可定制多目标视频生成;LLM驱动的文生图;控制视频生成中运动目标轨迹;扩散模型做全景分割;实时多功能SAM;各种分割任务统一模型
本文首发于公众号:机器感知
可定制多目标视频生成;LLM驱动的文生图;控制视频生成中运动目标轨迹;扩散模型做全景分割;实时多功能SAM;各种分割任务统一模型
LoMA: Lossless Compressed Memory Attention

The ability to handle long texts is one of the most important capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs), but as the text length increases, the consumption of resources also increases dramatically. At present, reducing resource consumption by compressing the KV cache is a common approach. Although there are many existing compression methods, they share a common drawback: the compression is not lossless. We propose a new method, Lossless Compressed Memory Attention (LoMA), which allows for lossless compression of information into special memory token KV pairs according to a set compression ratio.
Image Translation as Diffusion Visual Programmers
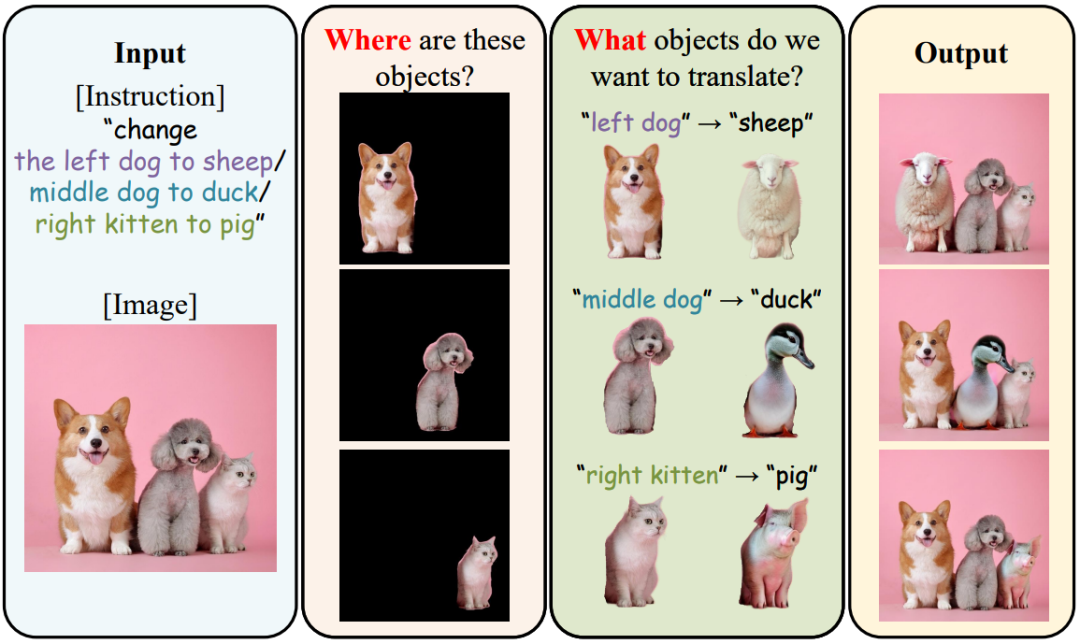
We introduce the novel Diffusion Visual Programmer (DVP), a neuro-symbolic image translation framework. Our proposed DVP seamlessly embeds a condition-flexible diffusion model within the GPT architecture, orchestrating a coherent sequence of visual programs (i.e., computer vision models) for various pro-symbolic steps, which span RoI identification, style transfer, and position manipulation, facilitating transparent and controllable image translation processes.
CustomVideo: Customizing Text-to-Video Generation with Multiple Subjects
Customized text-to-video generation aims to generate high-quality videos guided by text prompts and subject references. Current approaches designed for single subjects suffer from tackling multiple subjects, which is a more challenging and practical scenario. In this work, we aim to promote multi-subject guided text-to-video customization. We propose CustomVideo, a novel framework that can generate identity-preserving videos with the guidance of multiple subjects. Also, we collect a multi-subject text-to-video generation dataset as a comprehensive benchmark, with 69 individual subjects and 57 meaningful pairs.
A-KIT: Adaptive Kalman-Informed Transformer

The extended Kalman filter (EKF) is a widely adopted method for sensor fusion in navigation applications. While common EKF implementation assumes a constant process noise, in real-world scenarios, the process noise varies, leading to inaccuracies in the estimated state and potentially causing the filter to diverge. To cope with such situations, we derive and introduce A-KIT, an adaptive Kalman-informed transformer to learn the varying process noise covariance online. The A-KIT outperforms the conventional EKF by more than 49.5% and model-based adaptive EKF by an average of 35.4% in terms of position accuracy.
