02|LangChain | 从入门到实战 -六大组件之Models IO
by:wenwenC9
上一篇文章
01|LangChain | 从入门到实战-介绍
一、Models IO 组成及其说明
与语言模型的交互,比如在线GPT系列,或各种离线模型
任何语言模型应用程序的核心元素都是XXX模型。LangChain 提供了与任何语言模型交互的构建块。
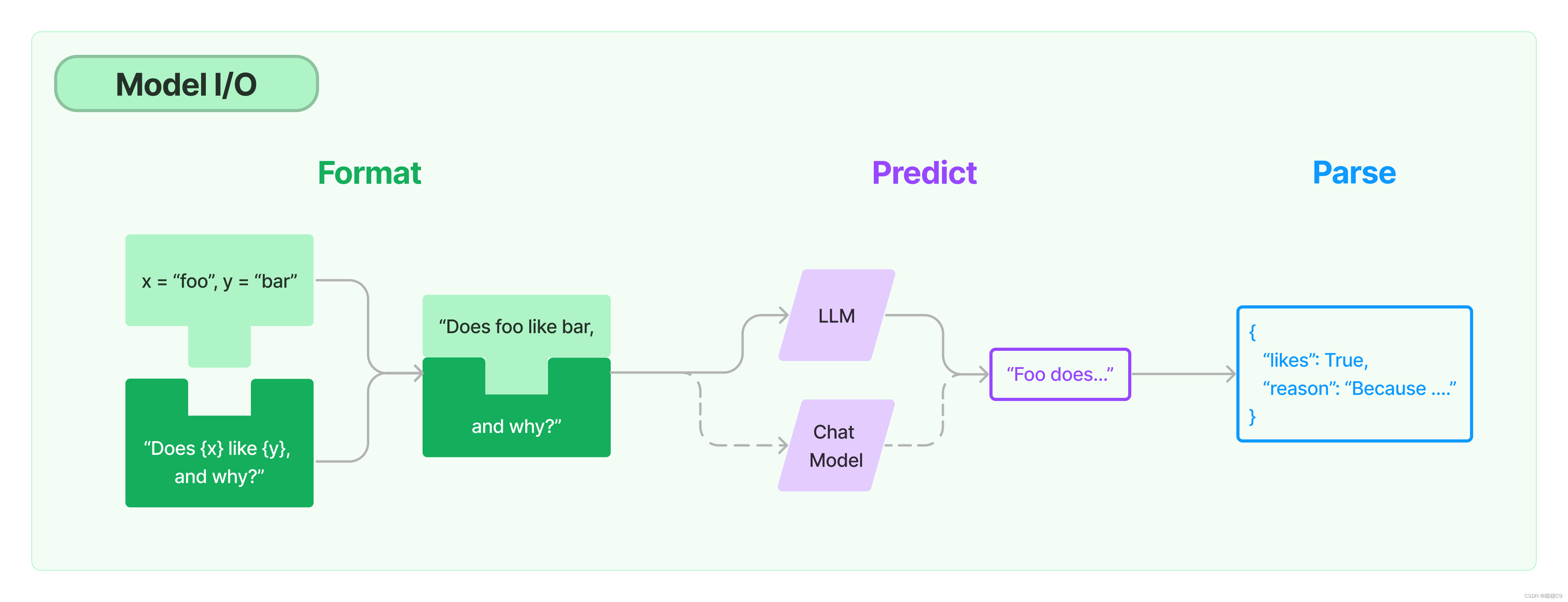
从案例理解prompt,下面是一个内容,占位字符串为 foo 跟 bar,在python中可以根据format,将需要传入的内容代入
template = """我最喜欢的运动是{args1},平时最喜欢去{args2}
"""
template = template.format(args1='foo',args2='bar')我最喜欢的运动是foo,平时最喜欢去bar
langchain,提供了prompt工程,可以通过规定风格,将提示内容代入到各类模型,以便告知模型,你的想法或执行内容;
对于LLM的输出,我们也能进行解析,比如,要求输出为json格式,等等格式要求
其主要交互组件如下图
注意
内容所出现的代码,我都忽略了key的配置,你们可以自己加
import os
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = ''
二、Prompt 提示工程

语言模型的提示是用户提供的一组指令或输入,用于指导模型的响应,帮助模型理解上下文并生成相关且连贯的基于语言的输出,例如回答问题、完成句子或参与某项活动。对话。
LangChain 提供了几个类和函数来帮助构建和使用提示。
1、提示模板:参数化模型输入
2、示例选择器:动态选择要包含在提示中的示例
1、关于模板的使用
(1)基础模板 PromptTemplate
(1.1)使用预设值实例化
from langchain.prompts.prompt import PromptTemplateprompt_template = PromptTemplate(input_variables=["content"], template="告诉我一个笑话关于 {content}")
prompt = prompt_template.format(content="兔子")
print(prompt_template)
print(type(prompt_template))
print(prompt)
print(type(prompt))--------打印结果----------
input_variables=['content'] template='告诉我一个笑话关于 {content}'
<class 'langchain.prompts.prompt.PromptTemplate'>
告诉我一个笑话关于 兔子
<class 'str'>
(1.2)使用from_template实例化
from langchain.prompts.prompt import PromptTemplateprompt_template = PromptTemplate.from_template(template="告诉我一个笑话 {adjective} 关于 {content}."
)
prompt = prompt_template.format(adjective="funny", content="chickens")
print(prompt_template)
print(type(prompt_template))
print(prompt)
print(type(prompt))--------打印结果----------
input_variables=['adjective', 'content'] template='告诉我一个笑话 {adjective} 关于 {content}.'
<class 'langchain.prompts.prompt.PromptTemplate'>
告诉我一个笑话 funny 关于 chickens.
<class 'str'>
(1.3)在对话中使用模板
from langchain import PromptTemplate
from langchain.llms import OpenAIinvalid_prompt = PromptTemplate(input_variables=["adjective"],template="Tell me a {adjective} joke about cat. 中文回复我"
)# llm = ChatOpenAI()
llm = OpenAI()
# 定义一个函数来生成回答
def generate_joke(adjective, content):prompt = invalid_prompt.format(adjective=adjective)response = llm(prompt)print(response)# return response.choices[0].text.strip()# 调用函数生成一个笑话
joke = generate_joke("funny", "cats")
print(joke)
"""
这只猫真有趣:它把自己看作是一只狗!
