单链表❀数据结构
目录
- ❀顺序表的优点和缺点
- ❀单链表
- ❀定义结点
- ❀创建简单单链表结构
- ❀打印链表
- ❀尾插
- 链表为空的情况下去尾插
- ❀头插
- 链表为空的情况下去头插
- 链表的头插尾插比较
- ❀头删
- ❀尾删
- ❀查找+修改
- ❀在pos位置前插入
- 是否需要断言
- ❀删除pos位置的值
- ❀在pos后插入
- ❀删除pos后的值
- ❀顺序表和链表的比较
❀顺序表的优点和缺点
优点:
1、顺序表内的元素在物理上时连续存放的,只需要知道起始位置的一个地址,就可以访问之后的所有数据。
2、使用下标可以随机访问。
缺点:
1、空间不够,需要扩容。扩容有一定的消耗,扩少了,要频繁扩容,扩多了,空间会浪费。(一般2倍)
2、头部、中间位置插入删除需要移动数据,效率低。
优化:即链表
1、按需申请释放空间;存多少值申请多少空间,空间不用就释放。
2、头部、中间位置的插入删除不需要移动数据。
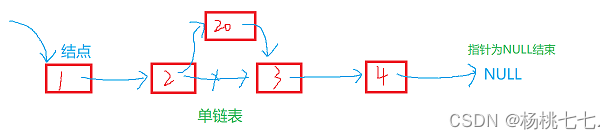
❀单链表
❀定义结点
typedef int SLTDataType;//定义数据类型
typedef struct SListNode
{
SLTDataType data;
struct SListNode* next;//指向下一个结点的结构体指针
}SLTNode;
❀创建简单单链表结构
void TestSList1()
{
//创建结点
//struct SListNode*
SLTNode* n1 = (SLTNode*)malloc(sizeof(SLTNode));
assert(n1);//检查指针的有效性
SLTNode* n2 = (SLTNode*)malloc(sizeof(SLTNode));
assert(n2);
SLTNode* n3 = (SLTNode*)malloc(sizeof(SLTNode));
assert(n3);
SLTNode* n4 = (SLTNode*)malloc(sizeof(SLTNode));
assert(n4);
n1->data = 1;
n2->data = 2;
n3->data = 3;
n4->data = 4;
//连接结点
n1->next = n2;
n2->next = n3;
n3->next = n4;
n4->next = NULL;
int main()
{
TestSList1();
return 0;
}
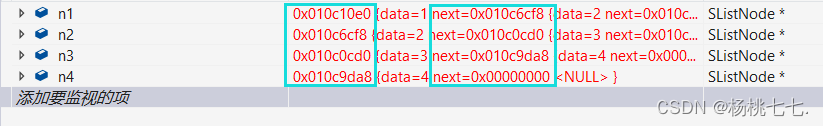
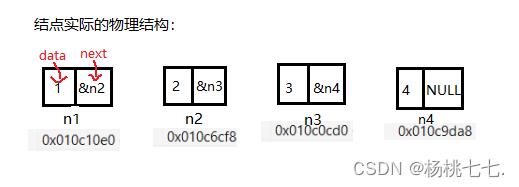
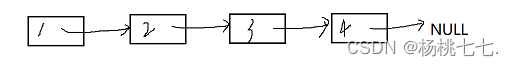
因此每个结点在物理上不一定是连续的。
结点之间并不存在箭头,实际上的连接方式就是next要存放下一个结点的地址。
❀打印链表
void SListPrint(SLTNode* phead);
void SListPrint(SLTNode* phead)
{
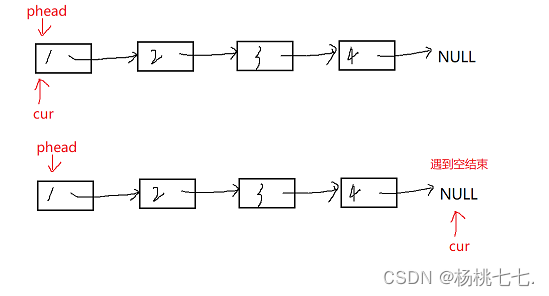
SLTNode* cur = phead;//一般不要改变phead的值
while (cur != NULL)
{
printf("%d->", cur->data);
cur = cur->next;//cur->next是访问当前结点里的next成员,而next内存放的是下一个结点的地址
}
printf("NULL\n");
}
//测试:
void TestSList1()
{
SListPrint(n1);
}

打印不需要传指针地址,不改变plist,改变的是cur。
❀尾插
void SListPushBack(SLTNode* phead, SLTDataType x);
void SListPushBack(SLTNode* phead, SLTDataType x)
{
SLTNode* newnode = (SLTNode*)malloc(sizeof(SLTNode));
SLTNode* cur = phead;
while (cur != NULL)
{
cur = cur->next;
}
cur = newnode;
}
cur为局部变量没有意义。
此写法并没有实现真正的物理连接。要使得结点4内的next存放结点5的地址才可以。
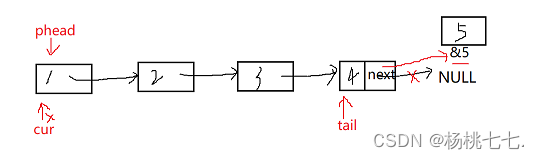
void SListPushBack(SLTNode* phead, SLTDataType x)
{
SLTNode* newnode = (SLTNode*)malloc(sizeof(SLTNode));
assert(newnode);
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
//找尾结点
SLTNode* tail = phead;
while (tail->next != NULL)