DiffusionGPT: LLM-Driven Text-to-Image Generation System
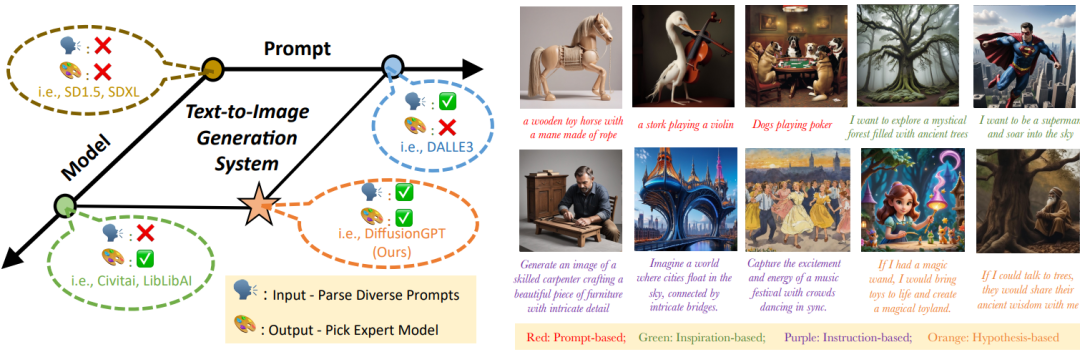
A major challenge persists in current text-to-image systems are often unable to handle diverse inputs, or are limited to single model results. Current unified attempts often fall into two orthogonal aspects: i) parse Diverse Prompts in input stage; ii) activate expert model to output. To combine the best of both worlds, we propose DiffusionGPT, which leverages Large Language Models (LLM) to offer a unified generation system capable of seamlessly accommodating various types of prompts and integrating domain-expert models. Moreover, we introduce Advantage Databases, where the Tree-of-Thought is enriched with human feedback, aligning the model selection process with human preferences.
Motion-Zero: Zero-Shot Moving Object Control Framework for Diffusion-Based Video Generation
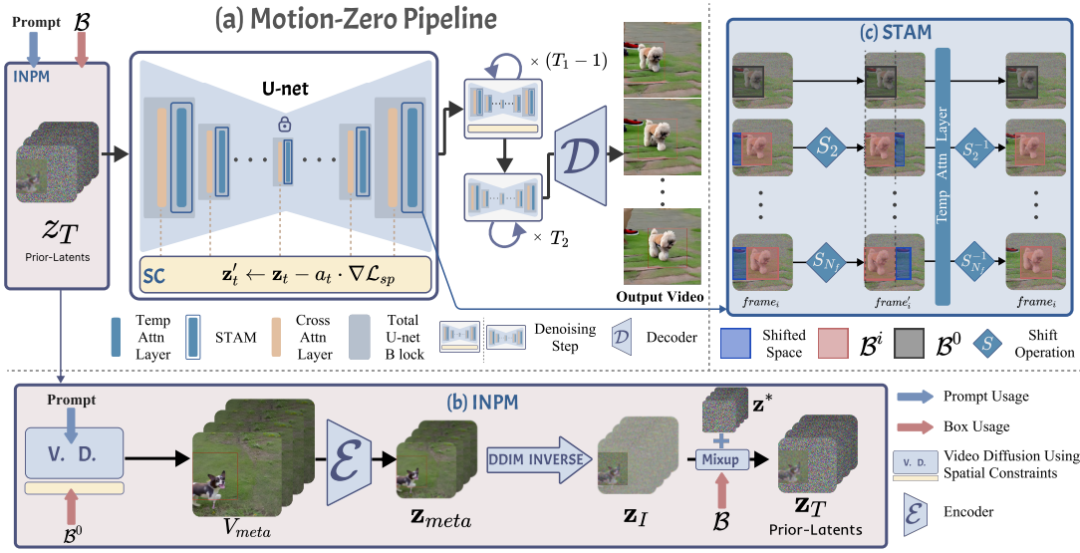
In this paper, we propose a novel zero-shot moving object trajectory control framework, Motion-Zero, to enable a bounding-box-trajectories-controlled text-to-video diffusion model.To this end, an initial noise prior module is designed to provide a position-based prior to improve the stability of the appearance of the moving object and the accuracy of position. In addition, based on the attention map of the U-net, spatial constraints are directly applied to the denoising process of diffusion models, which further ensures the positional and spatial consistency of moving objects during the inference. Furthermore, temporal consistency is guaranteed with a proposed shift temporal attention mechanism.
