9月23日计算机视觉基础学习笔记——经典机器学习
文章目录
- 前言
- 一、Week 3 homework
- 二、线性模型的改进方法
- 1、加上常数 b
- 2. 曲线模型
- 3、用二分类进行多分类:感知机
- 三、用逻辑回归进行多类别分类
- 四、神经网络:反向传播
前言
本文为9月23日计算机视觉基础学习笔记——经典机器学习,分为四个章节:
- Week 3 homework;
- 线性模型的改进方法;
- 用逻辑回归进行多类别分类;
- 神经网络:反向传播。
一、Week 3 homework
- 手动实现先行回归模型,解决数字图像分类问题:
import torch
from torch.autograd import Variable as V
import numpy as np
def generate_data():
# 本函数生成0-9,10个数字的图片矩阵
image_data = []
num_0 = torch.tensor(
[[0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]])
image_data.append(num_0)
num_1 = torch.tensor(
[[0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]])
image_data.append(num_1)
num_2 = torch.tensor(
[[0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]])
image_data.append(num_2)
num_3 = torch.tensor(
[[0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]])
image_data.append(num_3)
num_4 = torch.tensor(
[
[0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]])
image_data.append(num_4)
num_5 = torch.tensor(
[
[0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]])
image_data.append(num_5)
num_6 = torch.tensor(
[[0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]])
image_data.append(num_6)
num_7 = torch.tensor(
[
[0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]])
image_data.append(num_7)
num_8 = torch.tensor(
[[0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]])
image_data.append(num_8)
num_9 = torch.tensor(
[[0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]])
image_data.append(num_9)
image_label = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
return image_data, image_label
def get_feature(x, dim):
'''
添加提取图像x的特征feature的代码
'''
height = x.shape[0]
feature = torch.sum(x, dim)
feature = feature.float()
feat_dim = feature.shape[0]
# 归一化
for i in range(0, feat_dim):
feature[i] = feature[i] / sum(feature)
feature = feature.view(1, height)
return feature
def linear_model(feature, weights):
y = -1
feature = torch.cat((feature, torch.tensor(1.0).view(1, 1)), 1)
y = feature.mm(weights)
return y
# 训练模型
def train_model(weights, learning_rate, iters, num_data, image_data, image_label):
for epoch in range(iters):
loss = 0
for i in range(0, num_data):
feature = get_feature(image_data[i], weights)
y_pred = linear_model(feature, weights)
loss += 0.5 * (y_pred - image_label[i])**2
# 自动计算梯度
loss.backward()
# 跟新参数
weights.data.sub_(learning_rate * weights.grad.data)