"""
(1.4)源码
从源码层来说,都是源自这边,并且函数也说明了,是所有模板的基础,建议去看看源码
这里不过多说明
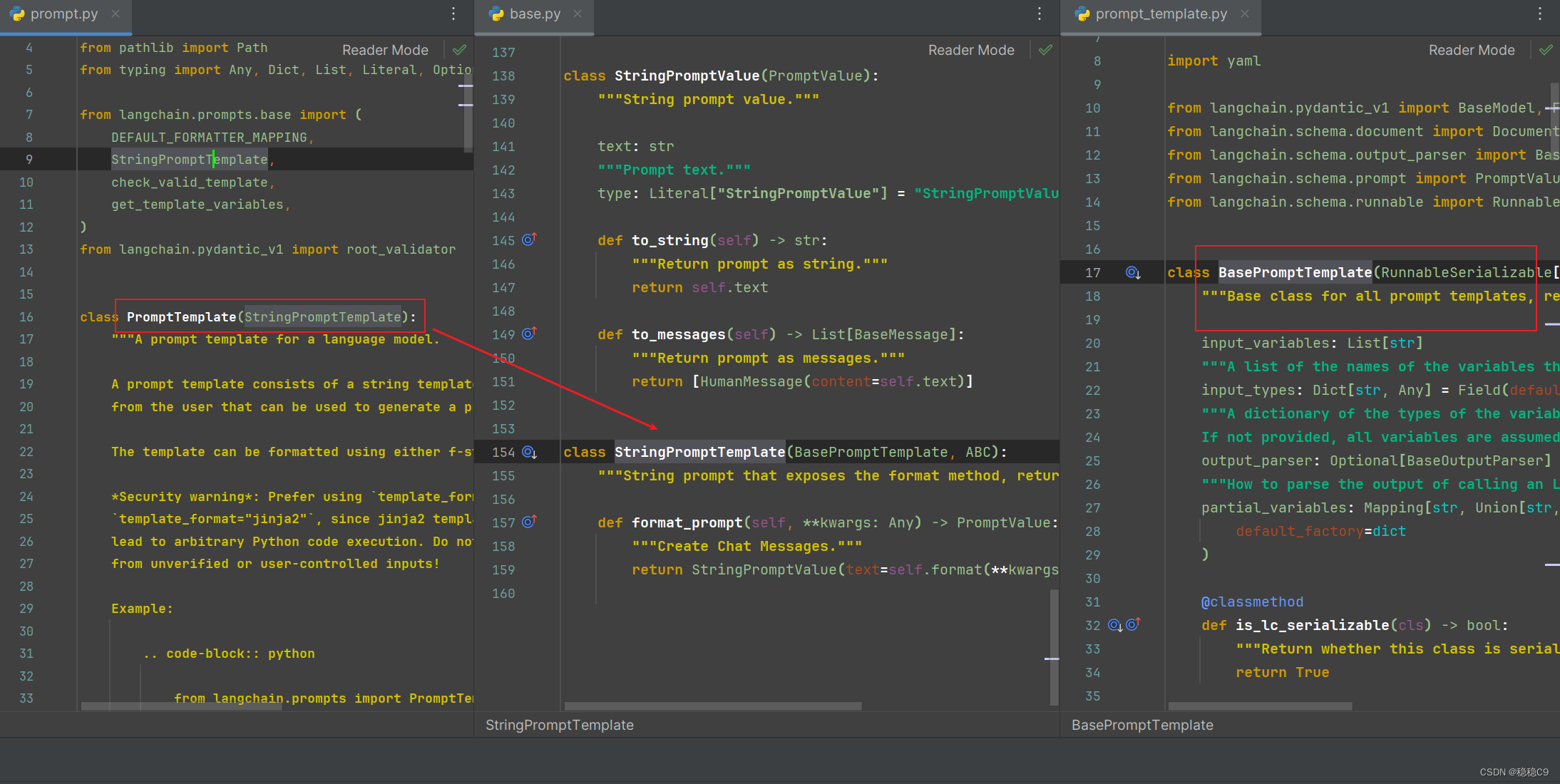
从源码可以看继承于StringPromptTemplate 字符串模板
而它又继承于 BasePromptTemplate,拥有如下功能函数

往往有时候,提供的基础模板不够我们使用场景,就需要我们自己创建自定义模板
(2) 自定义模板
举例使用场景:
- 用于某些业务实现
- 在自定义模板中,我们可以实现很多功能,比如加上日志记录
要创建自定义字符串提示模板,有两个要求:
1、它有一个 input_variables 属性,该属性公开提示模板所需的输入变量。
2、定义了一个 format 方法,该方法接受与预期的 input_variables 相对应的关键字参数并返回格式化的提示。
通过如下案例说明:
第一步,创建一个获取函数源码的函数
import inspect
def get_source_code(function_name):return inspect.getsource(function_name)
第二步,构建自定义提示模板
from langchain.prompts import StringPromptTemplate
from pydantic import BaseModel, validatorPROMPT = """给定函数名称和源代码,生成该函数的中文解释。.函数名称: {function_name}源代码:{source_code}解释:
"""class CustomPromptTemplate(StringPromptTemplate, BaseModel):""" 自定义提示模板,将函数名称作为输入,并格式化提示模板以提供函数的源代码。"""@validator("input_variables")def validate_input_variables(cls, v):"""验证输入变量是否正确。"""if len(v) != 1 or "function_name" not in v:raise ValueError("function_name must be the only input_variable.")return vdef format(self, **kwargs) -> str:# 获取源码source_code = get_source_code(kwargs["function_name"])# 生成要发送到语言模型的提示prompt = PROMPT.format(function_name=kwargs["function_name"].__name__, source_code=source_code)return promptdef _prompt_type(self):return "function-explainer"
第四步,使用它
fn_explainer = CustomPromptTemplate(input_variables=["function_name"])prompt = fn_explainer.format(function_name=get_source_code)
print(prompt)

(3)基础可选模板
可以实现从一组示例或示例选择器对象构建少量提示模板。
在实现这个前,先补充一下知识
Few-shot和zero-shot是机器学习中常用的术语,用于描述模型在处理新任务或新类别时的能力。
-
Few-shot(少样本学习):Few-shot学习是指在面对只有很少样本的新任务或新类别时,模型能够通过利用有限的样本进行学习和泛化。这意味着模型可以从少量的训练样本中快速学习,并在面对新任务时进行适应。 -
Zero-shot(零样本学习):Zero-shot学习是指在面对完全没有见过的新任务或新类别时,模型能够进行推理和泛化。这意味着模型可以在没有任何训练样本的情况下,通过利用先验知识或外部信息来进行预测和分类。
这些概念在自然语言处理、计算机视觉和强化学习等领域中被广泛应用,旨在提高模型的泛化能力和适应性,使其能够处理新领域、新任务或新类别的数据。
为此langchain也提供了,few-shot模板操作
from langchain.prompts.few_shot import FewShotPromptTemplate
from langchain.prompts.prompt import PromptTemplate
from langchain.prompts.example_selector import SemanticSimilarityExampleSelector
from langchain.vectorstores import Chroma
from langchain.embeddings import OpenAIEmbeddingsexamples = [{"question": "你是谁?","answer":"""我是wenwenc9"""},{"question": "爸爸叫什么","answer":"""叫爷爷"""},{"question": "朱自清是谁","answer":"""朱自清是文学家"""}
]
example_prompt = PromptTemplate(input_variables=["question", "answer"], template="Question: {question}\n{answer}")
prompt = FewShotPromptTemplate(examples=examples, # 少量示例example_prompt=example_prompt, # 用户格式化单个示例suffix="Question: {input}", # 前缀,也有后缀prefixinput_variables=["input"]
)example_selector = SemanticSimilarityExampleSelector.from_examples(# 可供选择的示例模板examples,# 用于生成用于测量语义相似性的嵌入的嵌入类。OpenAIEmbeddings(),# 向量数据库Chroma,# 这是要生成的实例数目k=1
)
构建问题,基于用户问题,选择合适的提示模板