{
tail = tail->next;
}
tail->next = newnode;
}
newnode是局部指针变量,出了范围会销毁,但是malloc的结点不会销毁。
//测试:
void TestSList1()
{
//对已有的链表进行插入
SLTNode* plist = n1;
SListPrint(plist);
SListPushBack(plist, 5);
SListPushBack(plist, 6);
SListPushBack(plist, 7);
SListPushBack(plist, 8);
SListPrint(plist);
}
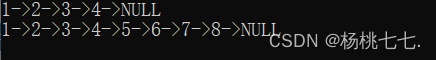
链表为空的情况下去尾插
//测试:
void TestSList1()
{
SLTNode* plist = NULL;
SListPushBack(&plist, 1);
SListPushBack(&plist, 2);
SListPushBack(&plist, 3);
SListPushBack(&plist, 4);
SListPrint(plist);
}

单链表为空,没有数据,表示一个结点都没有,因此指向第一个结点的一定是一个空指针。
程序崩溃的原因:没有一个结点,在while处崩溃。
因此要考虑第一个结点的插入。
void SListPushBack(SLTNode* phead, SLTDataType x)
{
SLTNode* newnode = (SLTNode*)malloc(sizeof(SLTNode));
assert(newnode);
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
if (phead == NULL)
{
phead = newnode;
}
else
{
//找尾结点
SLTNode* tail = phead;
while (tail->next != NULL)
{
tail = tail->next;
}
tail->next = newnode;
}
}

仍然达不到预期结果的原因:
newnode已成为第一个结点,形参phead是被newnode改变了,但是 实参plist 并没有被改变。
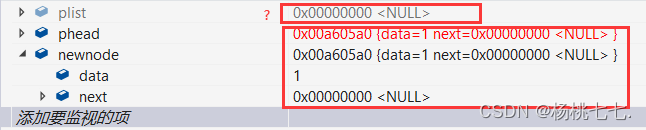
形参的改变不会影响实参的改变。
要改变结构体指针plist的内容,就要传plist的地址,要用二级指针。
//√
void SListPushBack(SLTNode** pphead, SLTDataType x);
//√
void SListPushBack(SLTNode** pphead, SLTDataType x)
{
assert(pphead);
SLTNode* newnode = (SLTNode*)malloc(sizeof(SLTNode));
assert(newnode);
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
if (*pphead == NULL)
{
*pphead = newnode;
}
else
{
//找尾结点
SLTNode* tail = *pphead;
while (tail->next != NULL)
{
tail = tail->next;
}
tail->next = newnode;
}
}
pphead即&plist,pphead是plist本身。plist->data访问结点的数据部分,即pphead->data也可以访问结点的数据部分。
//测试:
void TestSList1()
{
SLTNode* plist = NULL;
SListPushBack(&plist, 1);
SListPushBack(&plist, 2);
SListPushBack(&plist, 3);
SListPushBack(&plist, 4);
SListPrint(plist);
}

函数结束销毁的是局部指针变量,但是malloc创建的结点结构体不会销毁,链表仍会存在。
初始化时创建一个结点,即带哨兵位的;单链表暂不考虑此场景,没有意义。
❀头插
对于创建结点可以作为一个独立的模块。
SLTNode* BuySListNode(SLTDataType x);
//创建结点
SLTNode* BuySListNode(SLTDataType x)
{
SLTNode* newnode = (SLTNode*)malloc(sizeof(SLTNode));
assert(newnode);
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
return newnode;
}
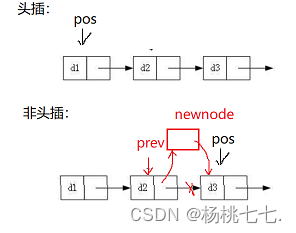
头插:
void SListPushFront(SLTNode** pphead, SLTDataType x);