# 梯度清零
weights.grad.data.zero_()
print('each epoch loss is {}'.format(loss.item()))
return weights
if __name__ == "__main__":
image_data, image_label = generate_data()
num_sample = len(image_data)
num_feat = 6
# 初始化
weights = torch.rand(num_feat + 1, 1, requires_grad=True)
learning_rate = 0.005
iters = 5000
num_data = 6
new_weights = train_model(weights, learning_rate, iters, num_data, image_data, image_label)
print("对每张图片进行识别:")
for i in range(num_sample):
x = image_data[i]
# 提取当前图片的特征
dim = 0
feature = get_feature(x, dim)
# 对特征进行分类
y = linear_model(feature, weights)
# 打印出分类结果
print("图像{}的分类结果:{}".format(i, y))
二、线性模型的改进方法
1、加上常数 b
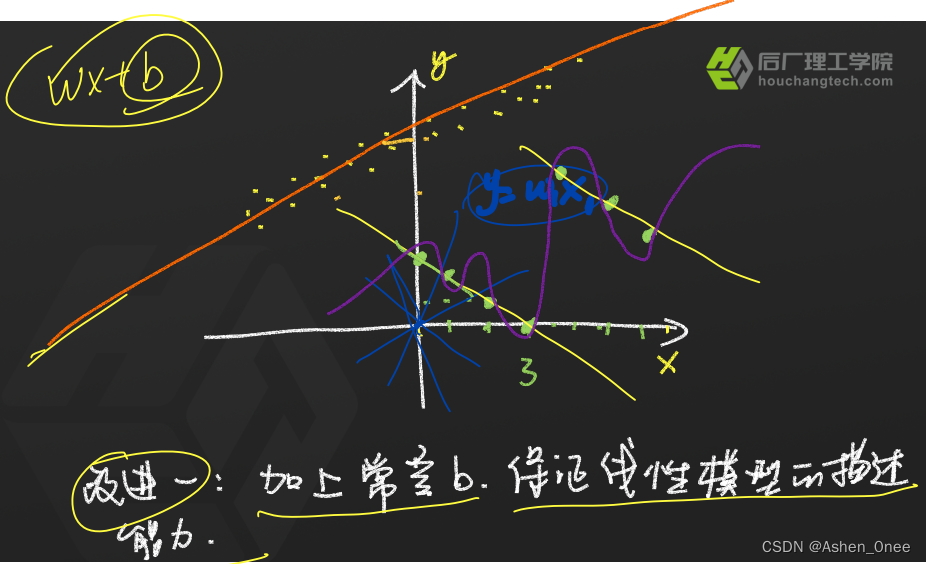
2. 曲线模型
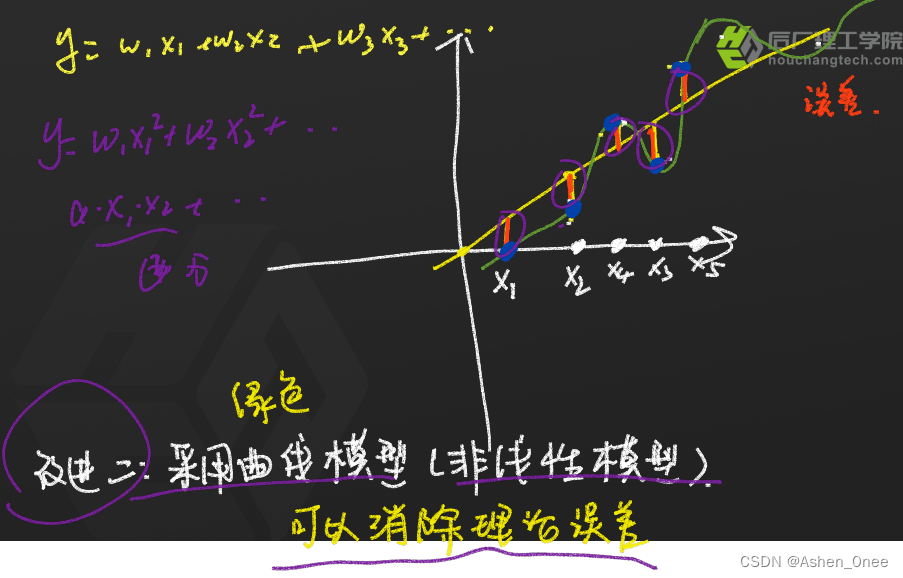
代码如下:
import torch
from itertools import product
import sys
def generate_data():
# 本函数生成0-9,10个数字的图片矩阵
image_data=[]
num_0 = torch.tensor(
[[0,0,1,1,0,0],
[0,1,0,0,1,0],
[0,1,0,0,1,0],
[0,1,0,0,1,0],
[0,0,1,1,0,0],
[0,0,0,0,0,0]])
image_data.append(num_0)
num_1 = torch.tensor(
[[0,0,0,1,0,0],
[0,0,1,1,0,0],
[0,0,0,1,0,0],
[0,0,0,1,0,0],
[0,0,1,1,1,0],
[0,0,0,0,0,0]])
image_data.append(num_1)
num_2 = torch.tensor(
[[0,0,1,1,0,0],
[0,1,0,0,1,0],
[0,0,0,1,0,0],
[0,0,1,0,0,0],
[0,1,1,1,1,0],
[0,0,0,0,0,0]])
image_data.append(num_2)
num_3 = torch.tensor(
[[0,0,1,1,0,0],
[0,0,0,0,1,0],
[0,0,1,1,0,0],
[0,0,0,0,1,0],
[0,0,1,1,0,0],
[0,0,0,0,0,0]])
image_data.append(num_3)
num_4 = torch.tensor(
[
[0,0,0,0,1,0],
[0,0,0,1,1,0],
[0,0,1,0,1,0],
[0,1,1,1,1,1],
[0,0,0,0,1,0],
[0,0,0,0,0,0]])
image_data.append(num_4)
num_5 = torch.tensor(
[
[0,1,1,1,0,0],
[0,1,0,0,0,0],
[0,1,1,1,0,0],
[0,0,0,0,1,0],
[0,1,1,1,0,0],
[0,0,0,0,0,0]])
image_data.append(num_5)
num_6 = torch.tensor(
[[0,0,1,1,0,0],
[0,1,0,0,0,0],
[0,1,1,1,0,0],
[0,1,0,0,1,0],
[0,0,1,1,0,0],
[0,0,0,0,0,0]])
image_data.append(num_6)
num_7 = torch.tensor(
[
[0,1,1,1,1,0],
[0,0,0,0,1,0],
[0,0,0,1,0,0],
[0,0,0,1,0,0],
[0,0,0,1,0,0],
[0,0,0,0,0,0]])
image_data.append(num_7)
num_8 = torch.tensor(
[[0,0,1,1,0,0],
[0,1,0,0,1,0],
[0,0,1,1,0,0],
[0,1,0,0,1,0],
[0,0,1,1,0,0],
[0,0,0,0,0,0]])
image_data.append(num_8)
num_9 = torch.tensor(
[[0,0,1,1,1,0],
[0,1,0,0,1,0],
[0,1,1,1,1,0],
[0,0,0,0,1,0],
[0,0,0,0,1,0],
[0,0,0,0,0,0]])
image_data.append(num_9)
image_label=[0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9]
return image_data,image_label
def get_feature(x):
'''
提取特征
'''