A Simple Latent Diffusion Approach for Panoptic Segmentation and Mask Inpainting
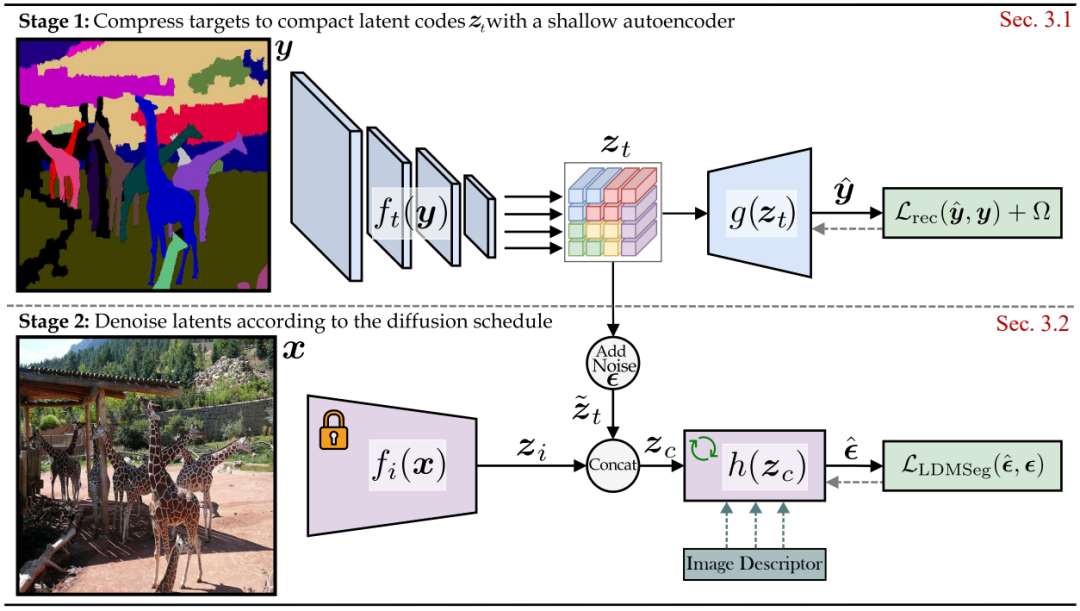
This work builds upon Stable Diffusion and proposes a latent diffusion approach for panoptic segmentation. The use of a generative model unlocks the exploration of mask completion or inpainting, which has applications in interactive segmentation. The experimental validation yields promising results for both panoptic segmentation and mask inpainting.
RAP-SAM: Towards Real-Time All-Purpose Segment Anything
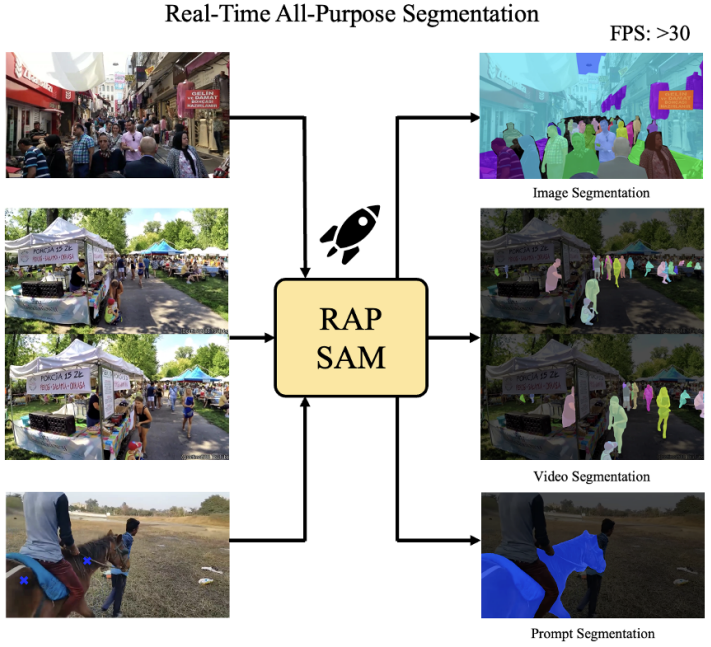
This work explores a new real-time segmentation setting, named all-purpose segmentation in real-time, to transfer VFMs in real-time deployment. It contains three different tasks, including interactive segmentation, panoptic segmentation, and video segmentation. We aim to use one model to achieve the above tasks in real-time. Then, we present Real-Time All Purpose SAM (RAP-SAM). It contains an efficient encoder and an efficient decoupled decoder to perform prompt-driven decoding.
OMG-Seg: Is One Model Good Enough For All Segmentation?