//头插 √
void SListPushFront(SLTNode** pphead, SLTDataType x)
{
assert(pphead);
SLTNode* newnode = BuySListNode(x);
newnode->next = *pphead;
*pphead = newnode;
}
//测试:
void TestSList2()
{
SLTNode* plist = NULL;
SListPushBack(&plist, 1);
SListPushBack(&plist, 2);
SListPushBack(&plist, 3);
SListPushBack(&plist, 4);
SListPrint(plist);
SListPushFront(&plist, 0);
SListPrint(plist);
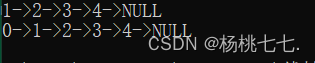
链表为空的情况下去头插
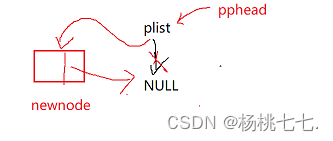
//测试:
void TestSList2()
{
SLTNode* plist = NULL;
SListPushFront(&plist, 0);
SListPushFront(&plist, 1);
SListPushFront(&plist, 2);
SListPushFront(&plist, 3);
SListPushFront(&plist, 4);
SListPrint(plist);
}
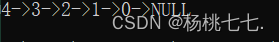
链表的头插尾插比较
链表的尾插效率不高,头插很快。
❀头删
void SListPopFront(SLTNode** pphead);
void SListPopFront(SLTNode** pphead)
{
free(*pphead);
*pphead = (*pphead)->next;
}
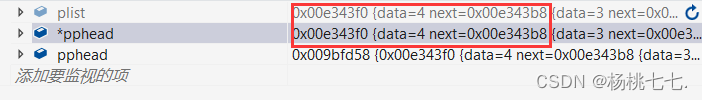
说明pphead即plist。
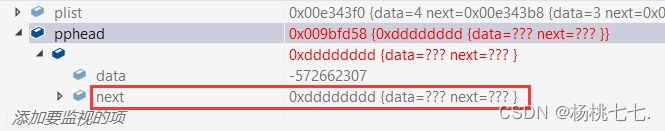
释放掉pphead后,即释放掉结点指针plist,置成随机值,访问不到结点内存放的next,将会找不到下一个结点。
因此要先将next保存起来,避免因空间释放而找不到。
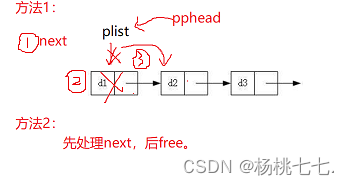
//方法1
void SListPopFront(SLTNode** pphead)
{
SLTNode* next = (*pphead)->next;//保存next
free(*pphead);
*pphead = next;
}
//测试:
void TestSList2()
{
//头插
SLTNode* plist = NULL;
SListPushFront(&plist, 0);
SListPushFront(&plist, 1);
SListPushFront(&plist, 2);
SListPushFront(&plist, 3);
SListPushFront(&plist, 4);
SListPrint(plist);
//头删
SListPopFront(&plist);
SListPrint(plist);
}
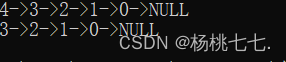
直到删空链表;
//测试:
void TestSList2()
{
//头删
SListPopFront(&plist);
SListPopFront(&plist);
SListPopFront(&plist);
SListPopFront(&plist);
SListPopFront(&plist);
SListPrint(plis
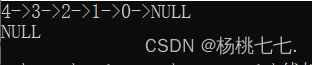
当链表为空,实际不能继续删。
//测试:
void TestSList2()
{
//头删
SListPopFront(&plist);
SListPopFront(&plist);
SListPopFront(&plist);
SListPopFront(&plist);
SListPopFront(&plist);
SListPopFront(&plist);//空链表继续删
SListPrint(plist);
}
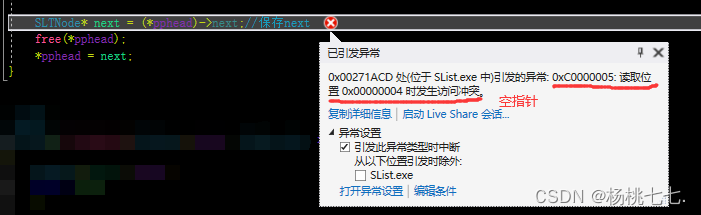
//√
void SListPopFront(SLTNode** pphead)
{
assert(pphead);
//断言暴力检查
assert(*pphead != NULL);
温柔检查
//if (*pphead == NULL)
// return;
SLTNode* next = (*pphead)->next;//保存next
