Python3学习第四天
文章目录
- Python3 基础语法
- 注释
- 单行注释
- 多行注释
- 行与缩进
- 数字(Number)类型
- 字符串(String)
- python保留字
- 空行
- 等待用户输入
- 同一行显示多条语句
- import 与 from...import
- 导入 sys 模块
- 导入 sys 模块的 argv,path 成员
- 命令行参数
Python3 基础语法
注释
单行注释
Python中单行注释以 # 开头,实例如下
#!/usr/bin/python3
# 第一个注释
print ("Hello, Python!") # 第二个注释
多行注释
多行注释可以用多个#号,还有 '''和"""
#!/usr/bin/python3
# 第一个注释
# 第二个注释
'''
第三注释
第四注释
'''
"""
第五注释
第六注释
"""
print ("Hello, Python!")
行与缩进
python最具特色的就是使用缩进来表示代码块,不需要使用大括号{}。
if True:
print ("True")
else:
print ("False")
数字(Number)类型
python中数字有四种类型:整数、布尔型、浮点数和复数。
| 类型 | 类型中文 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| int | 整数 | 只有一种整数类型 int,表示为长整型,没有 python2 中的 Long |
| bool | 布尔 | 如 True |
| float | 浮点数 | 如 1.23、3E-2 |
| complex | 复数 | 如 1 + 2j、 1.1 + 2.2j |
字符串(String)
python中单引号和双引号使用完全相同。
使用三引号('''或""")可以指定一个多行字符串。
转义符 '\'
反斜杠可以用来转义,使用r可以让反斜杠不发生转义。。 如 r"this is a line with \n" 则\n会显示,并不是换行。
按字面意义级联字符串,如"this " "is " "string"会被自动转换为this is string。
字符串可以用 + 运算符连接在一起,用 * 运算符重复。
Python 中的字符串有两种索引方式,从左往右以 0 开始,从右往左以 -1 开始。
Python中的字符串不能改变。
Python 没有单独的字符类型,一个字符就是长度为 1 的字符串。
字符串的截取的语法格式如下:变量[头下标:尾下标:步长]
word = '字符串'
sentence = "这是一个句子。"
paragraph = """这是一个段落,
可以由多行组成"""
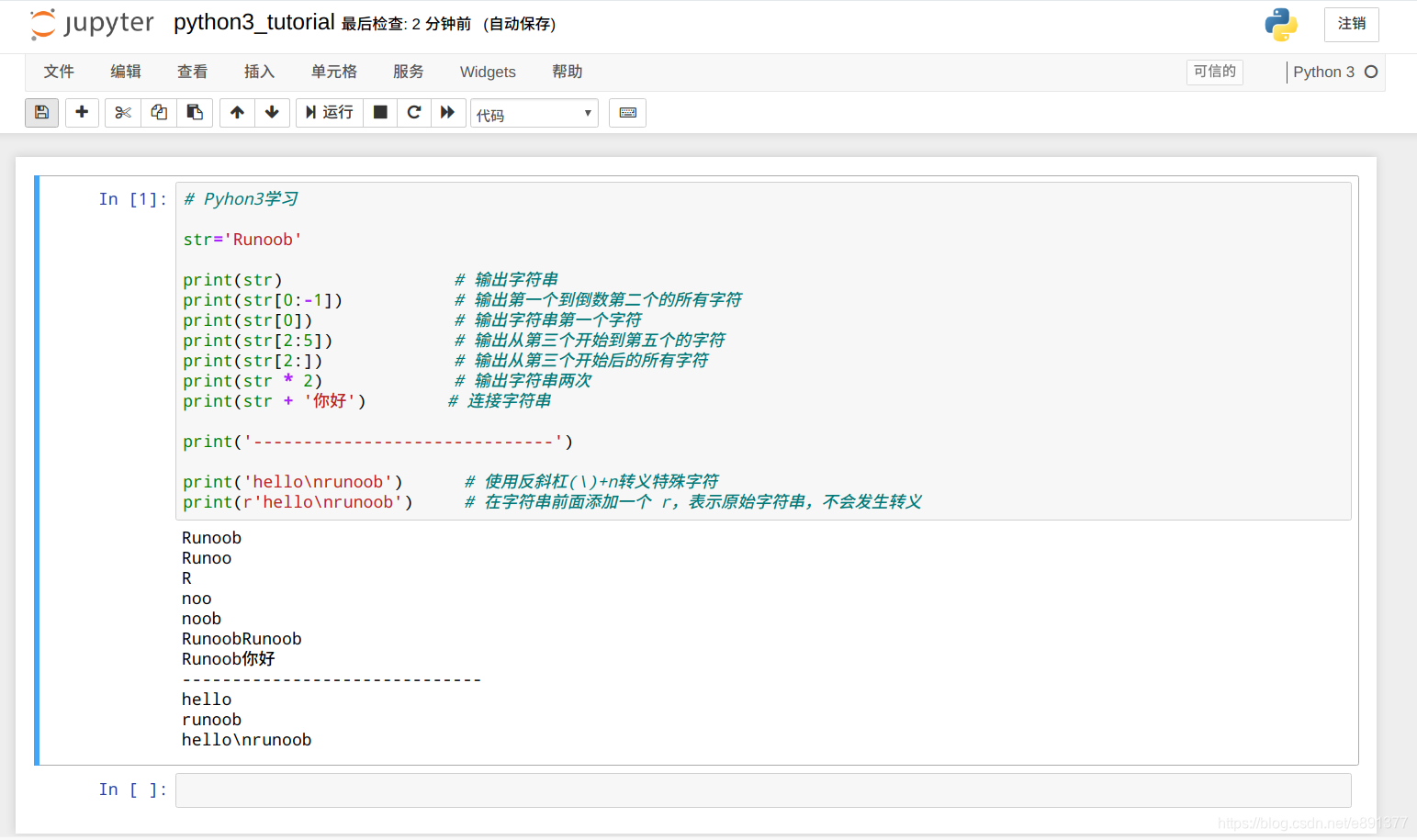
#!/usr/bin/python3
str='Runoob'
print(str) # 输出字符串
print(str[0:-1]) # 输出第一个到倒数第二个的所有字符
print(str[0]) # 输出字符串第一个字符
print(str[2:5]) # 输出从第三个开始到第五个的字符
print(str[2:]) # 输出从第三个开始后的所有字符
print(str * 2) # 输出字符串两次
print(str + '你好') # 连接字符串
print('------------------------------')
print('hello\nrunoob') # 使用反斜杠(\)+n转义特殊字符