# 创建一个问题
question = "朱自清"# 根据向量引擎从中选择一个符合
selected_examples = example_selector.select_examples({"question": question})
print(selected_examples)
执行输出结果
[{'answer': '\n 朱自清是文学家\n ', 'question': '朱自清是谁'}]
(4)聊天模板 ChatPromptTemplate
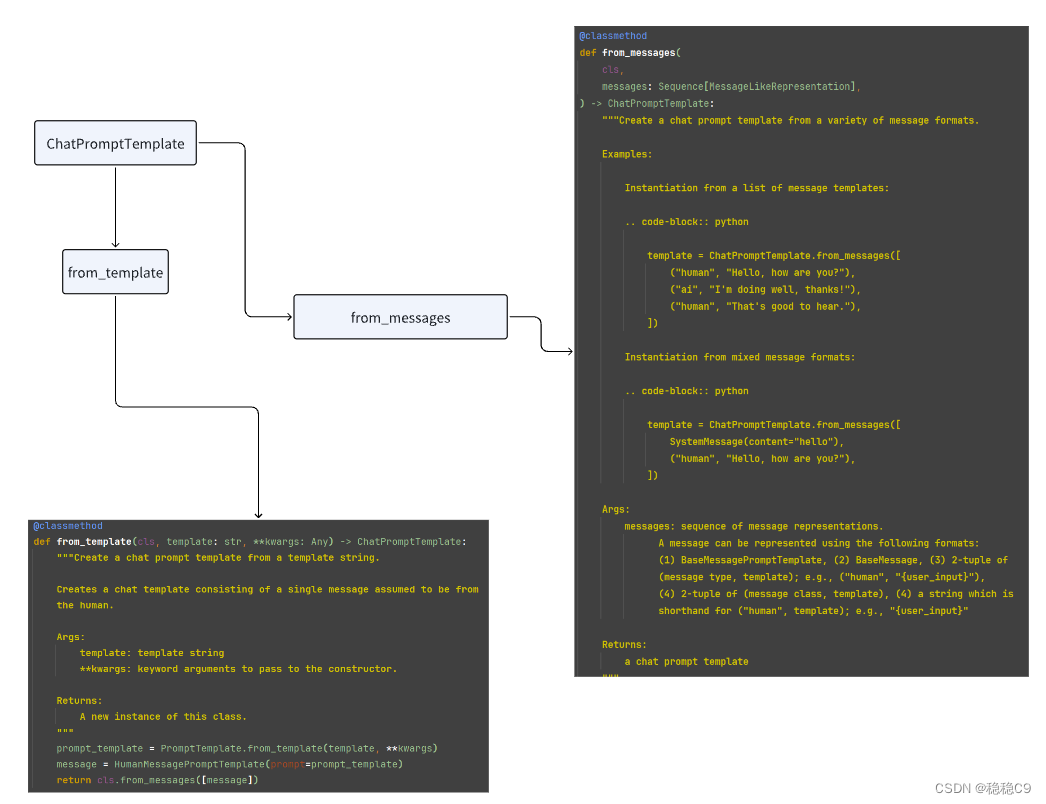
- from_messages
- from_template
在langchain中,ChatPromptTemplate是一个模版方法,它具有两个功能:from_messages和from_template。
-
from_messages:这个功能用于从一系列对话消息中创建聊天模版。您可以提供多个消息作为输入,并将它们转换为聊天模版,以便用于后续的对话生成。 -
from_template:这个功能用于从现有的聊天模版中创建新的聊天模版。您可以基于现有的模版进行修改或扩展,以便生成更多的对话内容。
from_messages用于从消息创建模版,而from_template用于基于现有模版创建新的模版。
(4.1) 二元数组方式
from langchain.chat_models import ChatOpenAI
from langchain.prompts import ChatPromptTemplatetemplate = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([("system", "你是一个优秀的助手. 你的名字是 {name}."),("human", "你好,你最近过的好嘛?"),("ai", "最近过的不错"),("human", "{user_input}"),
])messages = template.format_messages(name="小爱同学",user_input="你的名字是什么?"
)
# 实例化AI对象
llm = ChatOpenAI()# 响应
res = llm(messages)print(res)content='我的名字是小爱同学。有什么我可以帮助你的吗?'
(4.2)BaseMessage 或者 MessagePromptTemplate
from langchain.callbacks import get_openai_callback
from langchain.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
from langchain.prompts.chat import SystemMessage, HumanMessagePromptTemplate, HumanMessage
from langchain.chat_models import ChatOpenAItemplate = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([SystemMessage(content=("你是一个乐于助人的助手,可以将用户的文本重新写入""听起来更乐观""用中文回复我")),# HumanMessagePromptTemplate.from_template("{text}"), # 这里对应本小节前面,所示的from_template可以从已有模板进行修改HumanMessage(content=("{text}")),]
)llm = ChatOpenAI()
# 使用上下文管理器获取 token 使用情况
with get_openai_callback() as cb:res = llm(template.format_messages(text='我很难过'))print(res)
# 获取 token 使用总数
total_tokens = cb.total_tokens
print(f"Total tokens used: {total_tokens}")
content='亲爱的用户,你的文本让我感到有些沮丧。但是,无论遇到什么困难,我们都应该保持积极乐观的态度。相信自己,相信明天会更好。让我们一起努力,面对挑战,充满希望地前进吧!加油!'
Total tokens used: 155
(5)聊天Few-shot模板
关于few-shot的含义本文基础可选模板已经提到过
前面的few-shot 并没有带上chat二字
创建多个提示案例
from langchain.prompts import (FewShotChatMessagePromptTemplate,ChatPromptTemplate,
)# 生成具体回复
examples = [{"input": "2+2", "output": "4"},{"input": "2+3", "output": "5"},
]
确认单个实例化的样例
example_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([("human", "{input}"),("ai", "{output}"),]
)
组装promtp
few_shot_prompt = FewShotChatMessagePromptTemplate(example_prompt=example_prompt,examples=examples,
)final_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([("system", "You are a wondrous wizard of math."),few_shot_prompt,("human", "{input}"),]
)查看一下final_prompt 内容,可以看到下图,由3个消息提示模板
SystemMessagePromptTemplateFewShotChatMessagePromptTemplateHumanMessagePromptTemplate
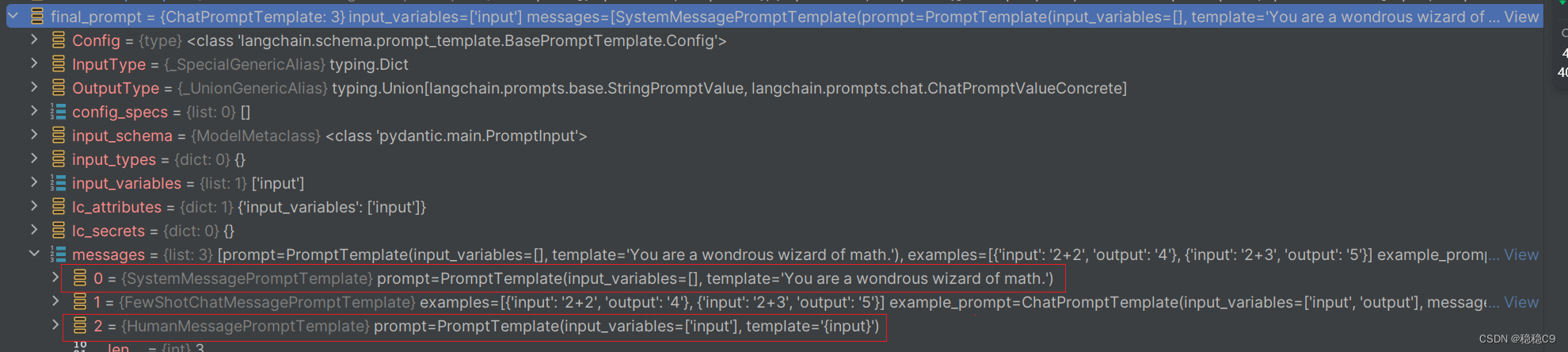