feature = [0, 0, 0, 0]
def get_shadow(x, dim):
feature = torch.sum(x, dim)
feature = feature.float()
# 归一化
for i in range(feature.shape[0]):
feature[i] = feature[i] / sum(feature)
feature = feature.view(1, 6)
return feature
feature = get_shadow(x, 0)
return feature
def model(feature, weights):
y = -1
feature = torch.cat((feature,torch.tensor(1.0).view(1,1)),1)
feature2 = feature.mul(feature)
y = feature.mm(weights[:, 0:1]) + feature2.mm(weights[:, 1:2])
return y
def train_model(image_data, image_label, weights, lr):
loss_value_before = 100000000.
loss_value = 1000000.
for epoch in range(0, 3000):
loss_value_before = loss_value
loss_value = 0
for i in range(0, 10):
feature = get_feature(image_data[i])
y = model(feature, weights)
loss = 0.5 * (y - image_label[i]) * (y - image_label[i])
# loss.data.add_(loss.data)
loss_value += loss.data.item()
loss.backward()
weights.data.sub_(weights.grad.data * lr)
weights.grad.data.zero_()
# loss.data=
print("epoch=%s,loss=%s/%s,weights=%s" % (epoch, loss_value, loss_value_before, weights.view(14)))
return weights
if __name__ == "__main__":
weights = torch.randn(7, 2, requires_grad=True)
image_data, image_label = generate_data()
# 打印出0的图像
print("数字0对应的图片是:")
print(image_data[0])
print("-" * 20)
# 打印出8的图像
print("数字8对应的图片是:")
print(image_data[8])
print("-" * 20)
lr = float(sys.argv[1])
# 对模型进行训练:
weights = train_model(image_data, image_label, weights, lr)
# 对每张图片进行识别
print("对每张图片进行识别")
for i in range(0, 10):
x = image_data[i]
# import pdb
# pdb.set_trace()
# 对当前图片提取特征
feature = get_feature(x)
# 对提取到得特征进行分类
y = model(feature, weights)
# 打印出分类结果
print("图像[%s]得分类结果是:[%s],它得特征是[%s]" % (i, y, feature))
3、用二分类进行多分类:感知机
y = WX + b y = \textbf{W}\textbf{X} + \textbf{b} y=WX+b

三、用逻辑回归进行多类别分类
代码如下:
import torch
from itertools import product
import sys
from mnist import MNIST
import cv2 as cv
import numpy as np
def generate_data():
# 本函数生成0-9,10个数字的图片矩阵
image_data=[]
num_0 = torch.tensor(
[[0,0,1,1,0,0],
[0,1,0,0,1,0],
[0,1,0,0,1,0],
[0,1,0,0,1,0],
[0,0,1,1,0,0],
[0,0,0,0,0,0]])
image_data.append(num_0)
num_1 = torch.tensor(
[[0,0,0,1,0,0],
[0,0,1,1,0,0],
[0,0,0,1,0,0],
[0,0,0,1,0,0],
[0,0,1,1,1,0],
[0,0,0,0,0,0]])
image_data.append(num_1)
num_2 = torch.tensor(
[[0,0,1,1,0,0],
[0,1,0,0,1,0],
[0,0,0,1,0,0],
[0,0,1,0,0,0],
[0,1,1,1,1,0],
[0,0,0,0,0,0]])
image_data.append(num_2)
num_3 = torch.tensor(
[[0,0,1,1,0,0],