print(r'hello\nrunoob') # 在字符串前面添加一个 r,表示原始字符串,不会发生转义
点击运行
python保留字
#python保留字
import keyword
keyword.kwlist
| python保留字 |
|---|
| [‘False’, ‘None’, ‘True’, ‘and’, ‘as’, ‘assert’, ‘break’, ‘class’, ‘continue’, ‘def’, ‘del’, ‘elif’, ‘else’, ‘except’, ‘finally’, ‘for’, ‘from’, ‘global’, ‘if’, ‘import’, ‘in’, ‘is’, ‘lambda’, ‘nonlocal’, ‘not’, ‘or’, ‘pass’, ‘raise’, ‘return’, ‘try’, ‘while’, ‘with’, ‘yield’] |
空行
函数之间或类的方法之间用空行分隔,表示一段新的代码的开始。类和函数入口之间也用一行空行分隔,以突出函数入口的开始。
空行与代码缩进不同,空行并不是Python语法的一部分。书写时不插入空行,Python解释器运行也不会出错。但是空行的作用在于分隔两段不同功能或含义的代码,便于日后代码的维护或重构。
记住:空行也是程序代码的一部分。
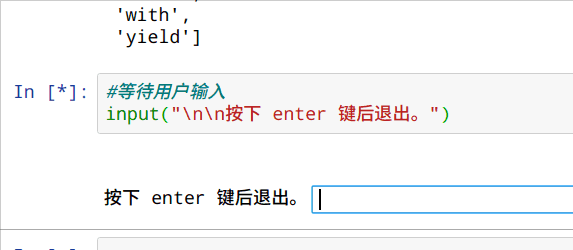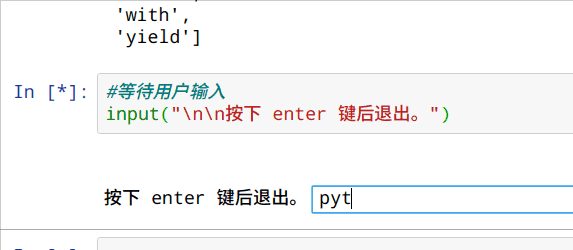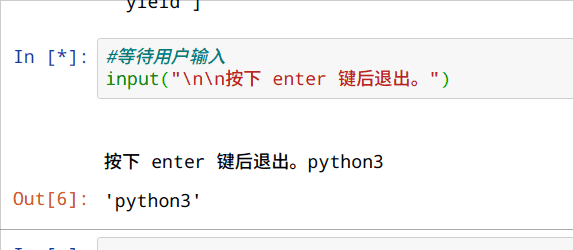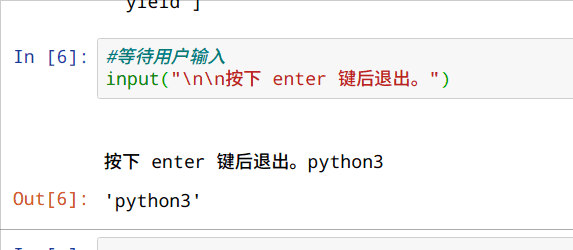
等待用户输入
input("\n\n按下 enter 键后退出。")
同一行显示多条语句
import sys; x = '你好python3'; sys.stdout.write(x + '\n')
结果你好python3
import 与 from…import
在 python 用 import 或者 from...import 来导入相应的模块。
将整个模块(somemodule)导入,格式为: import somemodule
从某个模块中导入某个函数,格式为: from somemodule import somefunction
从某个模块中导入多个函数,格式为: from somemodule import firstfunc, secondfunc, thirdfunc
将某个模块中的全部函数导入,格式为: from somemodule import *
导入 sys 模块
import sys
print('================Python import mode==========================')
print ('命令行参数为:')
for i in sys.argv:
print (i)
print ('\n python 路径为',sys.path)
导入 sys 模块的 argv,path 成员
from sys import argv,path # 导入特定的成员
print('===python from import===')
print('path:',path) # 因为已经导入path成员,所以此处引用时不需要加sys.path
命令行参数
$ python -h
$ python -h
usage: python [option] ... [-c cmd | -m mod | file | -] [arg] ...