free(*pphead);
*pphead = next;
}
❀尾删
void SListPopBack(SLTNode** pphead);
void SListPopBack(SLTNode** pphead)
{
SLTNode* tail = *pphead;
while (tail->next != NULL)
{
tail = tail->next;
}
free(tail);
}
//测试:
void TestSList3()
{
SLTNode* plist = NULL;
SListPushBack(&plist, 1);
SListPushBack(&plist, 2);
SListPushBack(&plist, 3);
SListPushBack(&plist, 4);
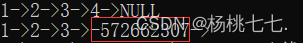
SListPrint(plist);
SListPopBack(&plist);
SListPrint(plist);
}
若只释放尾结点,前一个结点里的next就是野指针。
因此还要找到前一个结点。
void SListPopBack(SLTNode** pphead)
{
SLTNode* tailPrev = NULL;
SLTNode* tail = *pphead;
while (tail->next != NULL)
{
tailPrev = tail;
tail = tail->next;
}
free(tail);
tailPrev->next = NULL;
}
当删到没有结点,不能继续删
void SListPopBack(SLTNode** pphead)
{
assert(*pphead);
SLTNode* tailPrev = NULL;
SLTNode* tail = *pphead;
while (tail->next != NULL)
{
tailPrev = tail;
tail = tail->next;
}
free(tail);
tailPrev->next = NULL;
}
当剩最后一个结点,先释放结点,tailPrev里的next就是野指针,不能再被赋值为NULL。
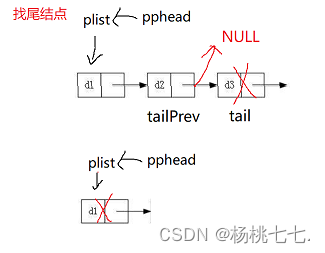

//√
void SListPopBack(SLTNode** pphead)
{
assert(pphead);
assert(*pphead);
if ((*pphead)->next == NULL)
{
//只有一个结点
free(*pphead);
*pphead = NULL;
}
else
{
//多个结点
//写法1:
SLTNode* tailPrev = NULL;
SLTNode* tail = *pphead;
while (tail->next != NULL)
{
tailPrev = tail;
tail = tail->next;
}
free(tail);
tailPrev->next = NULL;
//写法2:
//SLTNode* tailPrev = *pphead;
//while (tailPrev->next->next != NULL)
//{
// tailPrev = tailPrev->next;
//}
//free(tailPrev->next);
//tailPrev->next = NULL;
}
}
//测试:
void TestSList3()
{
SLTNode* plist = NULL;
SListPushBack(&plist, 1);
SListPushBack(&plist, 2);
SListPushBack(&plist, 3);
SListPushBack(&plist, 4);
SListPrint(plist);
SListPopBack(&plist);
SListPopBack(&plist);
SListPopBack(&plist);
SListPopBack(&plist);
SListPrint(plist);
SListPopBack(&plist);
SListPrint(plist);
}
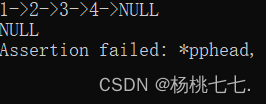
❀查找+修改
此时查找不需要对链表做出改变,就不需要二级指针。
SLTNode* SListFind(SLTNode* phead, SLTDataType x);
SLTNode* SListFind(SLTNode* phead, SLTDataType x)
{
SLTNode* cur = phead;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->data == x)
return cur;
cur = cur->next;
}
return NULL;
}
返回指针的原因:既可以查找,也可以修改。
因此可以不再单独写个修改模块。
//测试:
void TestSList4()
{
SLTNode* plist = NULL;
SListPushBack(&plist, 1);
SListPushBack(&plist, 2);
SListPushBack(&plist, 3);
SListPushBack(&plist, 4);
SListPrint(plist);
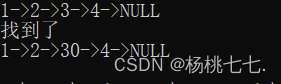
SLTNode* ret = SListFind(plist, 3);
if (ret)
{
printf("找到了\n");
ret->data = 30;//修改
}
SListPrint(plist);
}
❀在pos位置前插入
void SListInsert(SLTNode** pphead, int pos, SLTDataType x);
可以设计在pos下标的值前插入,但是不建议使用此方法。
一般顺序表使用下标,链表使用结点指针。
//√
void SListInsert(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* pos, SLTDataType x);
void SListInsert(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* pos, SLTDataType x)
{
assert(pphead);
if (pos == *pphead)
{
// 头插
SListPushFront(pphead, x);
}
else
{
SLTNode* prev = *pphead;
//找pos前一个结点
while (prev->next != pos)
{
prev = prev->next;
}
SLTNode* newnode = BuySListNode(x);
prev->next = newnode;
newnode->next = pos;
}
}
单链表在任意位置处插入效率不高。
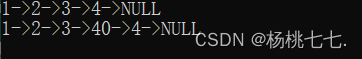
//测试:
void TestSList4()
{
SLTNode* plist = NULL;
SListPushBack(&plist, 1);
SListPushBack(&plist, 2);
SListPushBack(&plist, 3);
SListPushBack(&plist, 4);
SListPrint(plist);
//在pos前插入
SLTNode* pos = SListFind(plist, 4);//先找到pos位置的值
if (pos)
{
SListInsert(&plist, pos, 40);//再在pos前插入
}
SListPrint(plist);
}
//测试:
void TestSList4()
{
SLTNode* plist = NULL;
SListPushBack(&plist, 1);
SListPushBack(&plist, 2);
SListPushBack(&plist, 3);
SListPushBack(&plist, 4);
SListPrint(plist);
//在pos前插入
SLTNode* pos = SListFind(plist, 4);//先找到pos位置的值
if (pos)
{
SListInsert(&plist, NULL, 40);//再在pos前插入
}
SListPrint(plist);
}
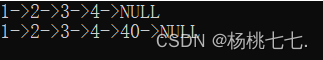
虽然相当于尾插,但是实际给值的时候给NULL显然是不合理的。
//√
void SListInsert(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* pos, SLTDataType x)
{
assert(pphead);
assert(pos);
if (pos == *pphead)
{
// 头插
SListPushFront(pphead, x);
}
else
{
SLTNode* prev = *pphead;
//找pos前一个结点
while (prev->next != pos)
{
prev = prev->next;
}
SLTNode* newnode = BuySListNode(x);
prev->next = newnode;
newnode->next = pos;
}
}
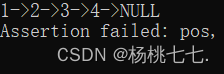
是否需要断言
根据实际情况确定是否需要检查。
1、无论是不是空链表,指向结构体头指针地址的指针即pphead不可能是空;就算是空链表,plist指向的结构体为空,但plist的地址不可能是空,因此指向plist的地址的二级指针一定不能是空指针,空指针肯定就属于出错,因此需要断言;