展开FewShotChatMessagePromptTemplate ,可以看到是通过2,实例出2个ChatPromptTemplate
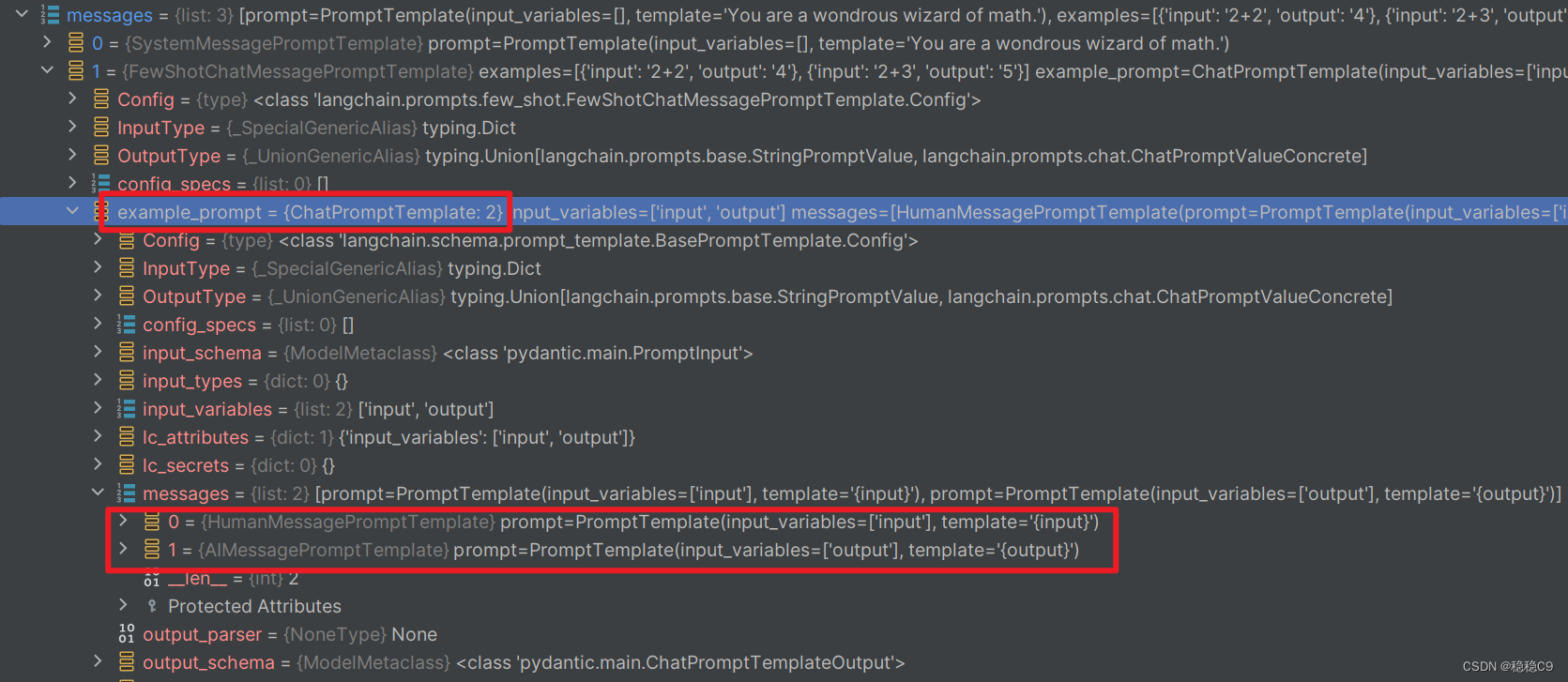
进行使用
方式一:
from langchain.chains import LLMChain
from langchain.chat_models import ChatOpenAI
# 创建LLM模型
llm = ChatOpenAI()
# 创建执行链
chain = LLMChain(llm=llm,prompt=final_prompt
)
res = chain.invoke({"input": "2+2 等于多少"})
res2 = chain.invoke({"input": "2+6 等于多少"})
print(res)
print(res2)
方式二:
from langchain.chat_models import ChatOpenAI# 创建执行链
chain = final_prompt | ChatOpenAI()res = chain.invoke({"input": "2+2 等于多少"})
res2 = chain.invoke({"input": "2+2 等于多少"})
print(res)
输出
{'input': '2+2 等于多少', 'text': '2+2等于4。'}
{'input': '2+6 等于多少', 'text': '2 + 6 等于 8。'}
(6)部分总结,一定要看
在开启下一小节时候,最好进行debug一下,理解模板,观察源码
(6.1)怎么创建模版
这2个模板都继承于 BasePromptTemplate
# 基础模版,与聊天模板,对象
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate, ChatPromptTemplate###################### PromptTemplate ######################
# type : <class 'langchain.prompts.prompt.PromptTemplate'>
base_prompt_obj = PromptTemplate.from_template("告诉我一个 {adjective} 的笑话关于 {content}.")# type :str
demo1 = base_prompt_obj.format(adjective="有趣", content="太阳")
# type : #<class 'langchain.prompts.base.StringPromptValue'>,需要通过转换为str才能使用
demo2 = base_prompt_obj.format_prompt(adjective="有趣", content="太阳")
demo2 = demo2.to_string()
# type :PromptTemplate
demo3 = base_prompt_obj.from_template("帮我解决一个问题,关于 :{input}")
# type:PromptTemplate
prompt_template = PromptTemplate(input_variables=["content"], template="告诉我一个笑话关于 {content}")
prompt = prompt_template.format(content="兔子")# ###################### ChatPromptTemplate ####################### type : ChatPromptTemplate
template = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([("system", "你是一个优秀的助手. 你的名字是 {name}."),("human", "你好,你最近过的好嘛?"),("ai", "最近过的不错"),("human", "{user_input}"),
])
# type :str
chat_prompt_1 = template.format(name='小哎', user_input='你好')
# type : ChatPromptTemplate
chat_prompt_2 = template.format_messages(name='小哎', user_input='你好')
# type : <class 'langchain.prompts.chat.ChatPromptValue'>
chat_prompt_3 = template.format_prompt(name='小哎', user_input='你好')
# type : ChatPromptTemplate
chat_prompt_4 = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template("帮我解决一个问题,关于 :{input}")
print('debug')
# type: ChatPromptTemplate
chat_prompt_5 = ChatPromptTemplate(input_variables=["content"], template="告诉我一个笑话关于 {content}")
prompt = chat_prompt_5 .format(content="兔子")
(6.2)对于模板的使用方法or如何模型对话
- 直接传入模型,进行对话 。模板要求为str
- 通过chain调用,对话(后面文章会开chain专栏)。模板要求对象
from langchain.llms import OpenAI,OpenAIChat
from langchain.llms import OpenAI,OpenAIChat
llm = OpenAI()
# llm = OpenAIChat() 自己试这个
res1 = llm(demo1) # demo1 为str
print(res1) # 成功响应
res2 = llm(demo3) # 报错 Argument `prompt` is expected to be a string.
