任意门:http://codeforces.com/contest/1118/problem/F1
You are given an undirected tree of nn vertices.
Some vertices are colored blue, some are colored red and some are uncolored. It is guaranteed that the tree contains at least one red vertex and at least one blue vertex.
You choose an edge and remove it from the tree. Tree falls apart into two connected components. Let's call an edge nice if neither of the resulting components contain vertices of both red and blue colors.
How many nice edges are there in the given tree?
The first line contains a single integer nn (2≤n≤3⋅1052≤n≤3⋅105) — the number of vertices in the tree.
The second line contains nn integers a1,a2,…,ana1,a2,…,an (0≤ai≤20≤ai≤2) — the colors of the vertices. ai=1ai=1 means that vertex ii is colored red, ai=2ai=2 means that vertex ii is colored blue and ai=0ai=0 means that vertex ii is uncolored.
The ii-th of the next n−1n−1 lines contains two integers vivi and uiui (1≤vi,ui≤n1≤vi,ui≤n, vi≠uivi≠ui) — the edges of the tree. It is guaranteed that the given edges form a tree. It is guaranteed that the tree contains at least one red vertex and at least one blue vertex.
Print a single integer — the number of nice edges in the given tree.
5 2 0 0 1 2 1 2 2 3 2 4 2 5
1
5 1 0 0 0 2 1 2 2 3 3 4 4 5
4
3 1 1 2 2 3 1 3
0
Here is the tree from the first example:
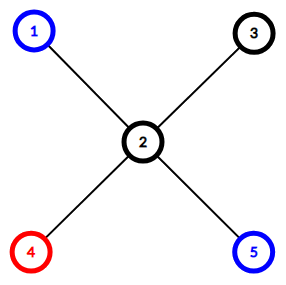
The only nice edge is edge (2,4)(2,4). Removing it makes the tree fall apart into components {4}{4} and {1,2,3,5}{1,2,3,5}. The first component only includes a red vertex and the second component includes blue vertices and uncolored vertices.
Here is the tree from the second example:

Every edge is nice in it.
Here is the tree from the third example:
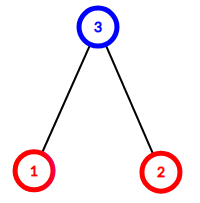
Edge (1,3)(1,3) splits the into components {1}{1} and {3,2}{3,2}, the latter one includes both red and blue vertex, thus the edge isn't nice. Edge (2,3)(2,3) splits the into components {1,3}{1,3} and {2}{2}, the former one includes both red and blue vertex, thus the edge also isn't nice. So the answer is 0.
题意概括:
给出一棵无向树,每个结点有一种颜色(1红 2蓝 0无色),如果删掉某条边可以把这棵树分成两部分刚好各部分只具有一种颜色,则这种边为nice边,求最多有多少条。
解题思路:
哈哈哈,一开始试着BFS暴力了一波,果然水不过。
正解DFS,很明显先预处理出 每个结点为跟的子树所具有的两种颜色的结点个数 dd[ x ][ 1 ] && dd[ x ][ 2 ];
DFS一遍整棵树,判断当前边所分成的两部分是否满足条件,一部分就是预处理的子树部分,另一部分就是用树的根节点部分减去子树部分。
AC code:


1 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 2 #define INF 0x3f3f3f3f 3 #define LL long long 4 using namespace std; 5 const int MAXN = 3e5+10; 6 int color[MAXN]; 7 int u[MAXN], v[MAXN]; 8 int dd[MAXN][3]; 9 bool vis[MAXN]; 10 int N, ans; 11 struct Edge 12 { 13 int v, nxt; 14 }edge[MAXN<<1]; 15 int head[MAXN], cnt; 16 17 void init() 18 { 19 memset(head, -1, sizeof(head)); 20 cnt = 0; 21 } 22 23 void add(int from, int to) 24 { 25 edge[cnt].v = to; 26 edge[cnt].nxt = head[from]; 27 head[from] = cnt++; 28 } 29 30 void dfs1(int x, int fa) 31 { 32 int v; 33 if(color[x] == 1) dd[x][1]+=1; 34 else if(color[x] == 2) dd[x][2]+=1; 35 for(int i = head[x]; i != -1; i = edge[i].nxt){ 36 v = edge[i].v; 37 if(v == x || v == fa) continue; 38 dfs1(v, x); 39 dd[x][1]+=dd[v][1]; 40 dd[x][2]+=dd[v][2]; 41 } 42 } 43 44 45 void dfs2(int x, int fa) 46 { 47 int v; 48 for(int i = head[x]; i != -1; i = edge[i].nxt){ 49 v = edge[i].v; 50 if(v == fa) continue; 51 if(dd[v][1] == 0 && (dd[1][2]-dd[v][2]) == 0){ 52 // printf("u:%d v:%d\n", x, v); 53 ans++; 54 } 55 else if(dd[v][2] == 0 && (dd[1][1]-dd[v][1]) == 0){ 56 // printf("u:%d v:%d\n", x, v); 57 ans++; 58 } 59 dfs2(v, x); 60 } 61 } 62 63 int main() 64 { 65 init(); 66 scanf("%d", &N); 67 for(int i = 1; i <= N; i++){ 68 scanf("%d", &color[i]); 69 } 70 for(int i = 1; i < N; i++){ 71 scanf("%d %d", &u[i], &v[i]); 72 add(u[i], v[i]); 73 add(v[i], u[i]); 74 } 75 76 dfs1(1, 0); 77 ans = 0; 78 dfs2(1, 0); 79 80 printf("%d\n", ans); 81 82 return 0; 83 }