2、又比如打印,plist即phead指向的结构体为空,即空链表,符合实际情况,空链表可以打印,允许为空指针,因此不需要断言;
3、删除操作时,空链表不能删除,因此需要断言。
❀删除pos位置的值
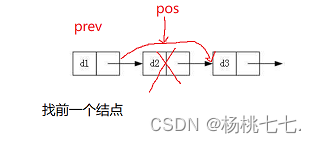
void SListErase(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* pos);
//√
void SListErase(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* pos)
{
assert(pphead);
assert(pos);//在检查pos的同时就检查了是否为空链表,因此不用额外检查链表是否为空
if (*pphead == pos)
{
//头删
SListPopFront(pphead);
}
else
{
SLTNode* prev = *pphead;
while (prev->next != pos)
{
//找前一个结点
prev = prev->next;
}
prev->next = pos->next;
free(pos);
//pos = NULL;//可写可不写;本应该写,防止野指针,但是此时pos是个函数内的局部变量,此代码没有实际效果
}
}
//测试:
void TestSList4()
{
SLTNode* plist = NULL;
SListPushBack(&plist, 1);
SListPushBack(&plist, 2);
SListPushBack(&plist, 3);
SListPushBack(&plist, 4);
SListPrint(plist);
SLTNode* pos = SListFind(plist, 4);//先找到pos位置的值
if (pos)
{
SListErase(&plist, pos);//删除pos位置
}
SListPrint(plist);
}
由此看来,单链表没有完美的解决顺序表的问题,在pos位置前插入O(N)和删除pos位置的值O(N)效率很低,都需要找到前一个结点。
单链表删除pos后的值O(1)和在pos后插入O(1)效率稍高。
❀在pos后插入
void SListInsertAfter(SLTNode* pos, SLTDataType x);
void SListInsertAfter(SLTNode* pos, SLTDataType x)
{
assert(pos);
SLTNode* newnode = BuySListNode(x);
pos->next = newnode;
newnode->next = pos->next;
}
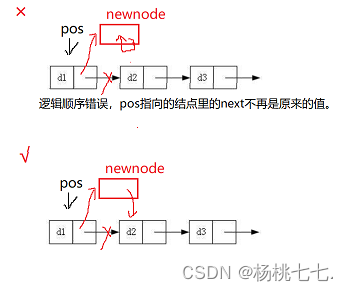
//√
void SListInsertAfter(SLTNode* pos, SLTDataType x)
{
assert(pos);
方法1:注意代码顺序
//SLTNode* newnode = BuySListNode(x);
//newnode->next = pos->next;
//pos->next = newnode;
//方法2:不需考虑链接顺序
SLTNode* newnode = BuySListNode(x);
SLTNode* next = pos->next;//设置一个变量将pos指向的结点里的next值存起来就不需考虑代码顺序
pos->next = newnode;
newnode->next = next;
}
❀删除pos后的值
void SListEraseAfter(SLTNode* pos);
void SListEraseAfter(SLTNode* pos)
{
assert(pos);
if (pos->next == NULL)
return;//当pos是尾,不用删
pos->next = pos->next->next;//此时pos和pos->next不可能为空,但是不方便释放结点
}
//√
void SListEraseAfter(SLTNode* pos)
{
assert(pos);
if (pos->next == NULL)
return;//当pos是尾,不用删
SLTNode* del = pos->next;
SLTNode* del = pos->next;
//pos->next = pos->next->next;
pos->next = del->next;
free(del);
//del = NULL;//可写可不写
}
❀顺序表和链表的比较
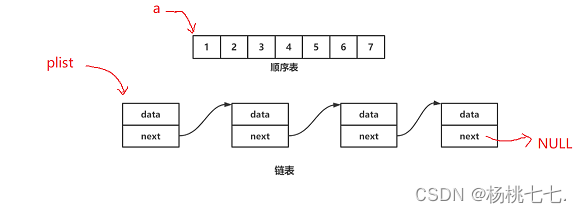
1、顺序表需要size确定数据的大小,需要capacity扩容。而链表不需要。
2、链表解决了顺序表头插效率低的问题。但单链表尾插尾删O(N)。
实际中多使用最优的双向循环链表。
单链表的意义:单链表会作为以后更复杂数据结构的子结构(哈希桶、图的邻接表)