print(res2) # 报错,说需要字符串这是因为,demo3,是一个模版对象,需要输入一个参数,直接与模型对话,发送str可以成功,但是传入对象却不行。
可以通过chain使用,解决
from langchain.llms import OpenAI,OpenAIChat
# llm = OpenAIChat()
llm = OpenAI()
from langchain.chains import LLMChain
chain = LLMChain(llm=llm, prompt=demo3)
res = chain.run({'input': '1+1等于几'})
print(res)
输出
1+1等于2。
2、模版其它功能
(1)多角色
LangChain提供不同类型的MessagePromptTemplate. 最常用的是
AIMessagePromptTemplate
SystemMessagePromptTemplate
HumanMessagePromptTemplate
分别创建人工智能消息、系统消息和人工消息。关于这个,前面内容也有提到,这里就截图部分


但是,如果聊天模型支持以任意角色获取聊天消息,则可以使用ChatMessagePromptTemplate,它允许用户指定角色名称。比如,厨师,老师,运动员
from langchain.prompts import ChatMessagePromptTemplate
prompt = "给我取一个公司名称,公司主要是做{content}"
chat_message_prompt = ChatMessagePromptTemplate.from_template(role="小红", template=prompt)
rest = chat_message_prompt.format(content="海运")

使用
from langchain.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
from langchain.llms import OpenAIChat
from langchain.chains import LLMChain
# 使用的时候,需要组装模版,不能直接使用
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([chat_message_prompt])
llm = OpenAIChat()
chain = LLMChain(llm=llm, prompt=prompt)
print(chain.run({"content":'拖拉机'}))
print(chain.run({"content":'拖拉机'}))
小红:好的,给您取一个公司名称:疾速农机有限公司
(2)MessagesPlaceholder
LangChain还提供了MessagesPlaceholder,全控制格式化期间要呈现的消息。当您不确定消息提示模板应使用什么角色或希望在格式化期间插入消息列表时,这会很有用。
from langchain.prompts import MessagesPlaceholder, HumanMessagePromptTemplate, ChatPromptTemplate# 创建一个模板内容
human_prompt = "总结对话,通过{word_count}个字"
# 使用人类消息模板
human_message_template = HumanMessagePromptTemplate.from_template(human_prompt)
# 构建模版,并且加入一个conversation 参数
chat_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([MessagesPlaceholder(variable_name="conversation"), human_message_template])
print(chat_prompt)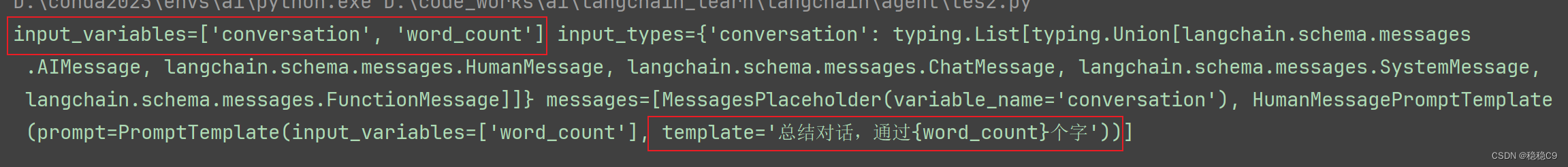
进行对话使用
from langchain.schema import HumanMessage, AIMessagehuman_message = HumanMessage(content="学习编程的最佳方式是什么?")
ai_message = AIMessage(content="""\
1.选择一种编程语言:决定你想学习的编程语言。
2.从基础知识开始:熟悉变量、数据类型和控制结构等基本编程概念。
3.练习,练习,练习:学习编程的最好方法是亲身体验\
""")
print(human_message)
print(type(human_message)) # <class 'langchain.schema.messages.HumanMessage'># 此时只是一个消息列表[。。。。]
chat_message = chat_prompt.format_prompt(conversation=[human_message, ai_message], word_count="10").to_messages()
print(chat_message)
# 转换为模板对象使用
final_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate(messages=chat_message)# 创建chain使用
from langchain.llms import OpenAIChat
llm = OpenAIChat()
from langchain.chains import LLMChain
chain = LLMChain(llm=llm, prompt=final_prompt)
print(chain.run({'word_count':11}))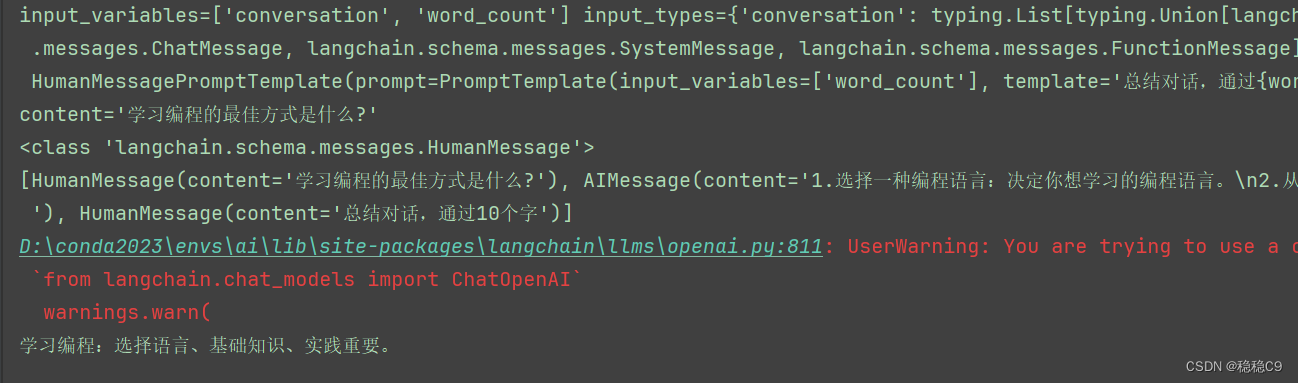
(3)模版输入参数
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplateprompt = PromptTemplate(template="{agrs1}{agrs2}", input_variables=["agrs1", "agrs1"])
partial_prompt = prompt.partial(agrs1="你好!") # 这个返回模版的输入参数
print(partial_prompt.format(agrs2="今天天气如何!")) # 也可以格式化操作prompt = PromptTemplate(template="{agrs1}{agrs2}", input_variables=["agrs1"], partial_variables={"agrs2": "今天天气如何!"} # 可以在这里提前传入部分参数)
print(prompt.format(agrs1="你好!"))
(4)混合模板使用 PipelinePromptTemplate
应用场景:自己灵活思考一下吧,比如应对各种业务,flow流的代入
下面这个例子中,创建了3个模板,并且有一个base模板,进行管道管理
from langchain.prompts.pipeline import PipelinePromptTemplate
from langchain.prompts.prompt import PromptTemplate# 创建模版
full_template = """{introduction}{example}{start}"""
full_prompt = PromptTemplate.from_template(full_template)
# 可以看到上面有3个参数# 介绍 1
introduction_template = """你在模拟{person}."""
introduction_prompt = PromptTemplate.from_template(introduction_template)# 例子 2
example_template = """下面是一个交互的例子:
Q: {example_q}
A: {example_a}"""
example_prompt = PromptTemplate.from_template(example_template)# 开始 3
start_template = """现在开始!Q: {input}
A:"""
start_prompt = PromptTemplate.from_template(start_template)### 组合模板 创建管道
input_prompts = [("introduction", introduction_prompt),("example", example_prompt),("start", start_prompt)
]
pipeline_prompt = PipelinePromptTemplate(final_prompt=full_prompt, pipeline_prompts=input_prompts)
# 打印输入参数
print(pipeline_prompt.input_variables)主要两个参数
final_prompt最后输出的模版样式pipeline_prompts组合模版

(5) 序列化模版
导入方法
from langchain.prompts import load_prompt
正常来说,prompt代码不要存储在py文件中。在大型工程中,在相应配置文件中方便维护
langchain是支持存储
- json
- yaml
- txt等文件中
(5.1) 从JSON文件中加载
创建一个json文件 simple_prompt.json
{"_type": "prompt","input_variables": ["adjective", "content"],"template": "Tell me a {adjective} joke about {content}."}
prompt = load_prompt("simple_prompt.json")
print(prompt.format(adjective="funny", content="chickens"))
(5.2) 从YAML文件中加载
创建一个json文件 simple_prompt.yaml
_type: promptinput_variables:["adjective", "content"]template: Tell me a {adjective} joke about {content}.
