2019独角兽企业重金招聘Python工程师标准>>> 
写在前面:
每当提到损失函数,很多人都有个误解,以为用在GridSearchCV(网格搜索交叉验证“Cross Validation”)里边的scoring就是损失函数,其实并不是。我们使用构造函数构造XGBRegressor的时候,里边的objective参数才是真正的损失函数(loss function)。xgb使用sklearn api的时候需要用到的损失函数,其返回值是一阶导和二阶导,而GridSearchCV使用的scoring函数,返回的是一个float类型的数值评分(或叫准确率、或叫偏差值)。
You should be careful with the notation.
There are 2 levels of optimization here:
- The loss function optimized when the
XGBRegressoris fitted to the data.- The scoring function that is optimized during the grid search.
I prefer calling the second scoring function instead of loss function, since loss function usually refers to a term that is subject to optimization during the model fitting process itself.
Scikit-Learn: Custom Loss Function for GridSearchCV
因此,下文对于objective,统一叫“目标函数”;而对scoring,统一叫“评价函数”。
========== 原文分割线 ===================
许多特定的任务需要定制目标函数,来达到更优的效果。这里以xgboost的回归预测为例,介绍一下objective函数的定制过程。一个简单的例子如下:
def customObj1(real, predict):
grad = predict - real
hess = np.power(np.abs(grad), 0.5)
return grad, hess网上有许多教程定义的objective函数中的第一个参数是preds,第二个是dtrain,而本文由于使用xgboost的sklearn API,因此定制的objective函数需要与sklearn的格式相符。调用目标函数的过程如下:
model = xgb.XGBRegressor(objective=customObj1,
booster="gblinear")下面是不同迭代次数的动画演示:
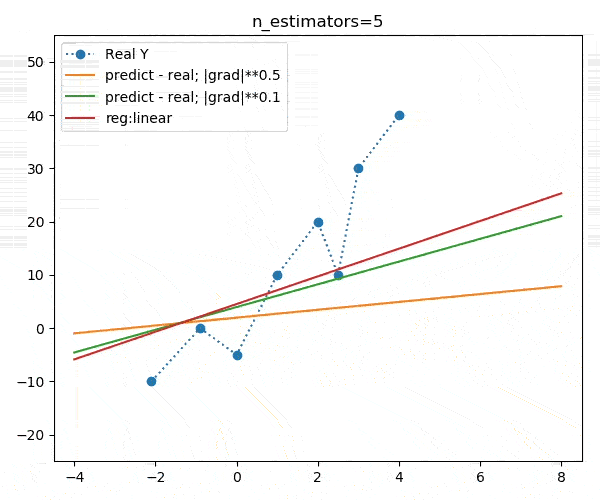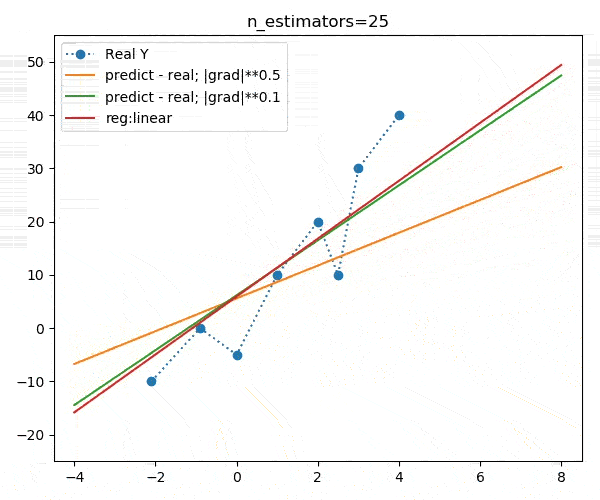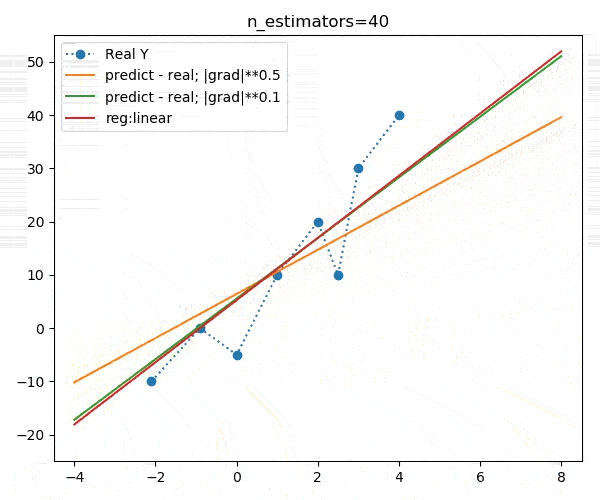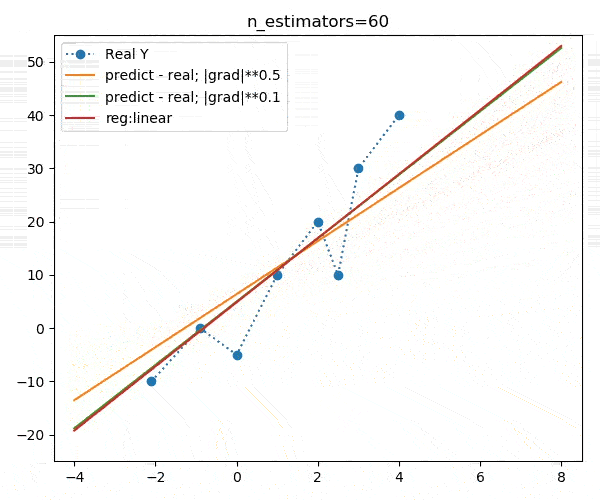
我们发现,不同的目标函数对模型的收敛速度影响较大,但最终收敛目标大致相同,如下图:

完整代码如下:
# coding=utf-8
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import xgboost as xgb
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams.update({'figure.autolayout': True})
df = pd.DataFrame({'x': [-2.1, -0.9, 0, 1, 2, 2.5, 3, 4],
'y': [ -10, 0, -5, 10, 20, 10, 30, 40]})
X_train = df.drop('y', axis=1)
Y_train = df['y']