[0,0,0,0,1,0],
[0,0,1,1,0,0],
[0,0,0,0,1,0],
[0,0,1,1,0,0],
[0,0,0,0,0,0]])
image_data.append(num_3)
num_4 = torch.tensor(
[
[0,0,0,0,1,0],
[0,0,0,1,1,0],
[0,0,1,0,1,0],
[0,1,1,1,1,1],
[0,0,0,0,1,0],
[0,0,0,0,0,0]])
image_data.append(num_4)
num_5 = torch.tensor(
[
[0,1,1,1,0,0],
[0,1,0,0,0,0],
[0,1,1,1,0,0],
[0,0,0,0,1,0],
[0,1,1,1,0,0],
[0,0,0,0,0,0]])
image_data.append(num_5)
num_6 = torch.tensor(
[[0,0,1,1,0,0],
[0,1,0,0,0,0],
[0,1,1,1,0,0],
[0,1,0,0,1,0],
[0,0,1,1,0,0],
[0,0,0,0,0,0]])
image_data.append(num_6)
num_7 = torch.tensor(
[
[0,1,1,1,1,0],
[0,0,0,0,1,0],
[0,0,0,1,0,0],
[0,0,0,1,0,0],
[0,0,0,1,0,0],
[0,0,0,0,0,0]])
image_data.append(num_7)
num_8 = torch.tensor(
[[0,0,1,1,0,0],
[0,1,0,0,1,0],
[0,0,1,1,0,0],
[0,1,0,0,1,0],
[0,0,1,1,0,0],
[0,0,0,0,0,0]])
image_data.append(num_8)
num_9 = torch.tensor(
[[0,0,1,1,1,0],
[0,1,0,0,1,0],
[0,1,1,1,1,0],
[0,0,0,0,1,0],
[0,0,0,0,1,0],
[0,0,0,0,0,0]])
image_data.append(num_9)
image_label=[0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9]
return image_data,image_label
def get_feature(x):
feature=[0,0,0,0]
xa = np.array(x)
xt = torch.from_numpy(xa.reshape(28,28))
# 提取图像x的特征 feature
def get_shadow(x,dim):
feature =torch.sum(x,dim)
feature = feature.float()
# 归一化
for i in range(0,feature.shape[0]):
feature[i]=feature[i]/sum(feature)
feature = feature.view(1,28)
return feature
feature = get_shadow(xt,0)
return feature
def label2ground_truth(image_label):
gt = torch.ones(10,10)
gt = gt*-1.0
#for label in image_label:
for i in range(0,10):
gt[i,i]=float(image_label[i])
return gt
def model(feature,weights):
y=-1
# 对feature进行决策的代码,判定出feature 属于[0,1,2,3,...9]哪个类别
feature = torch.cat((feature,torch.tensor(1.0).view(1,1)),1)
feature2=feature.mul(feature)
h = feature.mm(weights)
y = 1.0/(1.0+torch.exp(-1.*h))
return y
def one_hot(gt):
gt_vector = torch.ones(1,10)
gt_vector *= -1.0*0.1
gt_vector[0,gt] = 1.0*0.9
return gt_vector
def get_acc(image_data, image_label, weights, start_i, end_i):
correct = 0
for i in range(start_i, end_i):
feature = get_feature(image_data[i])
y = model(feature, weights)
gt = image_label[i]
pred = torch.argmin(
torch.from_numpy(np.array([torch.min((torch.abs(y - j))).item() for j in range(0, 10)]))).item()
if gt == pred:
correct += 1
return float(correct / float(end_i - start_i))
def train_model(image_data, image_label, weights, lr):
loss_value_before = 1000000000000000.