prompt = load_prompt("simple_prompt.yaml")
print(prompt.format(adjective="funny", content="chickens"))
(5.3) 从TXT文件中加载
创建一个txt文件
方式一Tell me a {adjective} joke about {content}.方式二{"_type": "prompt","input_variables": ["adjective", "content"],"template_path": "simple_template.txt"}
prompt = load_prompt("xxx.txt")
print(prompt.format(adjective="funny", content="chickens"))
(5.4) 配置多个prompt
上面的内容都是单个prompt,那么多个prompt的也能操作,以下只给出参考样例。
(5.4.1)json
examples.json
[{"input": "happy", "output": "sad"},{"input": "tall", "output": "short"}]
(5.4.2)yaml
examples.yaml
- input: happyoutput: sad- input: talloutput: short
(5.4.2)yaml与json混合使用
创建few_shot_prompt.yml,这里是yaml文件调用json文件
_type: few_shotinput_variables:["adjective"]prefix: Write antonyms for the following words.example_prompt:_type: promptinput_variables:["input", "output"]template:"Input: {input}\nOutput: {output}"examples:examples.json # 这里换成examples.yaml 也是一样的suffix:"Input: {adjective}\nOutput:"
使用
prompt = load_prompt("few_shot_prompt.yaml")
print(prompt.format(adjective="funny"))
打印
Write antonyms for the following words.Input: happyOutput: sadInput: tallOutput: shortInput: funnyOutput:
当然还有很多结合使用,具体使用用的上在纠结要不要学。
(6)快速实现模板生产
对于之前的模板创建方法,过程上都是没有问题,langchain也提供简化版本
(6.1)使用字符串
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate
prompt = (PromptTemplate.from_template("告诉我一个关于 {topic}的笑话")+ ", 听起来要有趣"+ "\n\并且使用 {language}"
)

在langchain中使用这个模板
from langchain.chat_models import ChatOpenAI
from langchain.chains import LLMChain
llm = ChatOpenAI()
chain = LLMChain(llm=llm, prompt=prompt)
res = chain.run(topic="太阳", language="zh")输出

(6.2)对象形式
构建流程:从消息,到消息模板对象,到模版对象,即可使用
from langchain.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate, HumanMessagePromptTemplate
from langchain.schema import HumanMessage, AIMessage, SystemMessage
创建消息对象
prompt = SystemMessage(content="你是一个厨师")
关于prompt的值,跟type
content='你是一个厨师'
<class 'langchain.schema.messages.SystemMessage'>
进行消息模版组合
new_prompt = (prompt + HumanMessage(content="hi") + AIMessage(content="what?") + "{input}"
)
关于此时的值,跟type,在此时,创建了一个CahtPromptTemplate的示例,可以像之前那样使用它
input_variables=['input'] messages=[SystemMessage(content='你是一个厨师'), HumanMessage(content='hi'), AIMessage(content='what?'), HumanMessagePromptTemplate(prompt=PromptTemplate(input_variables=['input'], template='{input}'))]
<class 'langchain.prompts.chat.ChatPromptTemplate'>
使用它
# 模版因为预留了一个输入参数
new_prompt.format_messages(input="i said hi")
通过chain使用它
from langchain.chat_models import ChatOpenAI
from langchain.chains import LLMChain
model = ChatOpenAI()
chain = LLMChain(llm=model, prompt=new_prompt)
chain.run("你好!")
(6.3)模版验证参数
通常而言,模版如果有 {xx} 的,那么在使用的时候,就需要传入,否则报错
可以通过设置参数,不进行调用
template = "我正在学习langchain,因为{reason}."prompt_template = PromptTemplate(template=template,input_variables=["reason", "foo"]) # 提示传值错误
prompt_template = PromptTemplate(template=template,input_variables=["reason", "foo"],validate_template=False) # 没有任何错误
3、模版进阶
(1)自定义选择样例
有什么用处了?比如,我们设定3个客服,每个客服的性格语气
我们可以服务客户的时候,随机选择一个招待用户,让用户体验体验,。。。
from langchain.prompts.example_selector.base import BaseExampleSelector
from typing import Dict, List
import numpy as npclass CustomExampleSelector(BaseExampleSelector):def __init__(self, examples: List[Dict[str, str]]):self.examples = examplesdef add_example(self, example: Dict[str, str]) -> None:"""存储的新示例"""self.examples.append(example)def select_examples(self, input_variables: Dict[str, str]) -> List[dict]:"""根据输入选择要使用的示例"""return np.random.choice(self.examples, size=2, replace=False)examples = [{"foo": "1"},{"foo": "2"},{"foo": "3"}
]# 初始化选择器
example_selector = CustomExampleSelector(examples)# 随机选择2个
example_selector.select_examples({"foo": "foo"})# 添加一个新的示例
example_selector.add_example({"foo": "4"})# 随机选择2个
example_selector.select_examples({"foo": "foo"})
(2)长度选择器
对于我理解而言,比如我设计了一个厨师AI,那么对于问题,应该是询问
要点菜,菜不超过10个,我可以这么操作,超过了,我就不给你做了!
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate
from langchain.prompts import FewShotPromptTemplate
from langchain.prompts.example_selector import LengthBasedExampleSelector# 创建一些例子
examples = [{"input": "happy", "output": "sad"},{"input": "tall", "output": "short"},{"input": "energetic", "output": "lethargic"},{"input": "sunny", "output": "gloomy"},{"input": "windy", "output": "calm"},
]example_prompt = PromptTemplate(input_variables=["input", "output"],template="Input: {input}\nOutput: {output}",
)
# 调用长度选择器 类型 LengthBasedExampleSelector
example_selector = LengthBasedExampleSelector(# 可供选择的示例。examples=examples,# 用于格式化示例的PromptTemplate。example_prompt=example_prompt,# 格式化示例的最大长度。# 长度由下面的get_text_Length函数测量。max_length=25,# 用于获取字符串长度的函数# 以确定要包括哪些示例。它被注释掉是因为# 如果未指定,则将其作为默认值提供。# get_text_length:可调用[[str],int]=lambda x:len(re.split(“\n|”,x))
)dynamic_prompt = FewShotPromptTemplate(# 提供了ExampleSelector而不是示例。example_selector=example_selector,example_prompt=example_prompt,prefix="给出每个输入的反义词",suffix="Input: {adjective}\nOutput:",input_variables=["adjective"],
)
进行使用
print(dynamic_prompt.format(adjective="big"))给出每个输入的反义词
Input: happy
Output: sadInput: tall
Output: shortInput: energetic
Output: lethargicInput: sunny
Output: gloomyInput: windy
Output: calmInput: big
Output:
输入长文本的时候,因为不超过25,所以看到的output为空
long_string = "big and huge and massive and large and gigantic and tall and much much much much much bigger than everything else"
print(dynamic_prompt.format(adjective=long_string))
给出每个输入的反义词
Input: happy
Output: sad
Input: big and huge and massive and large and gigantic and tall and much much much much much bigger than everything else
Output:
(3)算法选择器
(3.1)最大边界选择器
MaxMarginalRelevanceExampleSelector根据与输入最相似的示例的组合来选择示例,同时还针对多样性进行优化。它通过查找与输入具有最大余弦相似度的嵌入示例来实现这一点,然后迭代地添加它们,同时惩罚它们与已选择示例的接近程度。
from langchain.prompts.example_selector import (MaxMarginalRelevanceExampleSelector,SemanticSimilarityExampleSelector,
)
from langchain.vectorstores import FAISS
from langchain.embeddings import OpenAIEmbeddings
from langchain.prompts import FewShotPromptTemplate, PromptTemplateexample_prompt = PromptTemplate(input_variables=["input", "output"],template="Input: {input}\nOutput: {output}",
)# #创建反义词的假装任务的示例。
examples = [{"input": "happy", "output": "sad"},{"input": "tall", "output": "short"},{"input": "energetic", "output": "lethargic"},{"input": "sunny", "output": "gloomy"},{"input": "windy", "output": "calm"},
]
下面有 向量数据库FAISS OpenAIEmbeddings 这个后续文章会讲到
可以理解,向量数据库,将内容编程很多数字,用户问题也数字化,并非传统的sql查询
example_selector = MaxMarginalRelevanceExampleSelector.from_examples(# 可供选择的示例列表。examples,# 用于生成用于测量的嵌入的嵌入类 (embedding)OpenAIEmbeddings(),# 用于生成测量嵌入的嵌入类(向量数据库)FAISS,# 返回结果数目k=2,
)
mmr_prompt = FewShotPromptTemplate(example_selector=example_selector,example_prompt=example_prompt,prefix="给出每个输入的反义词",suffix="Input: {adjective}\nOutput:",input_variables=["adjective"],
)
验证一下好不好用
print(mmr_prompt.format(adjective="happy"))
可以看到happy排第一(自己可以试试别的,这里没什么好说的)

(3.2)余弦
使用余弦相似度 SemanticSimilarityExampleSelector 自己体验吧,
example_selector = SemanticSimilarityExampleSelector.from_examples(examples,OpenAIEmbeddings(),FAISS,k=2,
)
(3.3)相似度
SemanticSimilarityExampleSelector 参考上面案例改下选择器即可
(3.4)Ng
参考上面案例改下选择器即可
NGramOverlapExampleSelector根据 ngram 重叠分数,根据与输入最相似的示例来选择示例并对其进行排序。ngram 重叠分数是 0.0 到 1.0 之间的浮点数(含 0.0 和 1.0)。
选择器允许设置阈值分数。ngram 重叠分数小于或等于阈值的示例被排除。默认情况下,阈值设置为 -1.0,因此不会排除任何示例,只会对它们重新排序。将阈值设置为 0.0 将排除与输入没有 ngram 重叠的示例。
三、语言模型
查看本章前,吃透前面二小节

.
