);d2 = d3;return 0;
}(3)没有显式实现时,编译器会自动生成⼀个默认赋值运算符重载,默认赋值运算符重载行为跟默认拷贝构造函数类似,对内置类型成员变量会完成值拷贝/浅拷贝(⼀个字节⼀个字节的拷贝),对自定义类型成员变量会调用他的赋值重载函数。
(4)像Date这样的类成员变量全是内置类型且没有指向什么资源,编译器自动生成的赋值运算符重载就可以完成需要的拷贝,所以不需要我们显示实现赋值运算符重载。像Stack这样的类,虽然也都是 内置类型,但是_a指向了资源,编译器自动生成的赋值运算符重载完成的值拷贝/浅拷贝不符合我们的需求,所以需要我们自己实现深拷贝(对指向的资源也进行拷贝)。像MyQueue这样的类型内部 主要是自定义类型Stack成员,编译器自动生成的赋值运算符重载会调用Stack的赋值运算符重载, 也不需要我们显示实现MyQueue的赋值运算符重载。这⾥还有⼀个小技巧,如果⼀个类显示实现 了析构并释放资源,那么他就需要显示写赋值运算符重载,否则就不需要。
将赋值运算符注释后,对于Date类成员变量,编译器会自动生成可完成所需要拷贝到赋值运算符,是否显示的写出来没有影响。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;class Date
{
public:Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}Date(const Date& d){_year = d._year;_month = d._month;_day = d._day;}//传引用返回减少拷贝//d2 = d3 //d2.operator= d3//Date& operator=(const Date& d)//{// // 检查⾃⼰给⾃⼰赋值的情况 if (this != &d)// {// _year = d._year;// _month = d._month;// _day = d._day;// }// // d2 = d3表达式的返回对象应该为d1,也就是*this// return *this;//}
private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
};int main()
{Date d1(2024, 9, 9);//拷贝构造用于一个已经存在的对象拷贝初始化给一个要创建的对象Date d2(d1);//赋值运算符重载用于两个已经存在的对象的直接拷贝赋值Date d3(2024, 6, 6);d2 = d3;return 0;
}显示的写出来的结果:

注释之后的结果:

2.3日期类实现
Date.h:
#pragma once
#include <assert.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;class Date
{// 友元函数声明friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Date& d);friend istream& operator>>(istream& in, Date& d);
public:Date(int year = 1900, int month = 1, int day = 1);void Print();int GetMonthDay(int year, int month){assert(month > 0 && month <= 13);static int MonthDayArr[] = { -1,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31 };if (month == 2 && (year % 4 == 0 & year % 100 != 0) || (year % 400 == 0)){return 29;}else{return MonthDayArr[month];}}bool CheckDate();bool operator<(const Date& d);bool operator<=(const Date& d);bool operator>(const Date& d);bool operator>=(const Date& d);bool operator==(const Date& d);bool operator!=(const Date& d);// d1 += 天数Date& operator+=(int day);Date operator+(int day);// d1 -= 天数Date& operator-=(int day);Date operator-(int day);// d1 - d2int operator-(const Date& d);// ++d1 -> d1.operator++()Date& operator++();// 为了区分,构成重载,给后置++,强⾏增加了⼀个int形参// 这个参数仅仅是为了跟前置++构成重载区分// d1++ -> d1.operator++(0)Date operator++(int);Date& operator--();Date operator--(int);// 流插⼊// 不建议,因为Date* this占据了⼀个参数位置,使⽤d<<cout不符合习惯//void operator<<(ostream& out);private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
};// 重载
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Date& d);
istream& operator>>(istream& in, Date& d);text.cpp:
#include "Date.h"Date::Date(int year, int month, int day)
{_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;if (!d.CheckDate()){cout << "日期非法" << endl;}
}void Date::Print()
{cout << _year << "-" << _month << "-" << _day << endl;
}bool Date::CheckDate()
{if (_month < 1 || _month>12 || _day<1 || _day>GetMonthDay(_year, _day)){return false;}else{return true;}}bool Date::operator<(const Date& d)
{if (_year < d._year){return true;}else if (_year == d._year && _month < d._month){return true;}else if (_year == d._year&& _month == d._month&& _day < d._day){return true;}return false;