Options and arguments (and corresponding environment variables):
-b : issue warnings about str(bytes_instance), str(bytearray_instance)
and comparing bytes/bytearray with str. (-bb: issue errors)
-B : don't write .pyc files on import; also PYTHONDONTWRITEBYTECODE=x
-c cmd : program passed in as string (terminates option list)
-d : debug output from parser; also PYTHONDEBUG=x
-E : ignore PYTHON* environment variables (such as PYTHONPATH)
-h : print this help message and exit (also --help)
-i : inspect interactively after running script; forces a prompt even
if stdin does not appear to be a terminal; also PYTHONINSPECT=x
-I : isolate Python from the user's environment (implies -E and -s)
-m mod : run library module as a script (terminates option list)
-O : remove assert and __debug__-dependent statements; add .opt-1 before
.pyc extension; also PYTHONOPTIMIZE=x
-OO : do -O changes and also discard docstrings; add .opt-2 before
.pyc extension
-q : don't print version and copyright messages on interactive startup
-s : don't add user site directory to sys.path; also PYTHONNOUSERSITE
-S : don't imply 'import site' on initialization
-u : force the stdout and stderr streams to be unbuffered;
this option has no effect on stdin; also PYTHONUNBUFFERED=x
-v : verbose (trace import statements); also PYTHONVERBOSE=x
can be supplied multiple times to increase verbosity
-V : print the Python version number and exit (also --version)
when given twice, print more information about the build
-W arg : warning control; arg is action:message:category:module:lineno
also PYTHONWARNINGS=arg
-x : skip first line of source, allowing use of non-Unix forms of #!cmd
-X opt : set implementation-specific option
--check-hash-based-pycs always|default|never:
control how Python invalidates hash-based .pyc files
file : program read from script file
- : program read from stdin (default; interactive mode if a tty)
arg ...: arguments passed to program in sys.argv[1:]
Other environment variables:
PYTHONSTARTUP: file executed on interactive startup (no default)
PYTHONPATH : ':'-separated list of directories prefixed to the
default module search path. The result is sys.path.
PYTHONHOME : alternate <prefix> directory (or <prefix>:<exec_prefix>).
The default module search path uses <prefix>/lib/pythonX.X.
PYTHONCASEOK : ignore case in 'import' statements (Windows).
PYTHONIOENCODING: Encoding[:errors] used for stdin/stdout/stderr.
PYTHONFAULTHANDLER: dump the Python traceback on fatal errors.
PYTHONHASHSEED: if this variable is set to 'random', a random value is used
to seed the hashes of str, bytes and datetime objects. It can also be
set to an integer in the range [0,4294967295] to get hash values with a
predictable seed.
PYTHONMALLOC: set the Python memory allocators and/or install debug hooks
on Python memory allocators. Use PYTHONMALLOC=debug to install debug
hooks.
PYTHONCOERCECLOCALE: if this variable is set to 0, it disables the locale
coercion behavior. Use PYTHONCOERCECLOCALE=warn to request display of
locale coercion and locale compatibility warnings on stderr.
PYTHONBREAKPOINT: if this variable is set to 0, it disables the default
debugger. It can be set to the callable of your debugger of choice.
PYTHONDEVMODE: enable the development mode.
我们在使用脚本形式执行 Python 时,可以接收命令行输入的参数,具体使用可以参照 Python 3 命令行参数。