LangChain提供了两种类型模型的接口和集成:
LLM:采用文本字符串作为输入并返回文本字符串的模型聊天模型:由语言模型支持的模型,但将聊天消息列表作为输入并返回聊天消息
LLM 与聊天
法学硕士和聊天模式有微妙但重要的不同。LangChain中的LLM指的是纯文本补全模型。它们包装的 API 将字符串提示作为输入并输出字符串完成。OpenAI 的 GPT-3 是作为法学硕士实施的。聊天模型通常由法学硕士支持,但专门针对对话进行了调整。而且,至关重要的是,他们的提供商 API 使用与纯文本完成模型不同的接口。他们采用聊天消息列表作为输入,而不是单个字符串。通常这些消息会标有说话者(通常是“系统”、“人工智能”和“人类”之一)。他们返回一条人工智能聊天消息作为输出。GPT-4 和 Anthropic 的 Claude 都是作为聊天模型实现的。
为了能够交换法学硕士和聊天模型,两者都实现了基本语言模型接口。这包括常用方法“predict”(接受字符串并返回字符串)和“predict messages”(接受消息并返回消息)。如果您使用特定模型,建议您使用特定于该模型类的方法(即,LLM 的“预测”和聊天模型的“预测消息”),但如果您正在创建一个应与不同类型一起使用的应用程序对于模型来说,共享界面会很有帮助。
关于模型更多的理解,在后面的章节文章会慢慢理解,这边没必要死磕
了解个大概
大型语言模型(LLM)是LangChain的核心组件。LangChain不为自己的LLM提供服务,而是提供一个标准接口来与许多不同的LLM进行交互。
有很多LLM厂商提供服务(OpenAI,Cohere、hugging face 等) - 该类LLM 所做的功能是封装了标准的接口
如下演示中,将使用OpenAI 的LLM 功能函数,实际上其它厂商的功能函数都是大抵相同的。
在前面内容的时候时常看到,两者有区别,带有Chat更适合聊天
from langchain.llms import OpenAIChat, OpenAI
注意!前面演示案例,其实都用过了,下面内容知识摘要代码
(1.1)OpenAI
基本使用,(当然也可以在chain中使用)
from langchain.llms import OpenAi
llm = OpenAi(openai_api_key='') # 如果不想环境变量设置密匙,可以在功能函数设置密匙
# 单条调用
res = llm("你好")
# 批量调用
res_list = llm.generate(["给我讲一个笑话", "告诉我明天天气"]*15)
l = len((res_list)) # 30 长度
""llm_result.generations[0]llm_result.generations[-1]
""
输出结果
llm_result.llm_output{'token_usage': {'completion_tokens': 3903, 'total_tokens': 4023, 'prompt_tokens': 120}}
(1.2)ChatOpenAI
(1.2.1)在chain中使用
from langchain.chat_models import ChatOpenAI
from langchain import LLMChain
from langchain.prompts.chat import (ChatPromptTemplate,SystemMessagePromptTemplate,HumanMessagePromptTemplate
)# 设置模板
sys_temp_pro = SystemMessagePromptTemplate.from_template("""你是一个翻译机器人"""
)
human_temp_pro = HumanMessagePromptTemplate.from_template("""{text}"""
)
# 组装模板
chat_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([sys_temp_pro, human_temp_pro])# 使用
llm = ChatOpenAI()
chain = LLMChain(llm=llm, prompt=chat_prompt)
# 获取响应
resp = chain.run("我喜欢苹果")print(resp)(1.2.2)直接使用LLM
from langchain.chat_models import ChatOpenAI
from langchain.prompts.chat import (ChatPromptTemplate,SystemMessagePromptTemplate,HumanMessagePromptTemplate
)# 系统
sys_template = "你是一个翻译机器人负责将{input_language}翻译成{output_language}"
sys_message_prompt_1 = SystemMessagePromptTemplate.from_template(sys_template)
syst_message_prompt_2 = SystemMessagePromptTemplate(prompt=PromptTemplate(template="你是一个翻译机器人负责将{input_language}翻译成{output_language}",input_variables=["input_language", "output_language"],
))# 用户
human_template = "{text}"
human_message_prompt = HumanMessagePromptTemplate.from_template(human_template)# 组装聊天
chat_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([sys_message_prompt_1, human_message_prompt])# 实例化对象
llm = ChatOpenAI()# 进行提问
res = llm(chat_prompt.format_prompt(input_language="English", output_language="中文", text="I love programming.").to_messages())
print(res)
四、输出解析器
查看本章前,吃透前面二小节

在语言模型输出文本的时候,可能想要获得更多结构化的信息,而不仅仅获得默认返回响应.
这个是时候,就可以使用output models.
输出解释器是帮助构建语言模型响应的类.