X_pred = [-4, -3, -2, -1, 0, 0.4, 0.6, 1, 1.4, 1.6, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]
def process_list(list_in):
result = map(lambda x: "%8.2f" % round(float(x), 2), list_in)
return list(result)
def customObj3(real, predict):
grad = predict - real
hess = np.power(np.abs(grad), 0.1)
# print 'predict', process_list(predict.tolist()), type(predict)
# print ' real ', process_list(real.tolist()), type(real)
# print ' grad ', process_list(grad.tolist()), type(grad)
# print ' hess ', process_list(hess.tolist()), type(hess), '\n'
return grad, hess
def customObj1(real, predict):
grad = predict - real
hess = np.power(np.abs(grad), 0.5)
return grad, hess
for n_estimators in range(5, 600, 5):
booster_str = "gblinear"
model = xgb.XGBRegressor(objective=customObj1,
booster=booster_str,
n_estimators=n_estimators)
model2 = xgb.XGBRegressor(objective="reg:linear",
booster=booster_str,
n_estimators=n_estimators)
model3 = xgb.XGBRegressor(objective=customObj3,
booster=booster_str,
n_estimators=n_estimators)
model.fit(X=X_train, y=Y_train)
model2.fit(X=X_train, y=Y_train)
model3.fit(X=X_train, y=Y_train)
y_pred = model.predict(data=pd.DataFrame({'x': X_pred}))
y_pred2 = model2.predict(data=pd.DataFrame({'x': X_pred}))
y_pred3 = model3.predict(data=pd.DataFrame({'x': X_pred}))
plt.figure(figsize=(6, 5))
plt.axes().set(title='n_estimators='+str(n_estimators))
plt.plot(df['x'], df['y'], marker='o', linestyle=":", label="Real Y")
plt.plot(X_pred, y_pred, label="predict - real; |grad|**0.5")
plt.plot(X_pred, y_pred3, label="predict - real; |grad|**0.1")
plt.plot(X_pred, y_pred2, label="reg:linear")
plt.xlim(-4.5, 8.5)
plt.ylim(-25, 55)
plt.legend()
# plt.show()
plt.savefig("output/n_estimators_"+str(n_estimators)+".jpg")
plt.close()
print(n_estimators)