loss_value = 10000000000000.
for epoch in range(0, 3000):
loss_value_before = loss_value
loss_value = 0
for i in range(0, 80):
feature = get_feature(image_data[i])
y = model(feature, weights)
gt = image_label[i]
# 只关心一个值
loss = torch.sum((y[0, gt:gt + 1] - gt).mul(y[0, gt:gt + 1] - gt))
loss_value += loss.data.item()
loss.backward()
weights.data.sub_(weights.grad.data * lr)
weights.grad.data.zero_()
train_acc = get_acc(image_data, image_label, weights, 0, 80)
test_acc = get_acc(image_data, image_label, weights, 80, 100)
print("epoch=%s,loss=%s/%s,train/test_acc=%s/%s," % (epoch, loss_value, loss_value_before, train_acc, test_acc))
return weights
if __name__ == "__main__":
weights = torch.randn(29, 10, requires_grad=True)
# hct66 dataset , 10 samples
image_data, image_label = generate_data()
# minst 2828 dataset 60000 samples
mndata = MNIST('./mnist/python-mnist/data/')
image_data_all, image_label_all = mndata.load_training()
# import pdb
# pdb.set_trace()
image_data = image_data_all[0:100]
image_label = image_label_all[0:100]
lr = float(sys.argv[1])
# 对模型进行训练:
weights = train_model(image_data, image_label, weights, lr)
# 测试:
correct = 0
for i in range(0, 10):
# print(image_label[i])
# y = model(get_feature(image_data[i]),weights)
feature = get_feature(image_data[i])
y = model(feature, weights)
# pdb.set_trace()
gt = image_label[i]
# pred=torch.argmin(torch.abs(y-gt)).item()
pred = torch.argmin(
torch.from_numpy(np.array([torch.min((torch.abs(y - j))).item() for j in range(0, 10)]))).item()
# pred = torch.argmin(torch.abs(y-1)).item()
print("图像[%s]得分类结果是:[%s]" % (gt, pred))
if gt == pred:
correct += 1
print("acc=%s" % (float(correct / 10.0)))
四、神经网络:反向传播
代码如下:
# coding:utf-8
# code for week2,recognize_computer_vision.py
# houchangligong,zhaomingming,20200602,
import torch
from itertools import product
import pdb
import sys
from mnist import MNIST
import cv2
import numpy as np
# mndata = MNIST('python-mnist/data/')
# images, labels = mndata.load_training()
def generate_data():
# 本函数生成0-9,10个数字的图片矩阵
image_data = []
num_0 = torch.tensor(
[[0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]])
image_data.append(num_0)
num_1 = torch.tensor(
[[0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]])
image_data.append(num_1)
num_2 = torch.tensor(
[[0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]])
image_data.append(num_2)
num_3 = torch.tensor(
[[0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]])
image_data.append(num_3)
num_4 = torch.tensor(
[
[0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]])
image_data.append(num_4)
num_5 = torch.tensor(
[
[0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]])
image_data.append(num_5)
num_6 = torch.tensor(
[[0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]])
image_data.append(num_6)
num_7 = torch.tensor(
[
[0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]])
image_data.append(num_7)
num_8 = torch.tensor(
[[0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]])
image_data.append(num_8)
num_9 = torch.tensor(
[[0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]])
image_data.append(num_9)