输出解释器必须实现两个主要的方法:
- 获取格式指令:返回一个字符串的方法
- 解析: 一种接受字符串(假设是来自语言模型的响应)并将其解析为某种结构的方法
然后是可选的一项
- “带有提示的解析”:一种方法,它接受一个字符串(假设是来自语言模型的响应)和一个提示(假设是生成这种响应的提示)并将其解析为某种结构。
提示主要是在 OutputParser 希望以某种方式重试或修复输出的情况下提供的,并且需要提示中的信息才能执行此操作。
langchain提供了很多常见的解析器
(1)常用解析器
最常用的也是这个 PydanticOutputParse
from langchain.prompts import (PromptTemplate,
)
from langchain.llms import OpenAI
from langchain.output_parsers import PydanticOutputParser # 输出解释器主要的类型
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field, validatormodel_name = "text-davinci-003"
temperature = 0.0
llm = OpenAI(temperature=temperature, model_name=model_name)# 验证器
class JOKE(BaseModel):setup: str = Field(description="讲一个笑话")punchline: str = Field(description="处理这个笑话")@validator('setup')def question_end_with_question_mark(cls, field):if field[-1] != '?':raise ValueError('字段检查失败')return field# 构建解释器
parser = PydanticOutputParser(pydantic_object=JOKE)prompt = PromptTemplate(template="回复用户的提问\n{format_instructions}\n{query}",input_variables=['query'], # 输入参数partial_variables={"format_instructions": parser.get_format_instructions()}
)
joke_query = "告诉我一个笑话"
_input = prompt.format_prompt(query=joke_query)output = llm(_input.to_string())print(parser.parse(output))
上面代码执行了什么
- 导入所需的模块和类。
- 定义了一个名为JOKE的Pydantic模型,用于验证和解析笑话的结构。
- 创建了一个OpenAI对象,用于与OpenAI的语言模型进行交互。
- 定义了一个PydanticOutputParser对象,用于解析模型输出并将其转换为JOKE对象。
- 创建了一个PromptTemplate对象,用于构建输入模板,其中包含了格式化指令和用户提问。
- 定义了一个笑话查询字符串。
- 使用PromptTemplate对象将查询字符串格式化为输入模板。
- 使用OpenAI对象调用模型并获取输出。
- 使用PydanticOutputParser对象解析模型输出并将其转换为JOKE对象。
- 打印解析后的结果。
(2)列表解释器
列表解释器 CommaSeparatedListOutputParser
当想要输出特定列表时候可以用这个
from langchain.output_parsers import CommaSeparatedListOutputParser
from langchain.prompts import (PromptTemplate,
)
from langchain.llms import OpenAIoutput_parser = CommaSeparatedListOutputParser()
# Your response should be a list of comma separated values, eg: `foo, bar, baz`format_instructions = output_parser.get_format_instructions()
print(format_instructions)
prompt = PromptTemplate(template="列举5个{subject}.\n{format_instructions}",input_variables=["subject"],partial_variables={"format_instructions": format_instructions}
)model = OpenAI(temperature=0)_input = prompt.format(subject="颜色")
output = model(_input) # 原始响应
print(output) # Red, Blue, Green, Yellow, Orange
# 也可以通过输出解释器过滤出来
resp = output_parser.parse(output)
print(resp) # ['Red', 'Blue', 'Green', 'Yellow', 'Orange']
(3)时间日期解析器
时间日期解释器 DatetimeOutputParser
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate
from langchain.output_parsers import DatetimeOutputParser
from langchain.llms import OpenAI
from langchain.chains import LLMChainoutput_parse = DatetimeOutputParser()
# format='%Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%S.%fZ'
template = """回答用户问题:{question}{format_instructions}
"""
prompt = PromptTemplate.from_template(template,partial_variables={"format_instructions": output_parse.get_format_instructions()}
)chain = LLMChain(prompt=prompt, llm=OpenAI())
output = chain.run(question="比特币是什么时候创立的")
print(output) # 2020-10-14T00:00:00.000000Z
resp = output_parse.parse(output)
print(resp) # 2020-10-14 00:00:00
(4)枚举解释器
EnumOutputParser
搜想构建一个枚举解析器
from langchain.output_parsers.enum import EnumOutputParser
from enum import Enum
class Colors(Enum):RED = "red"GREEN = "green"BLUE = "blue"
parser = EnumOutputParser(enum=Colors)
使用它
parser.parse("red")
parser.parse("green")
parser.parse("blue")
parser.parse("red") # 使用到红色的时候报错,因为只有三个内容可以枚举
from langchain.output_parsers import PydanticOutputParser
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
from typing import Listclass Actor(BaseModel):name: str = Field(description="导演名称")film_names: List[str] = Field(description="主演名单")actor_query = "生成一个随机演员的电影记录"
parser = PydanticOutputParser(pydantic_object=Actor)misformatted = "{'name': 'Tom Hanks', 'film_names': ['A','B','C']}"parsed_result = parser.parse(misformatted)
(5)重试解释器
RetryOutputParser
from langchain.prompts import (PromptTemplate,ChatPromptTemplate,HumanMessagePromptTemplate
)
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
from typing import List
from langchain.llms import OpenAI
from langchain.chat_models import ChatOpenAI
from langchain.output_parsers import (PydanticOutputParser,OutputFixingParser,RetryOutputParser
)template = """根据用户的问题,提供响应的操作步骤和操作输入
{format_instructions}
Question: {query}
Response:
"""class Action(BaseModel):action: str = Field(description="开始对话")action_input: str = Field(description="开始输入")parser = PydanticOutputParser(pydantic_object=Action)prompt = PromptTemplate(template="回答这个问题.\n{format_instructions}\n{query}\n",input_variables=["query"],partial_variables={"format_instructions": parser.get_format_instructions()}
)
# 假如这边提出了一个问题
prompt_values = prompt.format_prompt(query="今天几月几号")
假设模拟了LLM的响应,运行如下代码就会报错
# 得到了是一个这么的回复,而在上面的要求的响应是2个字段的回复
bad_response = '{"action": "search"}'
parser.parse(bad_response)
运行如上代码会报错,因为输出代码要求是2个字段,一个是action另外一个是action_input
尝试使用OutputFixingParser 修复错误,可以看到回复的内容是丢失了提问的
问的是 谁是冯小刚老婆,通过这个自动修复缺少了 提问的内容
fix_parser = OutputFixingParser.from_llm(parser=parser, llm=ChatOpenAI())
res = fix_parser.parse(bad_response)
print(res) # action='search' action_input='example'
可以使用RetryOutputParser 来进行处理
from langchain.output_parsers import RetryWithErrorOutputParserretry_parser = RetryWithErrorOutputParser.from_llm(parser=parser, llm=OpenAI(temperature=0)
)
res = retry_parser.parse_with_prompt(bad_response, prompt_values)
(6)结果化解释器
StructuredOutputParser
from langchain.output_parsers import (StructuredOutputParser,ResponseSchema,
)
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate, ChatPromptTemplate, HumanMessagePromptTemplate
from langchain.llms import OpenAI
from langchain.chat_models import ChatOpenAI# 定义接受响应的模式
response_schemas = [ResponseSchema(name="answer", description='回答用户的问题'),ResponseSchema(name="source", description="用于回答用户问题的来源,应该是一个网站。")
]
output_parser = StructuredOutputParser.from_response_schemas(response_schemas)# 得到一个字符串,其中包含格式化响应的说明,然后插入提示符中
format_instructions = output_parser.get_format_instructions()prompt = PromptTemplate(template="回答用户的问题.\n{format_instructions}\n{question}",input_variables=["question"],partial_variables={"format_instructions": format_instructions}
)model = OpenAI()
res = model(prompt=prompt.format_prompt(question="百度网站地址").to_string())print(res)
parsed = output_parser.parse(res)print(parsed)
查看输出,可以看到是一个标准的json,与我们定义的一样
{"answer": "百度的网站地址是https://www.baidu.com/","source": "https://www.baidu.com/"
}
在聊天模型中使用它的示例
chat_model = ChatOpenAI()
prompt2 = ChatPromptTemplate(messages=[HumanMessagePromptTemplate.from_template("回答用户问题\n{format_instructions}\n{question}")],input_variables=["question"],partial_variables={"format_instructions": format_instructions}
)res = chat_model(prompt2.format_prompt(question="百度网站地址是什么?").to_messages())
print(res)
parsed = output_parser.parse(res.content)
print(parsed)
结果
content='```json\n{\n "answer": "百度网站地址是www.baidu.com。",\n "source": "https://www.baidu.com"\n}\n```' additional_kwargs={} example=False
{'answer': '百度网站地址是www.baidu.com。', 'source': 'https://www.baidu.com'}