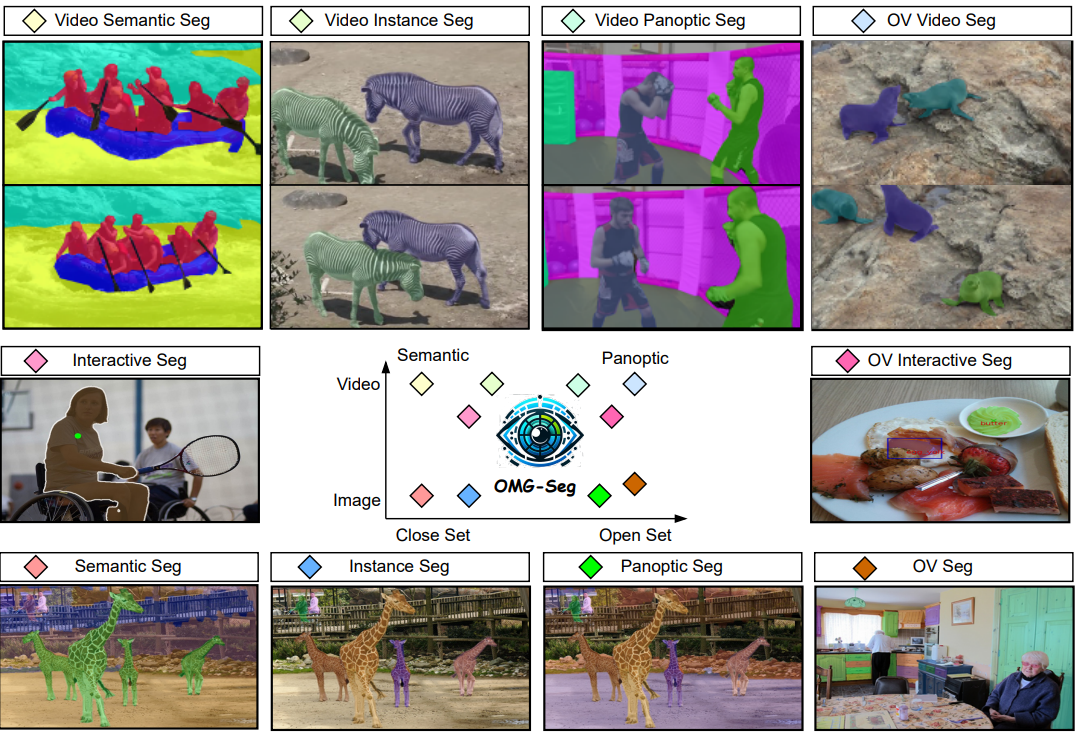
In this work, we address various segmentation tasks, each traditionally tackled by distinct or partially unified models. We propose OMG-Seg, One Model that is Good enough to efficiently and effectively handle all the segmentation tasks, including image semantic, instance, and panoptic segmentation, as well as their video counterparts, open vocabulary settings, prompt-driven, interactive segmentation like SAM, and video object segmentation. To our knowledge, this is the first model to handle all these tasks in one model and achieve satisfactory performance.
FreGrad: Lightweight and Fast Frequency-aware Diffusion Vocoder
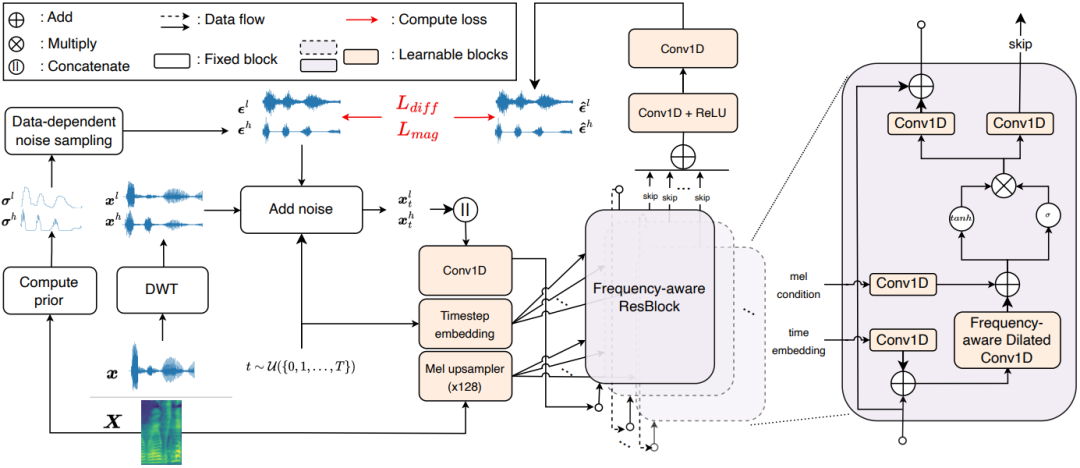
The goal of this paper is to generate realistic audio with a lightweight and fast diffusion-based vocoder, named FreGrad. In our experiments, FreGrad achieves 3.7 times faster training time and 2.2 times faster inference speed compared to our baseline while reducing the model size by 0.6 times (only 1.78M parameters) without sacrificing the output quality.