image_label = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
return image_data, image_label
def get_feature(x):
feature = [0, 0, 0, 0]
xa = np.array(x)
xt = torch.from_numpy(xa.reshape(28, 28))
# 下面添加提取图像x的特征feature的代码
def get_shadow(x, dim):
feature = torch.sum(x, dim)
feature = feature.float()
## 归一化
for i in range(0, feature.shape[0]):
feature[i] = feature[i] / sum(feature)
feature = feature.view(1, 28)
return feature
feature = get_shadow(xt, 0)
return feature
def model(feature, weights0, weights1):
y = -1
# 下面添加对feature进行决策的代码,判定出feature 属于[0,1,2,3,...9]哪个类别
feature = torch.cat((feature, torch.tensor(1.0).view(1, 1)), 1)
feature2 = feature.mul(feature)
h = feature.mm(weights0)
h1 = torch.tanh(h).mm(weights1)
y = torch.sigmoid(h1)
# y = 1.0/(1.0+torch.exp(-1.*h))
return y
def get_acc(image_data, image_label, weights0, weights1, start_i, end_i):
correct = 0
for i in range(start_i, end_i):
feature = get_feature(image_data[i])
y = model(feature, weights0, weights1)
# pdb.set_trace()
gt = image_label[i]
pred = torch.argmin(torch.min(torch.abs(y - 1))).item()
# print("图像[%s]得分类结果是:[%s]"%(gt,pred))
if gt == pred:
correct += 1
# print("acc=%s"%(float(correct/20.0)))
return float(correct / float(end_i - start_i))
def one_hot(gt):
gt_vector = torch.ones(1, 10)
gt_vector *= 0.0
gt_vector[0, gt] = 1.0
return gt_vector
def train_model(image_data, image_label, weights0, weights1, lr):
loss_value_before = 1000000000000000.
loss_value = 10000000000000.
for epoch in range(0, 300):
loss_value_before = loss_value
loss_value = 0
for i in range(0, 80):
# print(image_label[i])
# y = model(get_feature(image_data[i]),weights)
feature = get_feature(image_data[i])
y = model(feature, weights0, weights1)
gt = image_label[i]
# 只关心一个值
loss = torch.sum((y[0, gt:gt + 1] - gt).mul(y[0, gt:gt + 1] - gt))
gt_vector = one_hot(gt)
loss_value += loss.data.item()
loss.backward()
weights0.data.sub_(weights0.grad.data * lr)
weights0.grad.data.zero_()
weights1.data.sub_(weights1.grad.data * lr)
weights1.grad.data.zero_()
# loss.data=
train_acc = get_acc(image_data, image_label, weights0, weights1, 0, 80)
test_acc = get_acc(image_data, image_label, weights0, weights1, 80, 100)
print("epoch=%s,loss=%s/%s,train/test_acc:%s/%s" % (epoch, loss_value, loss_value_before, train_acc, test_acc))
return weights0, weights1
if __name__ == "__main__":
weights0 = torch.randn(29, 35, requires_grad=True)
weights1 = torch.randn(35, 10, requires_grad=True)
# hct66 dataset , 10 samples
image_data, image_label = generate_data()
# minst 2828 dataset 60000 samples
mndata = MNIST('./mnist/python-mnist/data/')
image_data_all, image_label_all = mndata.load_training()
image_data = image_data_all[0:100]
image_label = image_label_all[0:100]
lr = float(sys.argv[1])
# 对模型进行训练:
weights0, weight1 = train_model(image_data, image_label, weights0, weights1, lr)
# 测试:
correct = 0
for i in range(80, 100):
feature = get_feature(image_data[i])
y = model(feature, weights0, weights1)
# pdb.set_trace()
gt = image_label[i]
pred = torch.argmin(torch.min(torch.abs(y - 1))).item()
print("图像[%s]得分类结果是:[%s]" % (gt, pred))
if gt == pred:
correct += 1
print("acc=%s" % (float(correct / 20.0)))