}
//d1 <= d2
//*this是d1,d是d2
bool Date::operator<=(const Date& d)
{return *this < d || *this == d;
}bool Date::operator>(const Date& d)
{return !(*this <= d);
}
bool Date::operator>=(const Date& d)
{return *this > d || *this == d;
}
bool Date::operator==(const Date& d)
{return _year == d._year&& _month == d._month&& _day == d._day;
}
bool Date::operator!=(const Date& d)
{return !(*this == d);
}
//d1+=100
//改变了d1的值
Date& Date::operator+=(int day)
{if (day < 0){return *this -= -day;}_day += day;while (_day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month)){_day -= GetMonthDay(_year, _month);_month++;if (_month == 13){_month = 1;_year++;}}return *this;
}
//d1+100
//没有改变d1的值
Date Date::operator+(int day)
{//拷贝构造,将d1的值拷贝给tmpDate tmp = *this;tmp += day;return tmp;
}
//d2-=100
Date& Date::operator-=(int day)
{if (day < 0){return *this += -day;}_day -= day;while (_day <= 0){_day += GetMonthDay(_year, _month);_month--;if (_month == 0){_month = 12;_year--;}}return *this;
}
//d2-100
Date Date::operator-(int day)
{Date tmp = *this;tmp -= day;return tmp;
}int Date::operator-(const Date& d)
{Date max = *this;Date min = d;int flag = 1;while (*this < d) {max = d;min = *this;flag = -1;}int n = 0;while (min != max){min++;n++;}return n * flag;
}//++d1
Date& Date::operator++()
{*this += 1;return *this;
}
//d1++
Date Date::operator++(int)
{Date tmp(*this);*this += 1;return tmp;
}
//--d1
Date& Date::operator--()
{*this -= 1;return *this;
}
//d1--
Date Date::operator--(int)
{Date tmp(*this);*this -= 1;return tmp;
}ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Date& d)
{out << d._year << "年" << d._month << "月" << d._day << "日" << endl;return out;
}istream& operator>>(istream& in, Date& d)
{cout << "请依次输入年月日:>";in >> d._year >> d._month >> d._day;if (!d.CheckDate()){cout << "日期非法" << endl;}return in;
}text.cpp:
#include "Date.h"int main()
{Date d1(2024, 9, 9);Date d2(2024, 6, 6);d1 += 100;d1.Print();//2024-12-18d1 + 100;d1.Print();//2024-12-18Date ret1 = d1 + 100;ret1.Print();//2025-3-28d2 -= 200;d2.Print();//2023-11-19d2 - 100;d2.Print();//2023-11-19Date ret2 = d2 - 100;ret2.Print();//2023-8-10cout << d1 - d2 << endl;//395++d1;d1.Print();Date ret3 = d1++;ret3.Print();d1.Print();cout << d1 << d2;cin >> d1 >> d2;cout << d1 << d2 << endl;return 0;
}3.取地址运算符重载
3.1const成员函数
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Date
{
public:Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1){_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;}// void Print(const Date* const this) constvoid Print() const{cout << _year << "-" << _month << "-" << _day << endl;}
private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
};
int main()
{// 这⾥⾮const对象也可以调⽤const成员函数// 这是⼀种权限的缩⼩Date d1(2024, 9, 9);d1.Print();//const的修饰使得d2的内容不能被改变const Date d2(2024, 6, 6);d2.Print();return 0;
}3.2取地址运算符重载
class Date
{
public://显示的写了,便用写了的,编译器不会再自动生成Date* operator&(){return this;//return nullptr}const Date* operator&()const{return this;//return nullptr}
private:int _year; // 年int _month; // ⽉int _day; // ⽇};
